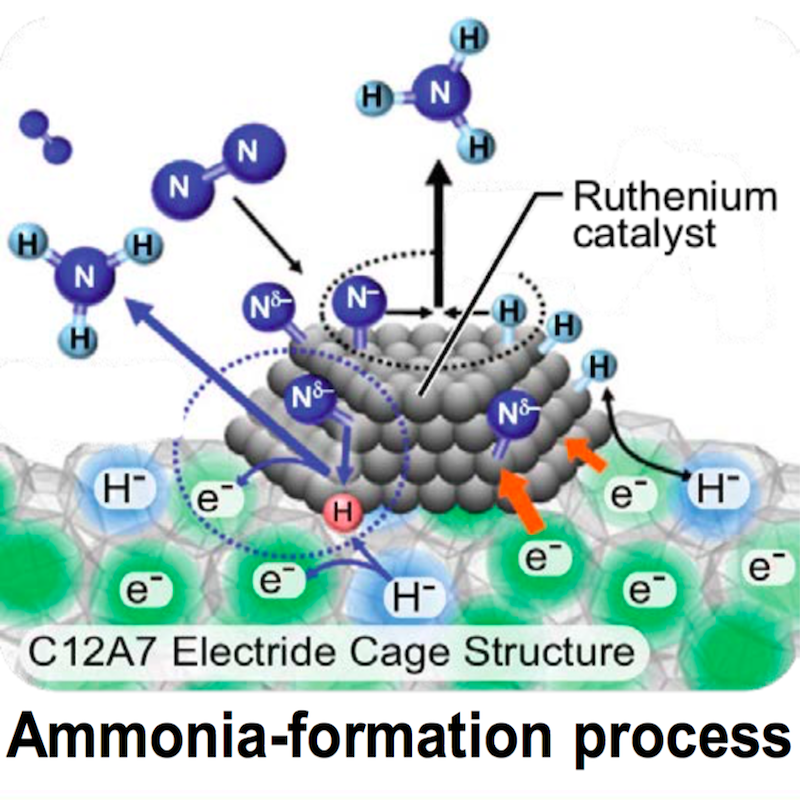
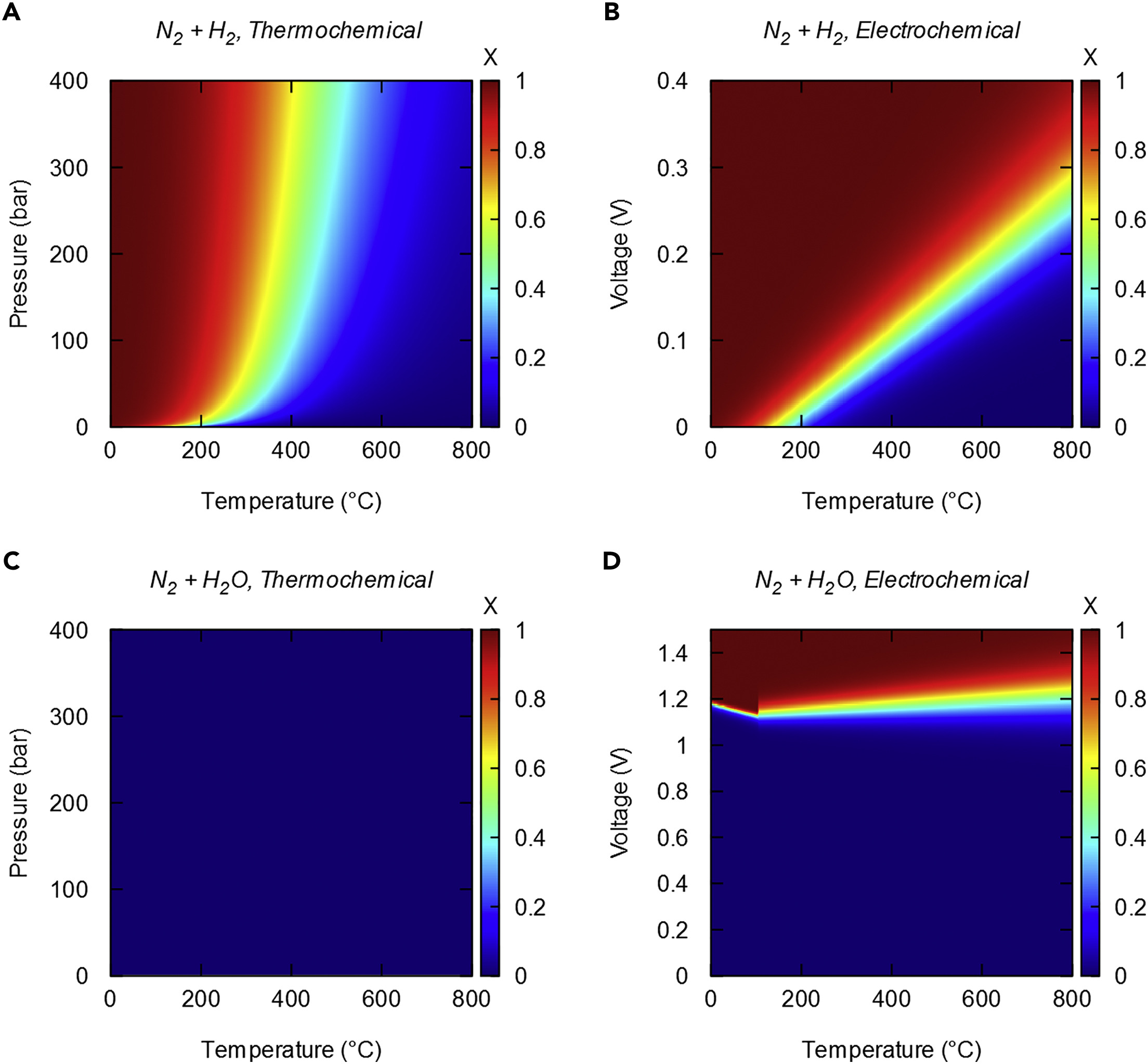
Ammonia from Offshore Wind: a techno-economic review on the US East Coast
A new study examines the technologies needed to produce renewable ammonia from offshore wind in the US, and analyzes the lifetime economics of such an operation. This is the latest in a years-long series of papers by a team of researchers from the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). And it is by far the closest they have come to establishing sustainable ammonia as being cost-competitive with fossil ammonia.