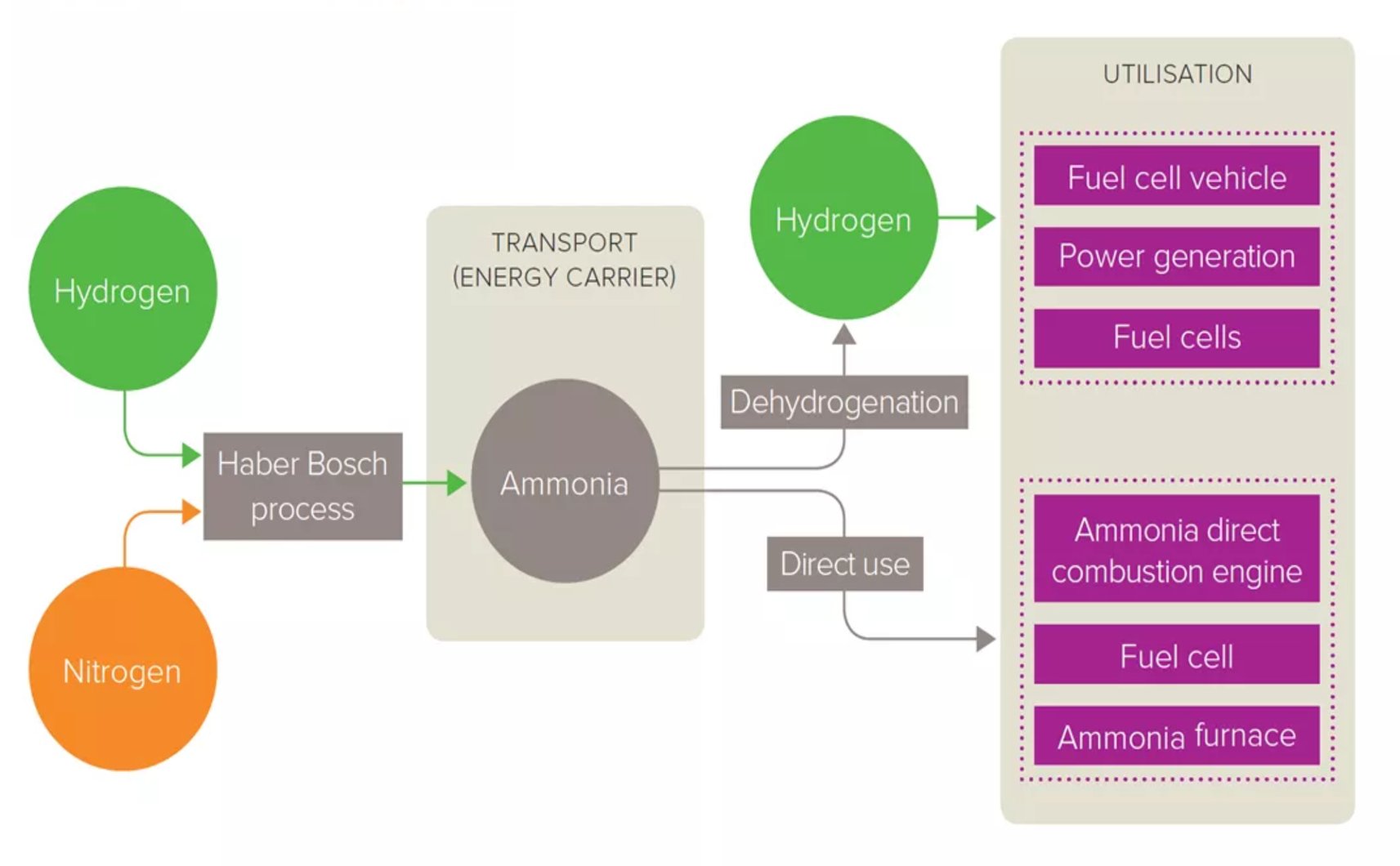
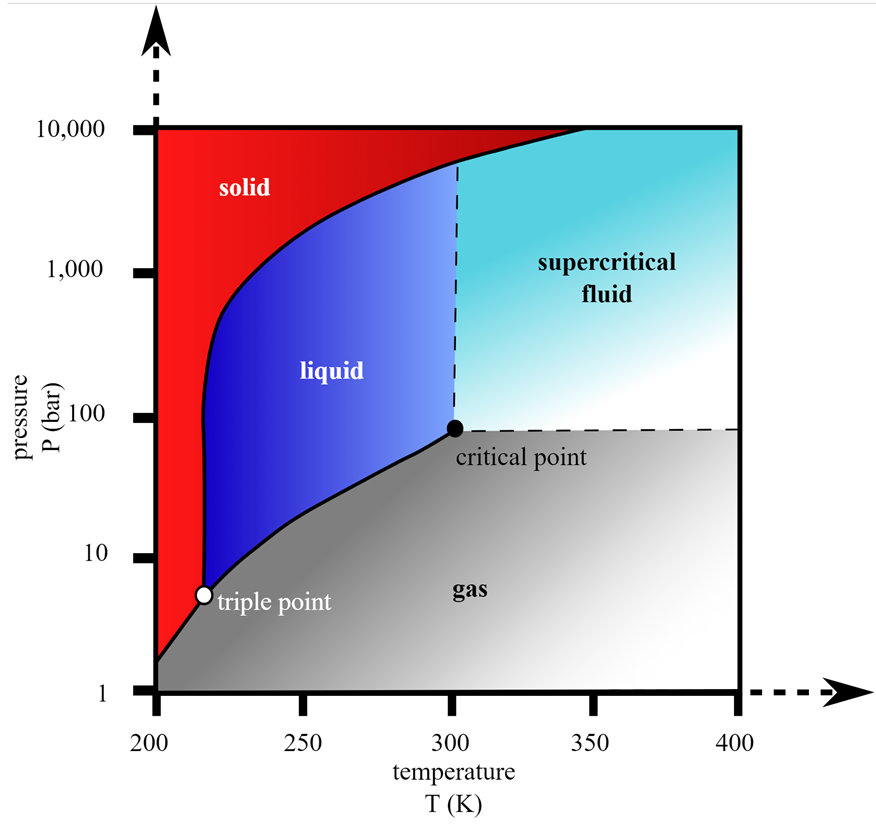
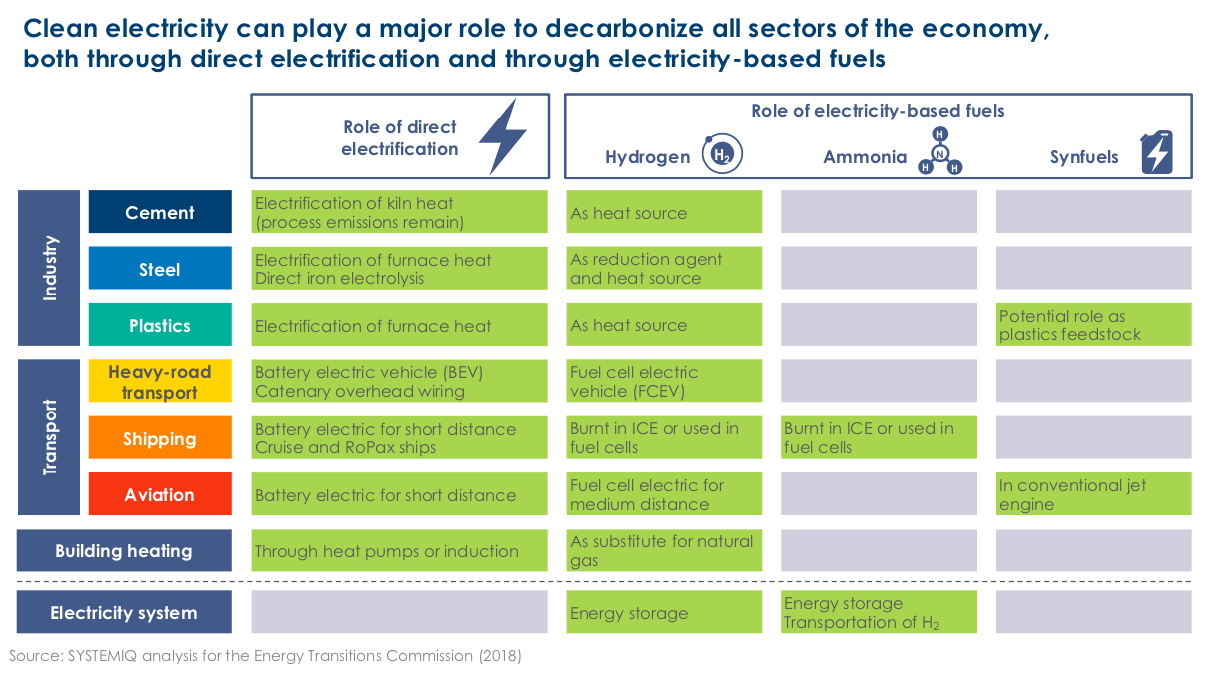
Ammonia's Role in the Hydrogen Society
Last month I had the opportunity to reflect on “Ammonia’s Role in the Hydrogen Society.” This was the title of a speech I gave at the Ammonia Energy International Workshop in Tokyo. The Workshop was held on January 25 by the Energy Carriers initiative of the Japanese Government’s Strategic Innovation Promotion Program (SIP) as it moves toward its terminal date of March 31, and as the Green Ammonia Consortium, which grew out of the Energy Carriers program, prepares for its official launch in the same time frame. The key takeaways from my speech are that ammonia is widely seen as a contributor to the viability of hydrogen energy, but the extent of its potential role is not appreciated.