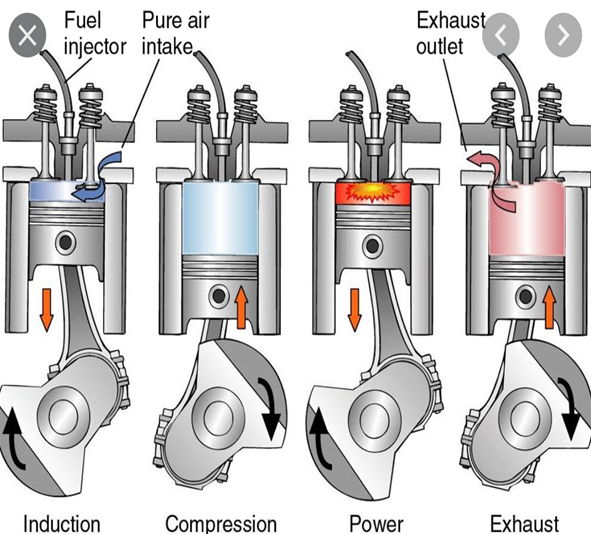
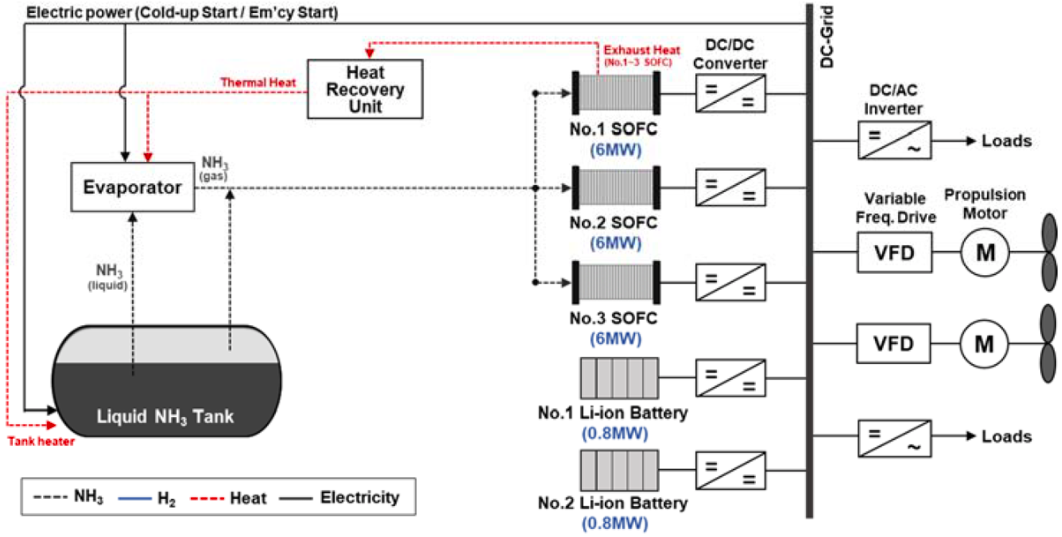
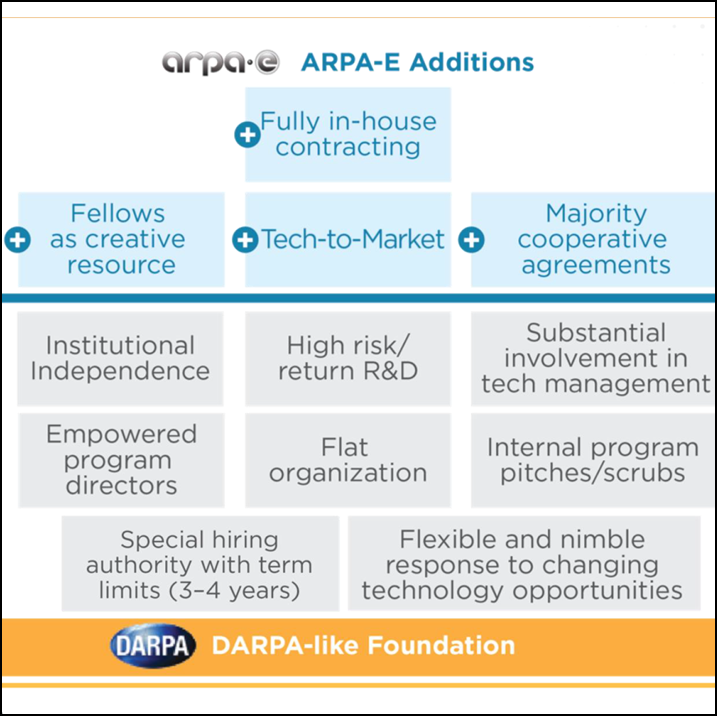
South Australia Planning Hydrogen Export Strategy
The state of South Australia earlier this month issued a tender for professional services under the title “Hydrogen Export Study, Modelling Tool and Prospectus.” The tender is a further step in the state’s campaign to become a major exporter of renewable energy in the form of green and/or blue hydrogen. The results of the study are expected to “inform key considerations such as locations for hydrogen production and export, volume of supply potential, the interdependencies of hydrogen supply chain infrastructure, and the landed cost of clean hydrogen exported from South Australia.”