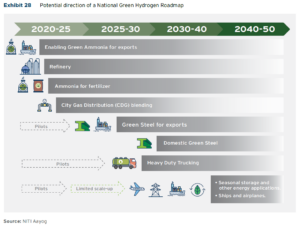
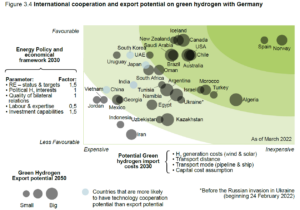
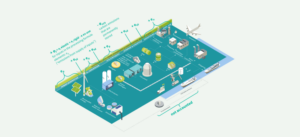
Maritime actors push on with overcoming ammonia fuel safety concerns
Two recent reports (one from Bureau Veritas & Total, the other from the Together in Safety consortium) illustrate just how seriously the maritime industry is pursuing low carbon ammonia fuel. While progress in the maritime ammonia space is impressive, safety risks are widely-acknowledged and work remains to be done.
Both reports identify key hazards facing adoption of ammonia as a maritime fuel, and echo points heard before in the development of methanol & LNG as maritime fuels: high-risk hazards currently exist that must be eliminated, mitigated or controlled. But Together in Safety concludes the way forward will be via collaboration & shared responsibility - something we’re already seeing in the multiple high-profile safety studies and consortia working around the globe. Thankfully, the willingness of significant maritime players to engage on ammonia and the momentum for change are both high.