Monash team publishes Ammonia Economy Roadmap
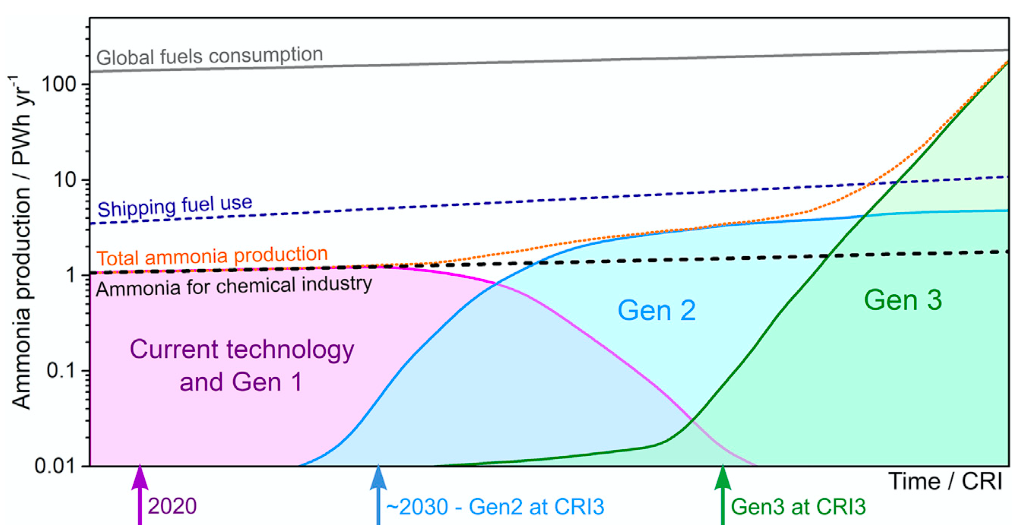
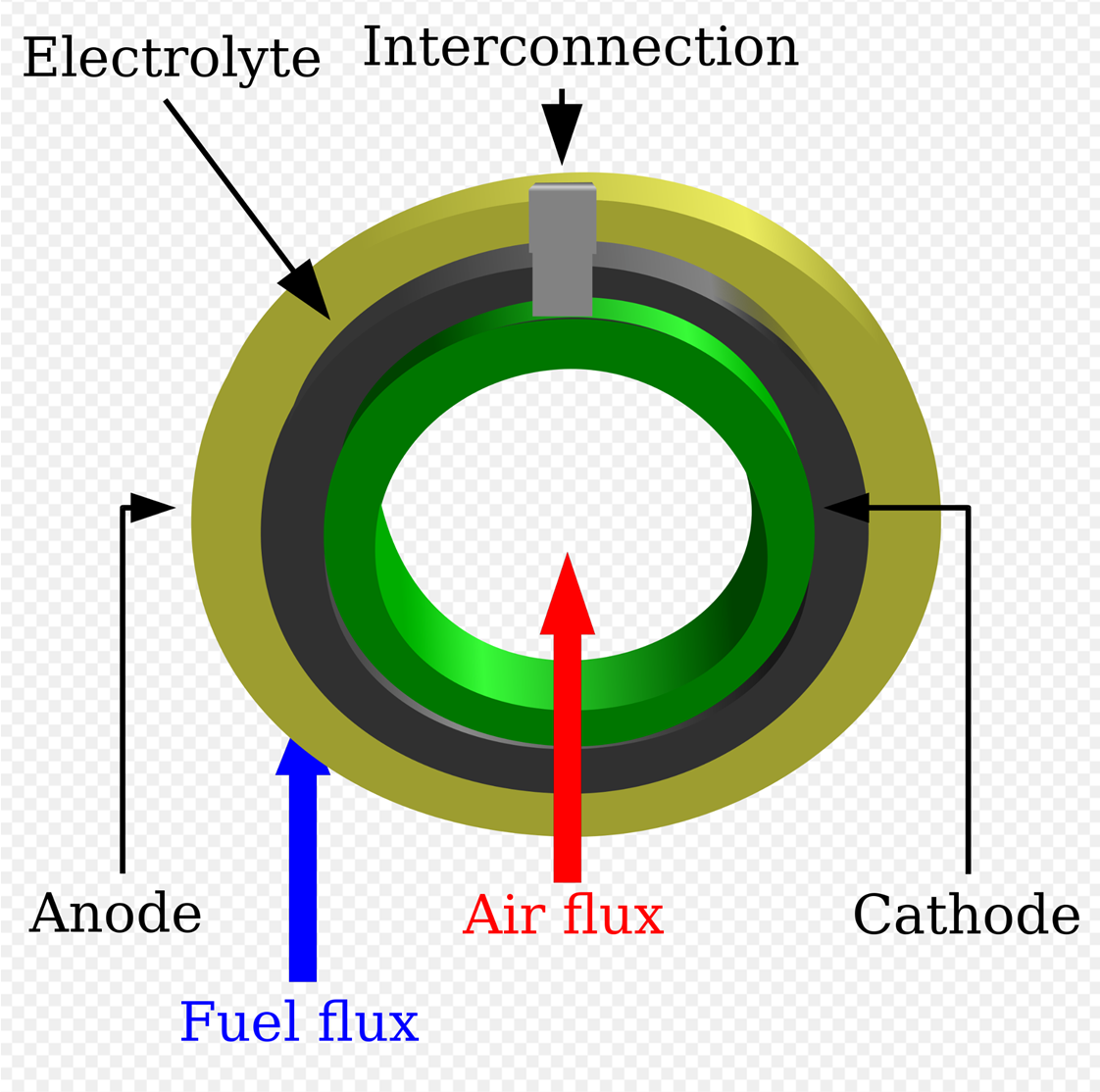
Earlier this month, Doug MacFarlane and his team of researchers at Monash University published A Roadmap to the Ammonia Economy in the journal Joule. The paper charts an evolution of ammonia synthesis “through multiple generations of technology development and scale-up.” It provides a clear assessment of “the increasingly diverse range of applications of ammonia as a fuel that is emerging,” and concludes with perspectives on the “broader scale sustainability of an ammonia economy,” with emphasis on the Nitrogen Cycle. The Roadmap is brilliant in its simple distillation of complex and competing technology developments across decades. It assesses the sustainability and scalability of three generations of ammonia synthesis technologies. Put simply, Gen1 is blue ammonia, Gen2 is green ammonia, and Gen3 is electrochemical ammonia. It also outlines the amount of research and development required before each could be broadly adopted (“commercial readiness”). The paper thus provides vital clarity on the role that each generation of technology could play in the energy transition, and the timing at which it could make its impact.