Syzygy Plasmonics launches light-powered ammonia cracking technology
By Julian Atchison on February 01, 2024
Successful validation, orders now available
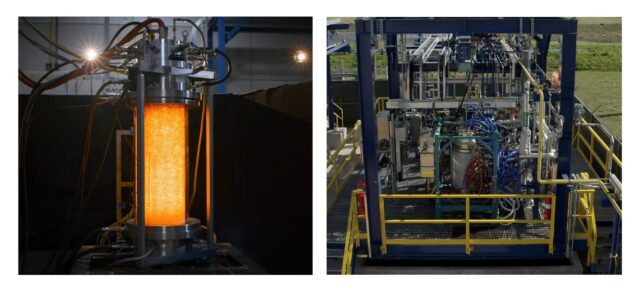
Click to learn more. Syzygy’s light-powered reactor technology during testing at its Houston laboratories. Source: Syzygy Plasmonics.
US-based Syzygy Plasmonics has announced successful final tests of its Rigel™ cell reactor technology. More than 1,500 hours of testing have validated the production of hydrogen from ammonia cracking in the reactor, which can be stacked to produce up to 5 tons of hydrogen per day. In 2025, Syzygy anticipates they can increase this installed capacity to 10 tons per day, followed by 100 tons per day in 2026.
Testing indicates the electricity input required will be 12 kWh/kg hydrogen produced in 2025, and then improved to 10 kWh/kg in 2026. Syzygy’s process avoids the combustion requirement of conventional ammonia cracking technology, meaning no NOx molecules are produced, and allowing for the process to be completely powered by renewable electricity.
Appearing at Ammonia Energy’s 2021 annual conference, Syzygy presented benchtop results indicating that their under-development reactor could operate at an energy intensity of 23 kWh/kg hydrogen produced, with a capacity of about 5 kg hydrogen production per day in a single-pass design. The new announcement demonstrates significant progress on that design – and that Syzygy is well on the path to reaching its 10 kWh/kg energy consumption goal. In late 2022, Syzygy and LOTTE Chemical announced they would deploy the technology at LOTTE’s Ulsan manufacturing headquarters.