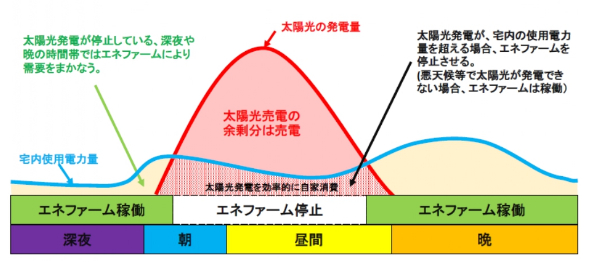
New Twists for Japanese Ene-Farms
Over the last two months, Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) has selected at least four natural gas utilities to participate in “verification projects” under its Building Virtual Power Plant Using Customer-Side Energy Resources program. Participating utilities so far include Osaka Gas, Tokyo Gas, Seibu Gas, and J Power. The program is intended to facilitate the development of renewable electricity in Japan and is shining a new light on the deployment of fuel cells in the country's built environment.