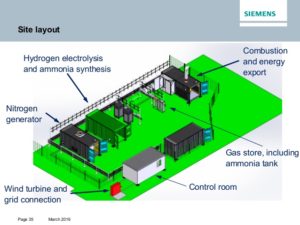
University of Minnesota's Ammonia Program
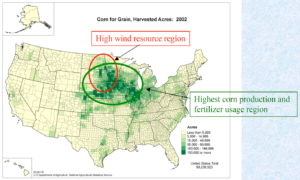
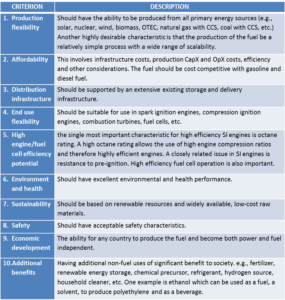
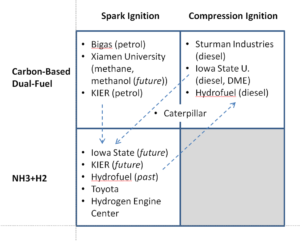
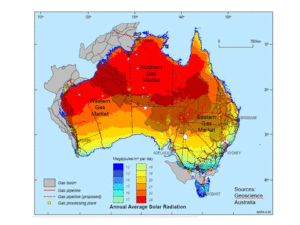
The American Institute of Chemical Engineers (AIChE) will present a Webinar on December 21 on "Distributed Ammonia Synthesis." The presenter will be Edward L. Cussler, Distinguished Institute Professor at the Chemical Engineering and Materials Science Department of the University of Minnesota. Distributed ammonia synthesis is one focus related to ammonia energy at the University of Minnesota - but just one. In fact, UMinn is the locus of a unique and globally significant collection of research efforts that promise to have significant impacts in the ammonia industry and the broader energy sector.