The Ammonia Wrap: Haldor Topsøe and Aquamarine to deploy solid oxide electrolysis, green ammonia to carry hydrogen for South Korean steel, and Namibia's national green ammonia strategy
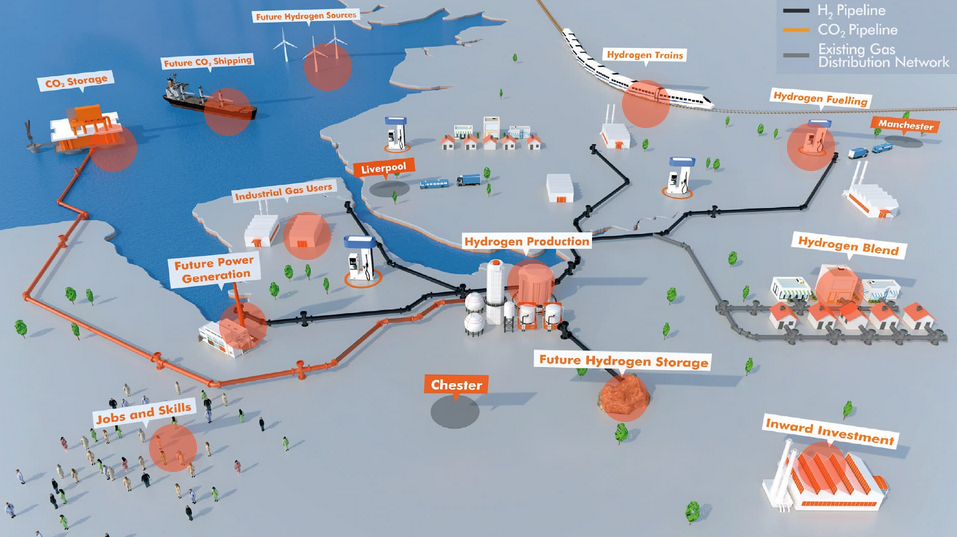
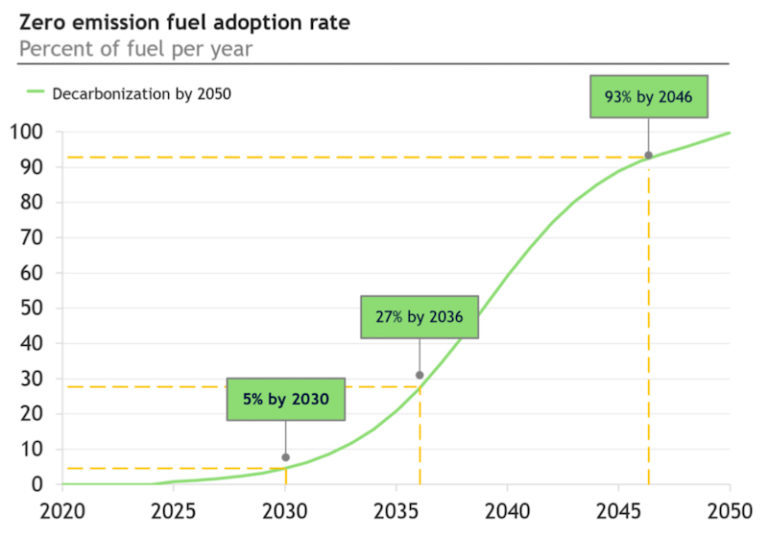
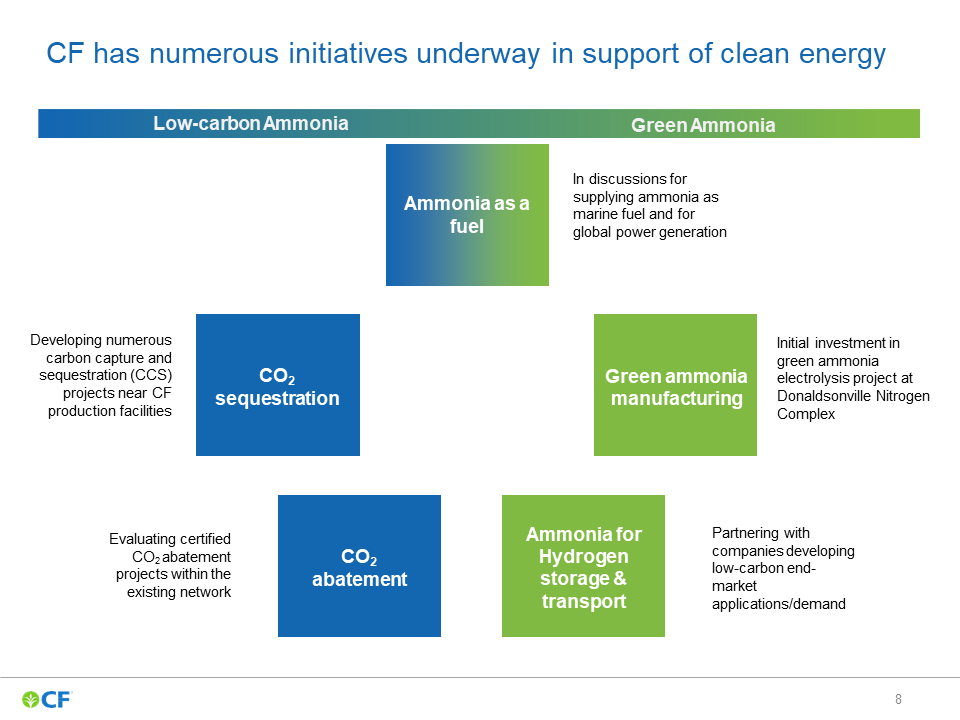
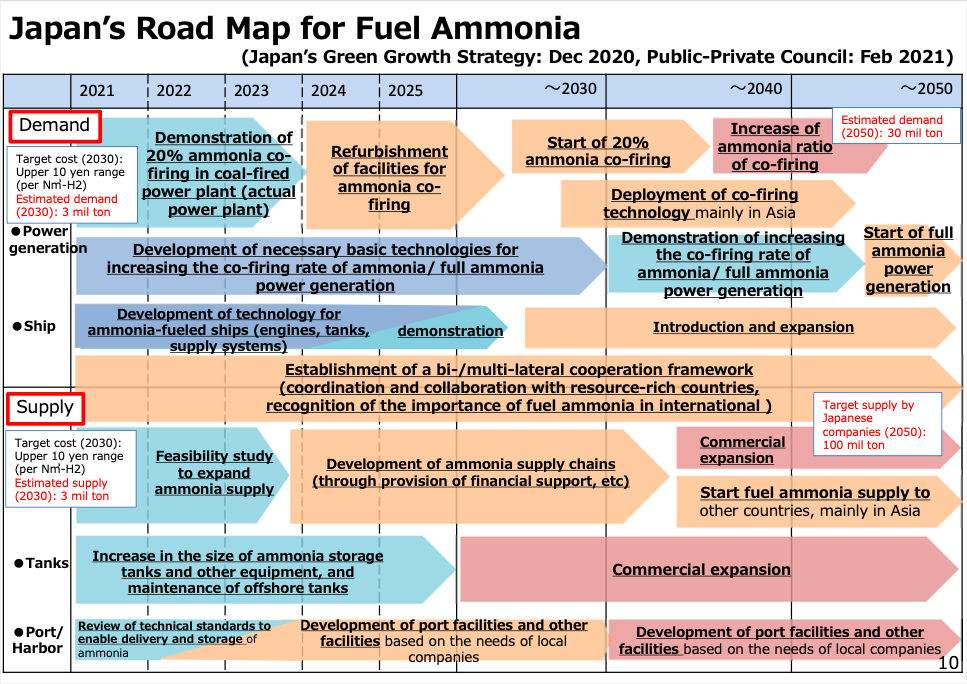
Welcome to the Ammonia Wrap: a summary of all the latest announcements, news items and publications about ammonia energy. This week: green ammonia from Haldor Topsøe and Aquamarine, "Transhydrogen Alliance", Origin Energy signs deal with Korean steel maker POSCO, Japanese electric utilities move towards ammonia, new funding for CF Industries low-carbon fertiliser in the UK, Japanese partners to study Indonesian blue ammonia output and Namibia's national hydrogen & ammonia strategy.