If green ammonia, whence urea? Stamicarbon's Innovation Agenda
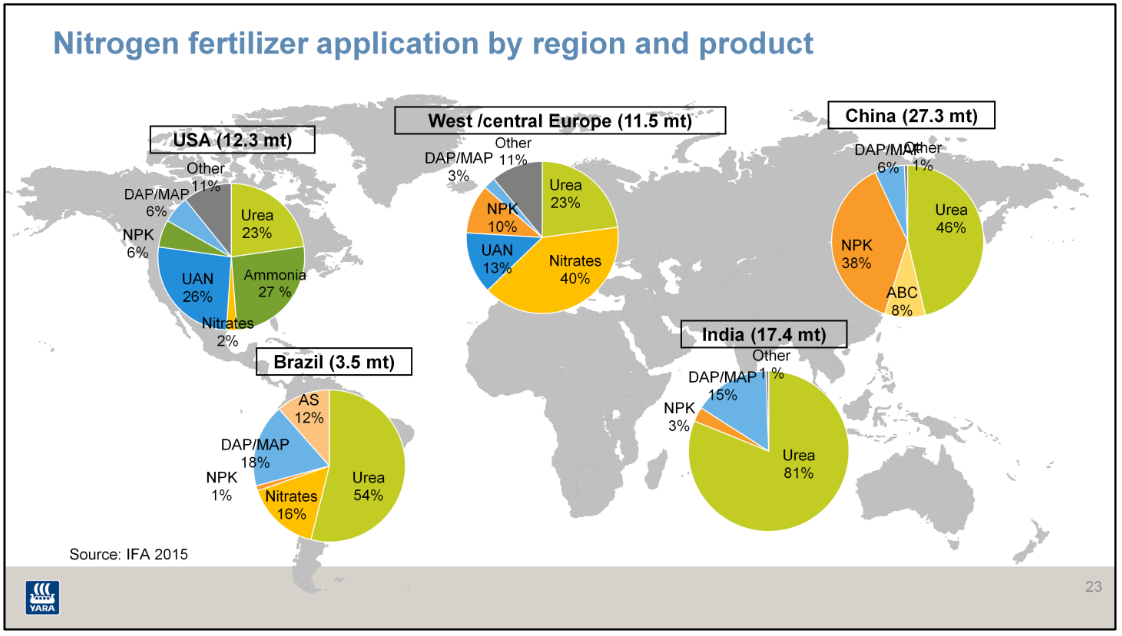
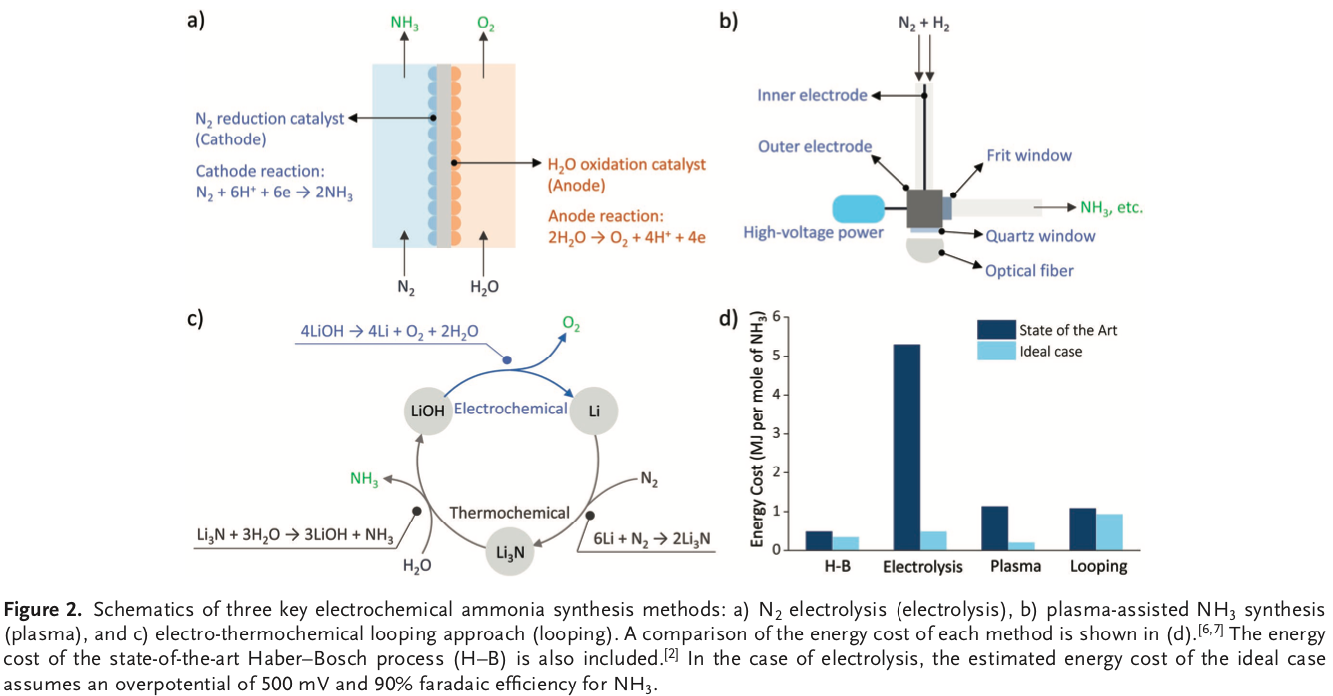
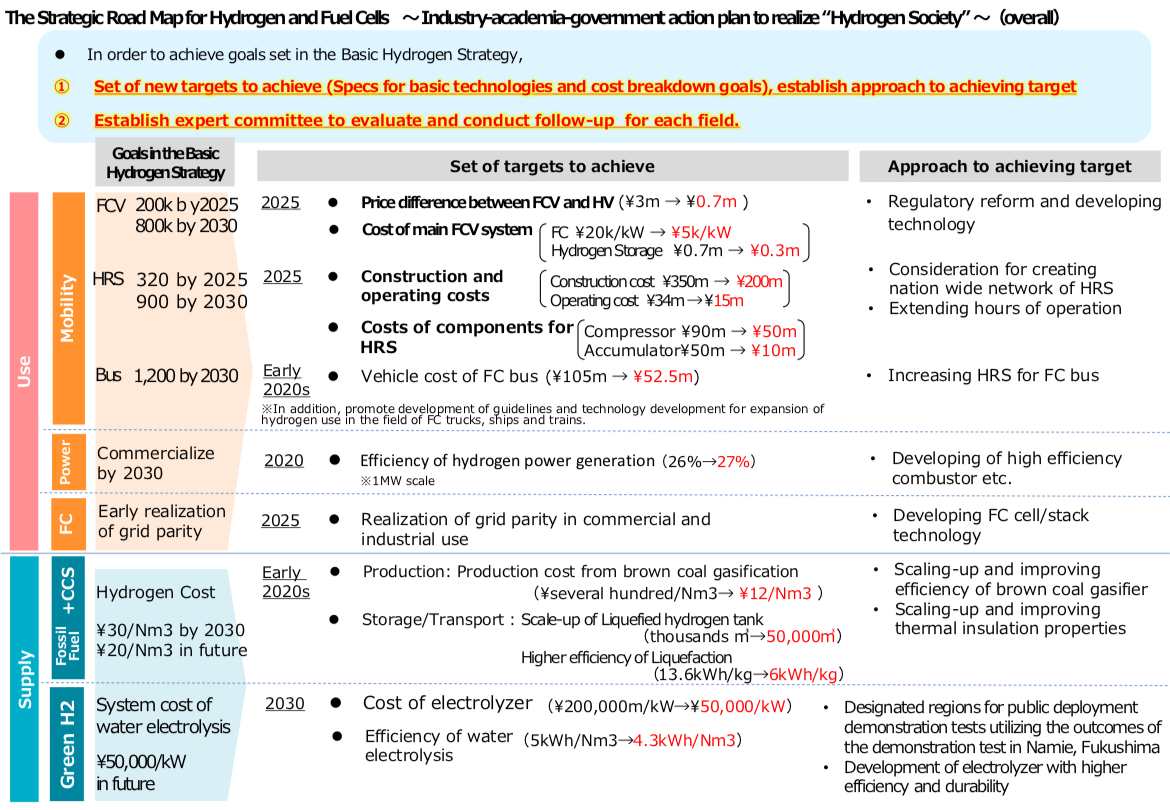
One of the most interesting unanswered questions surrounding green ammonia is this: what about urea? Last month, a major announcement by Stamicarbon ("the world market leader in design, licensing and development of urea plants") implies an answer: in the long-term context of climate change, urea as a fertilizer may simply need to be phased out. Stamicarbon announced its new Innovation Agenda at the company's "Future Day" event in Utrecht in April. Its Innovation Agenda covers three areas: speciality fertilizers, digitalization, and "Renewable production of fertilizer (using wind or solar energy to produce fertilizer)."