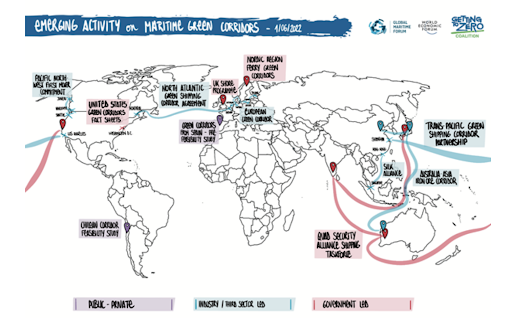
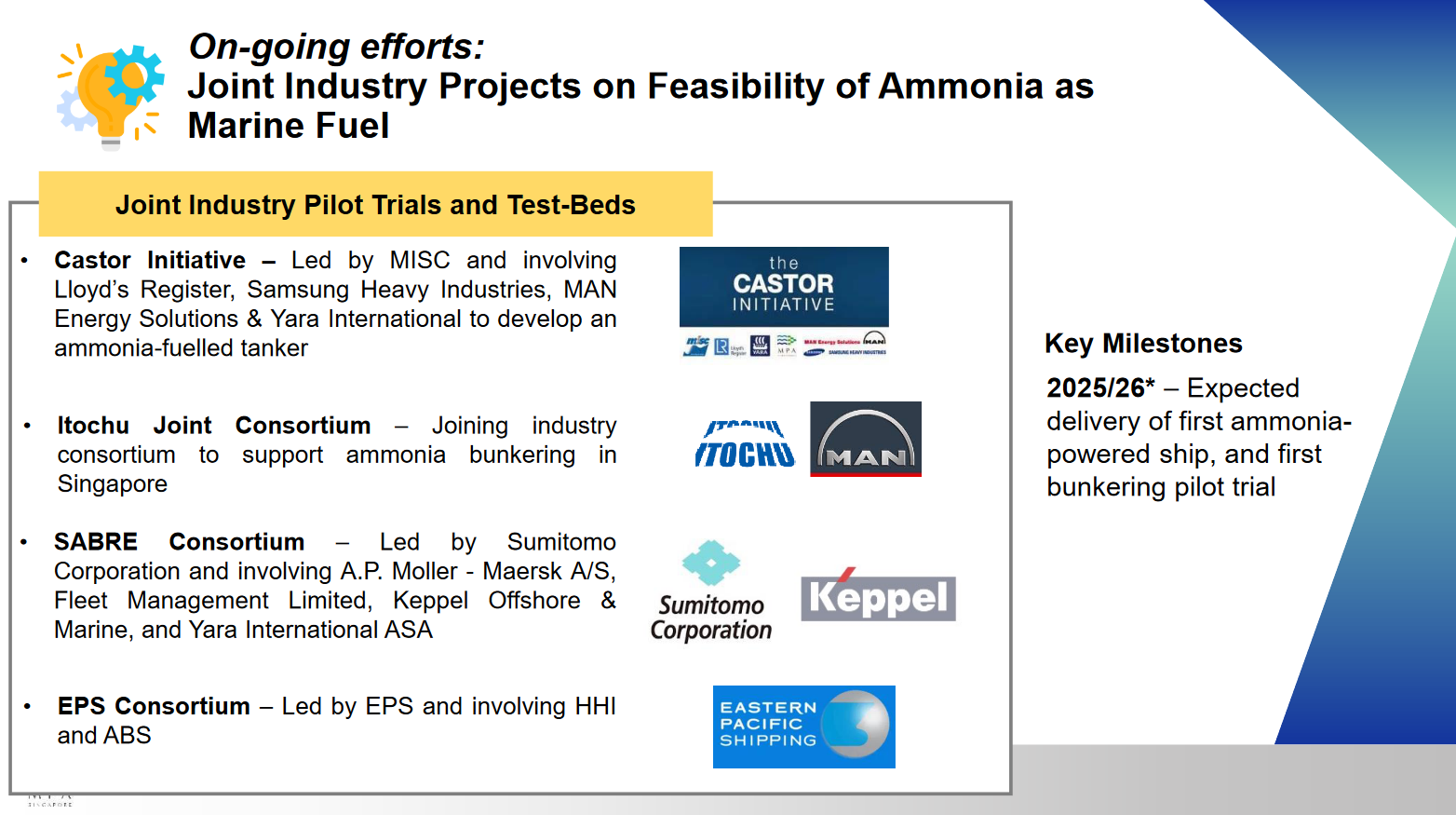
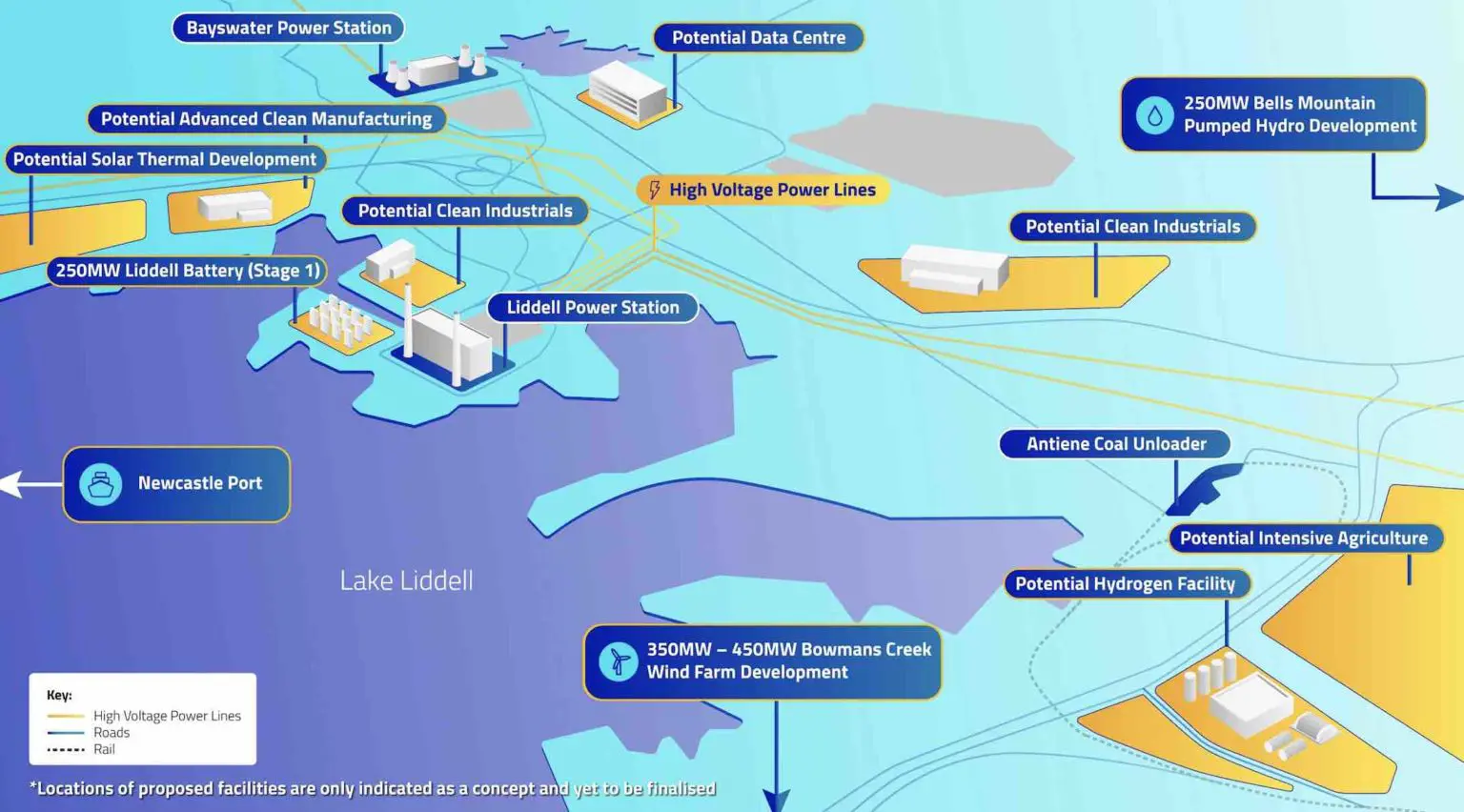
Ammonia combustion for power generation: updates from Korea, Malaysia and Singapore
Joint venture SK Plug Hyverse has agreed to deploy its Korean-manufactured PEM electrolysers overseas, and then supply Korea South-East Power (KOEN) with renewable hydrogen & ammonia imports for co-firing at natural gas and coal power plants. In Malaysia, power utility Tenaga Nasional Bhd, IHI Power Systems and Petronas announced they have successfully conducted 60% ammonia co-combustion trials. And in Singapore, Jurong Port, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and JERA will conduct a joint study on Jurong Island, where a 60MW, combined-cycle gas turbine will be fueled by 100% ammonia to produce zero-carbon electricity.