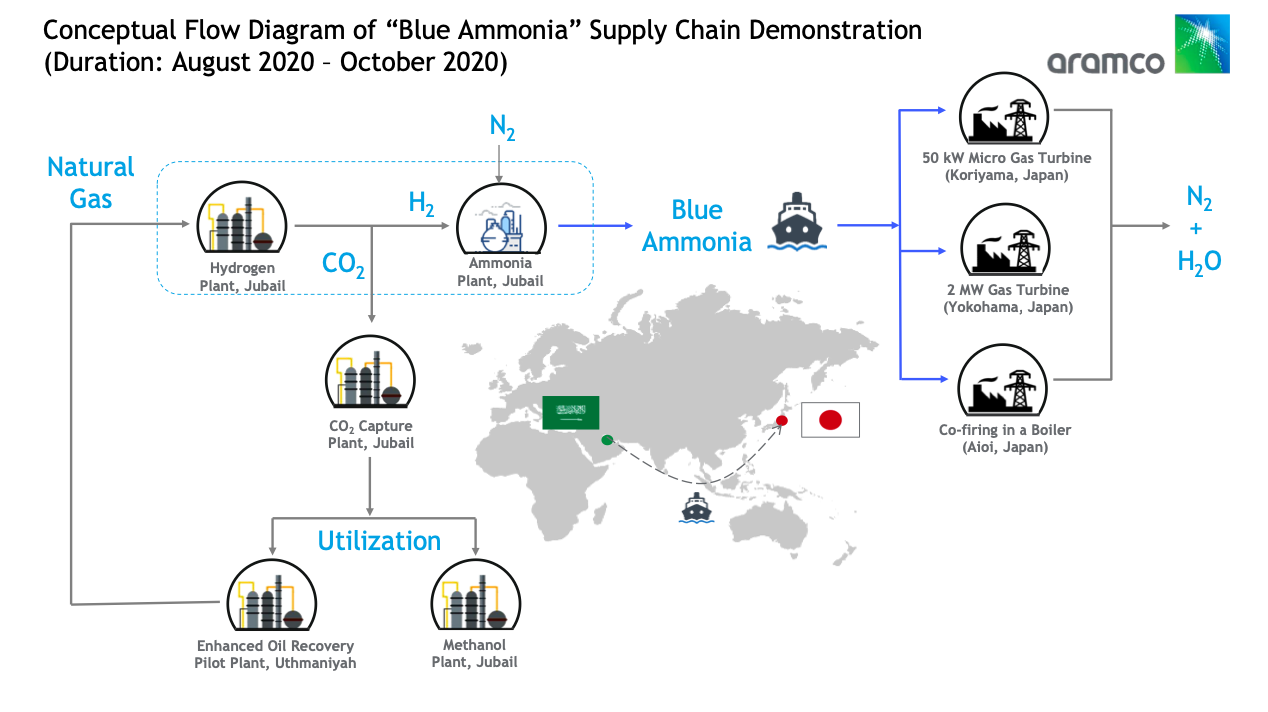
Fortescue Making Major Move into Green Energy
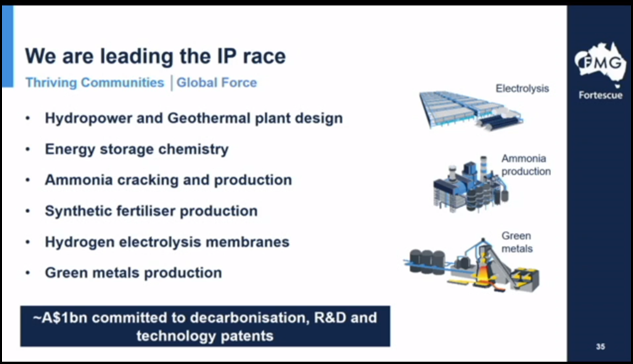
Last week the Sydney Morning Herald featured this headline: "Fortescue to take on fossil fuel giants with expansion into green energy." Bold words, but it turns out the headline does not overstate Fortescue’s ambitions for its new business, Fortescue Future Industries (FFI). “FFI will finance, develop and operate renewable energy projects including green hydrogen and green ammonia plants,” the accompanying story says, with the "aim to build 235 gigawatts of installed energy capacity.”