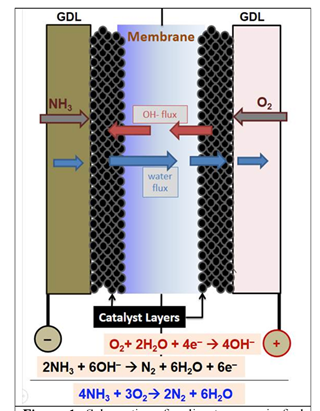
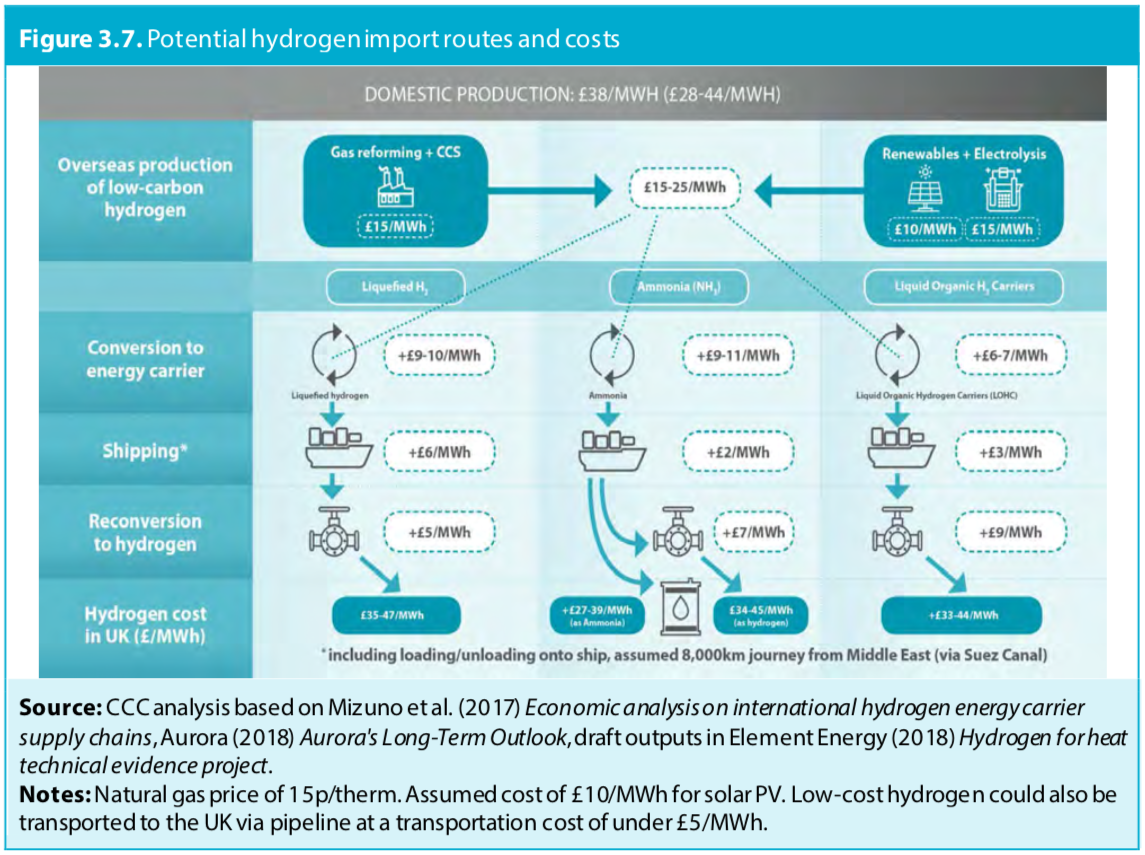
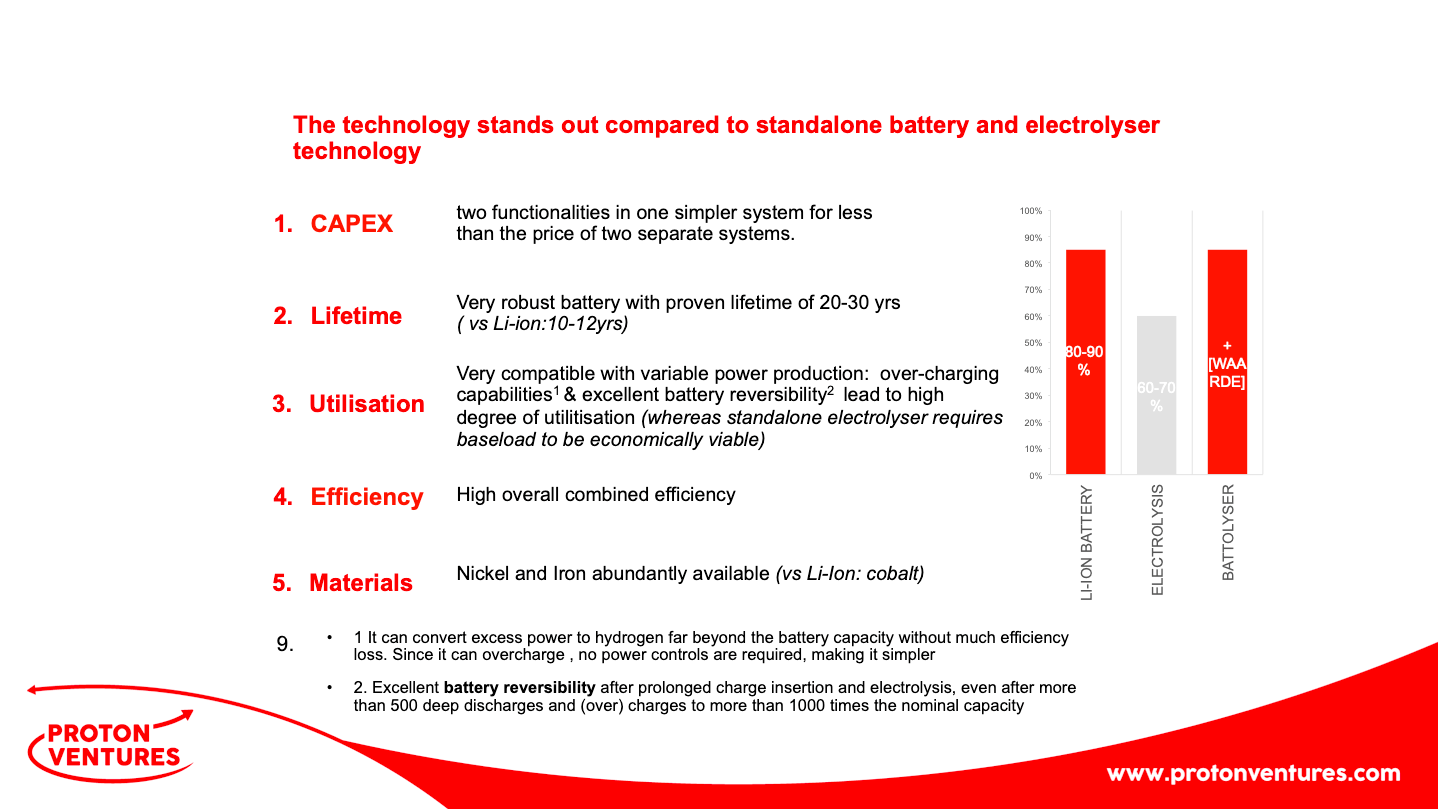
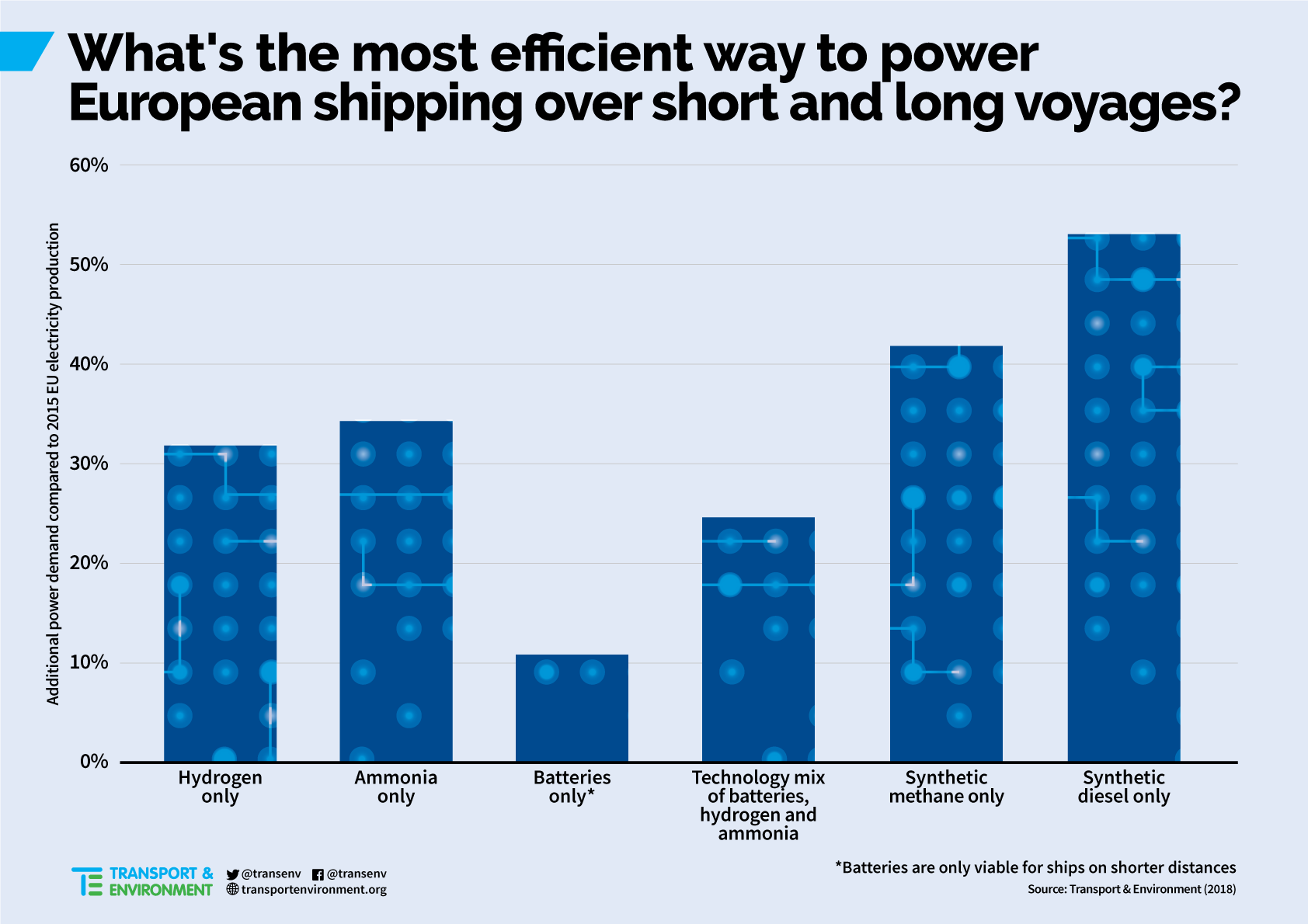
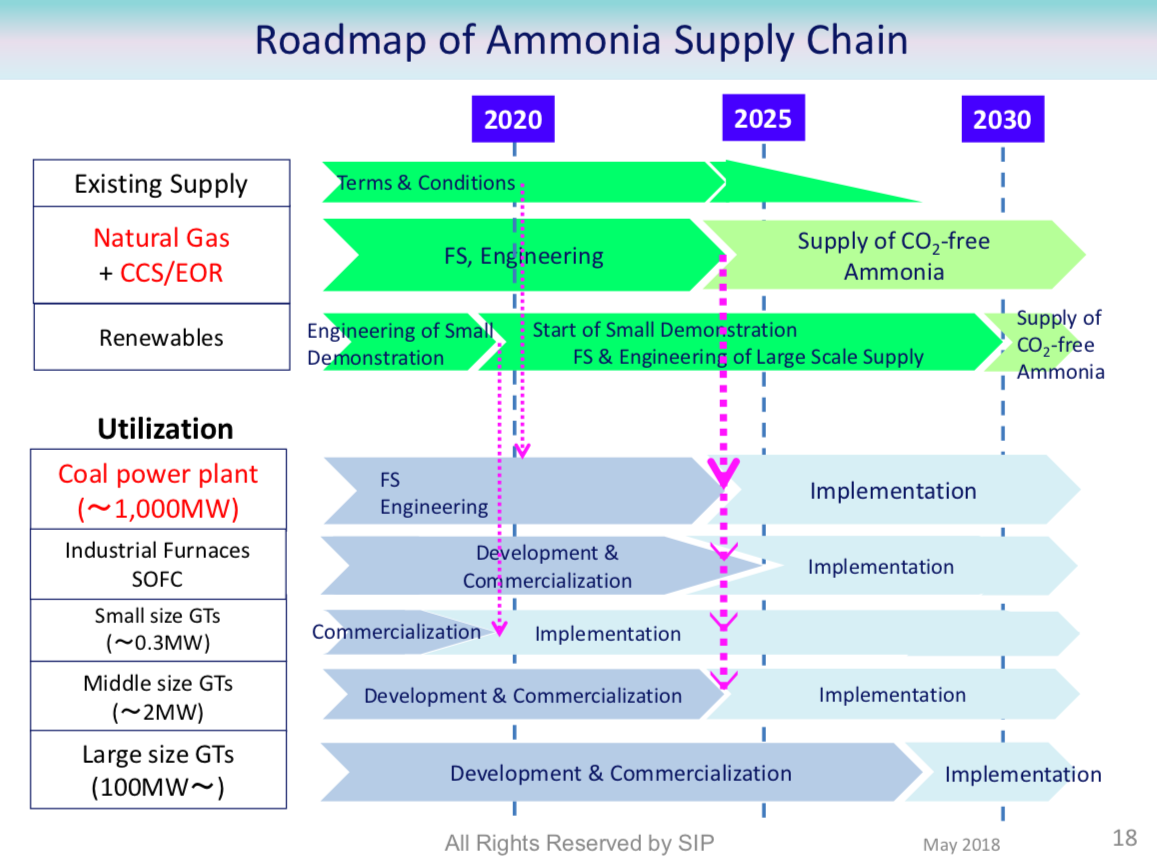
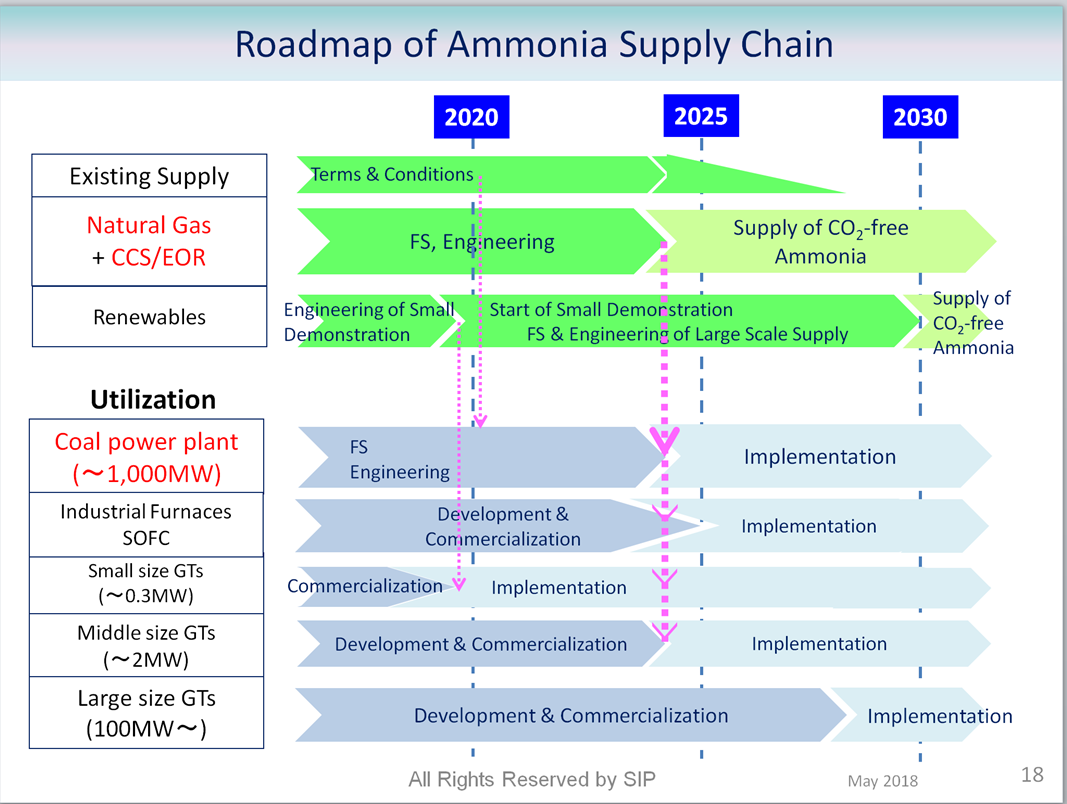
JGC Corporation demonstrates "world's first" carbon-free ammonia energy cycle
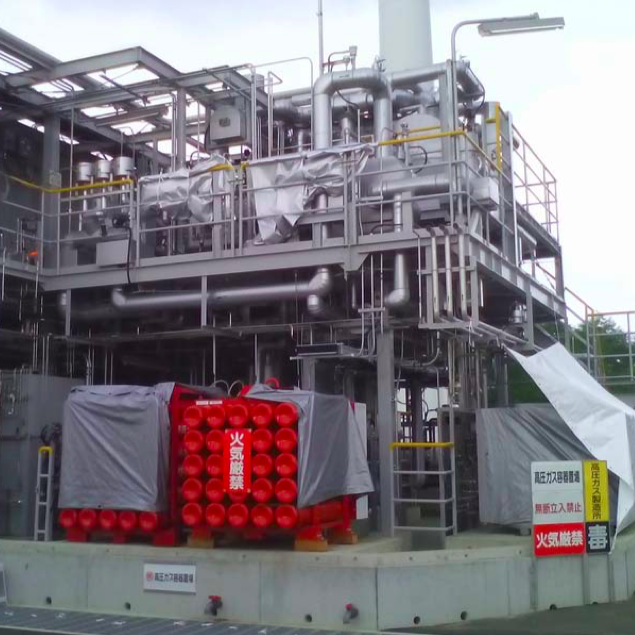
In late 2018, JGC Corporation issued a press release to celebrate a "world's first" in ammonia energy, demonstrating at its pilot plant in Koriyama both "synthesis of ammonia with hydrogen produced through the electrolysis of water by renewable energy, and generation of electricity through gas turbines fueled by synthesized ammonia." By demonstrating the feasibility of using ammonia on both sides of the renewable energy equation -- first, producing green ammonia from intermittent renewable electricity and, second, combusting this carbon-free fuel for power generation -- the project demonstrates the role of ammonia in the "establishment of an energy chain ... that does not emit CO2 (CO2-free) from production to power generation."