P2X, Ammonia Highlighted for Long-Haul Road Transport, Shipping
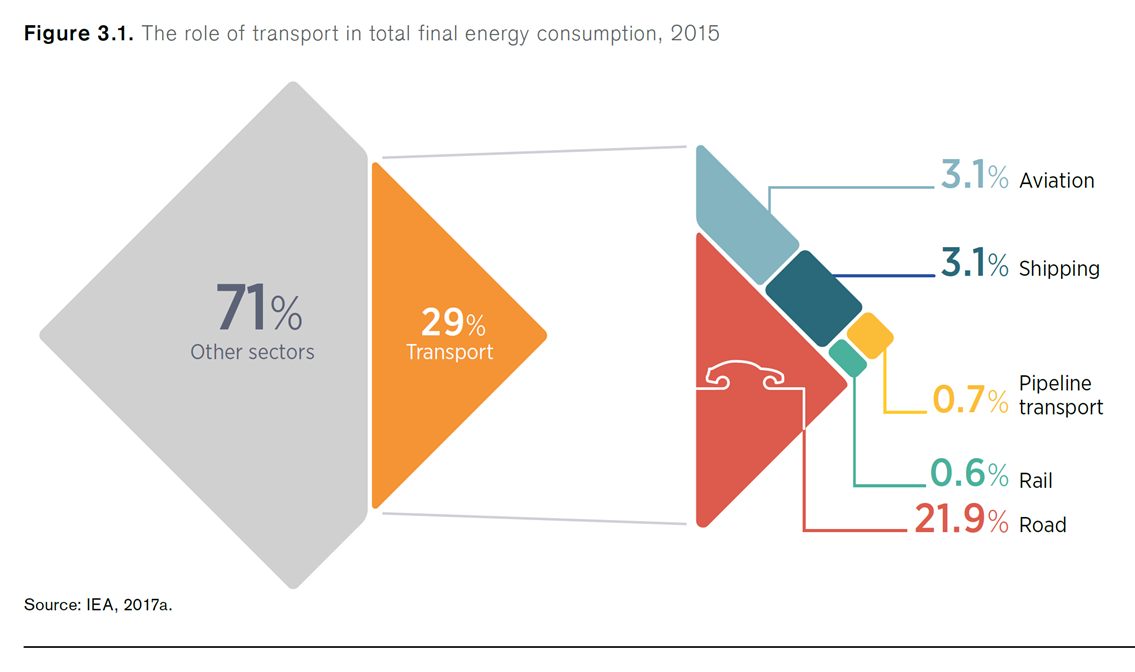
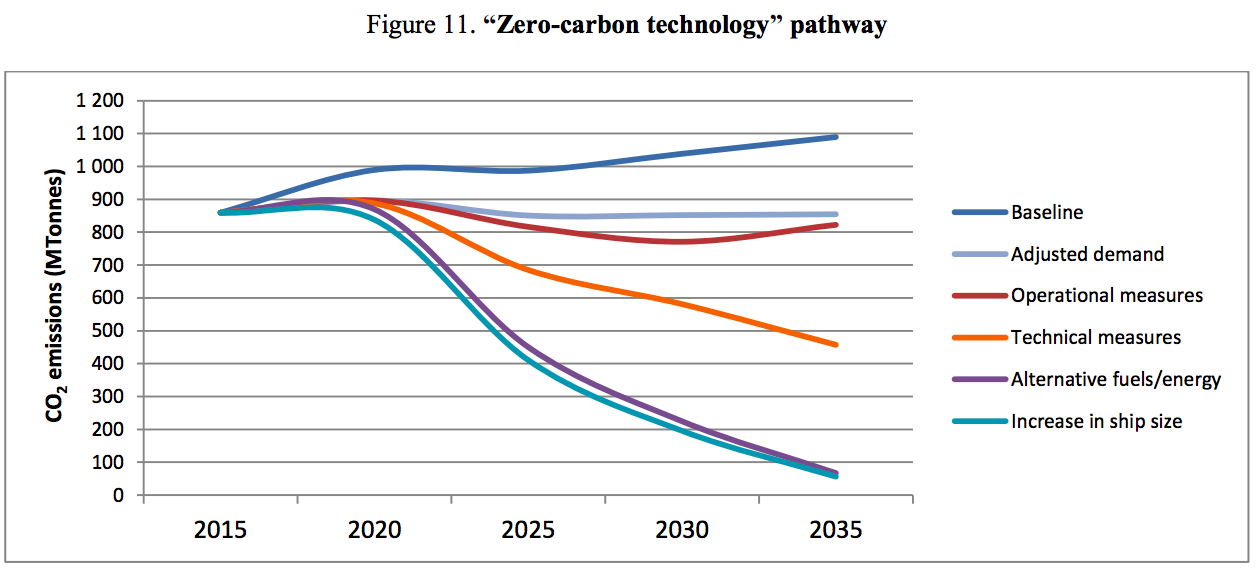
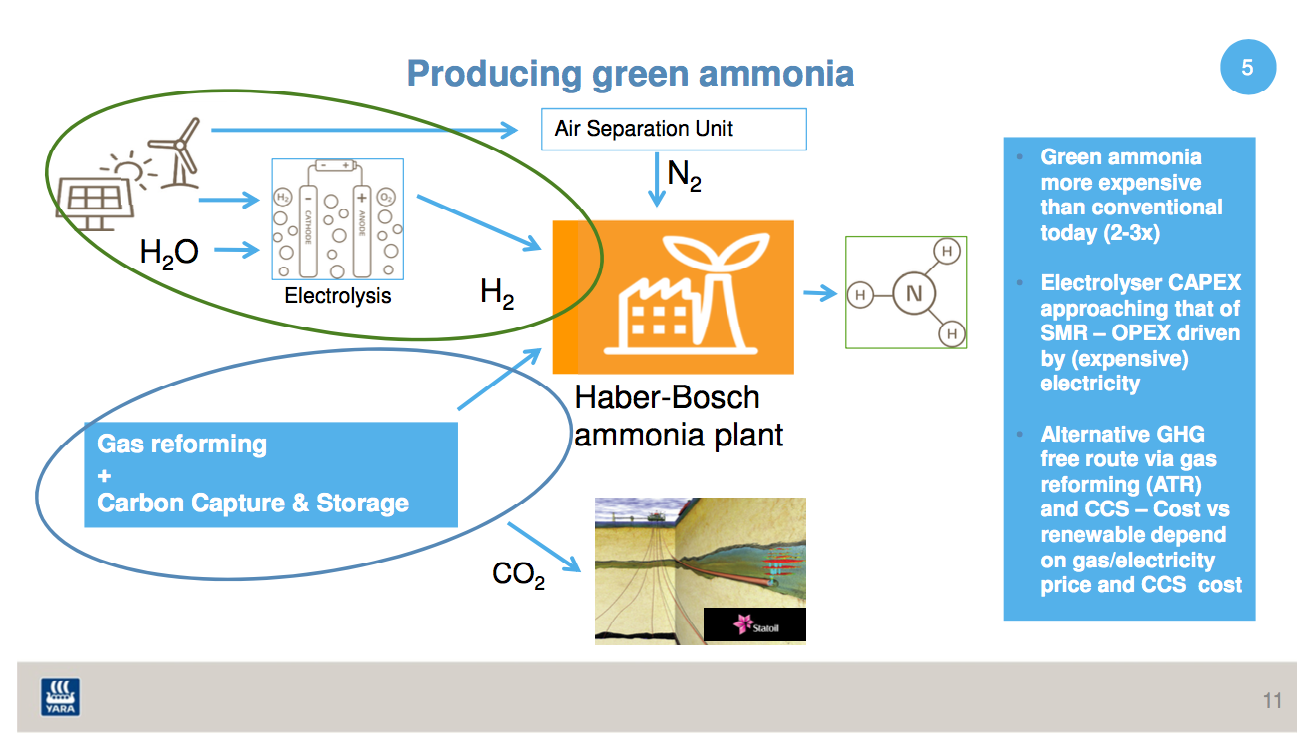
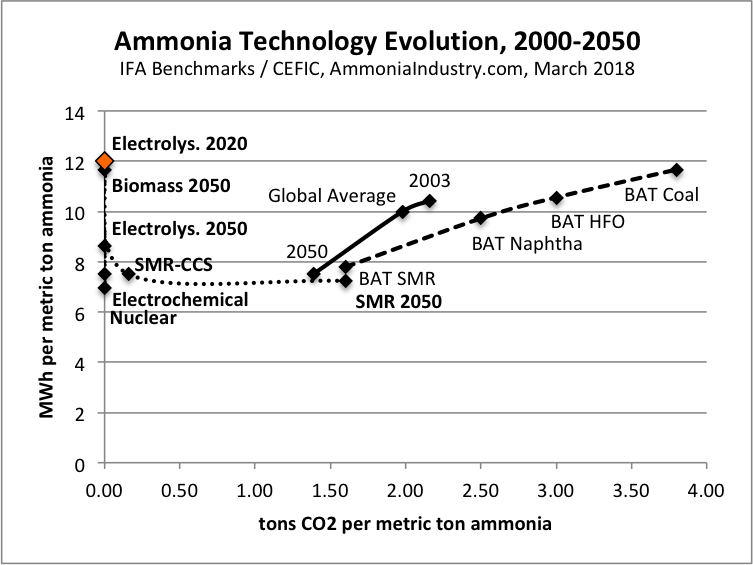
The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), in partnership with the International Energy Agency (IEA) and Renewable Energy Policy Network for the 21st Century (REN21), released a report this month entitled "Renewable Energy Policies in a Time of Transition." The 112-page document is a comprehensive survey of technologies, policies, and programs that have current or prospective roles in the global transition to a sustainable energy economy. For the ammonia energy community, one of its conclusions stands out in vivid relief: "Developing P2X is crucial because it plays a key role in decarbonising long haul road transport, aviation and shipping sectors that are difficult to decarbonize ... The overall recommendation for developing P2X is to focus on the development of ammonia for the shipping sector as well as long haul road transport, where few or no competing low carbon technologies exist and P2X is expected to be economically viable."