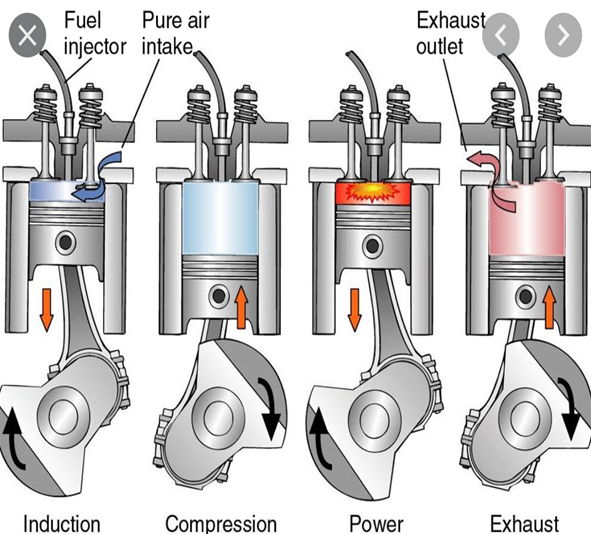
Green Financing Sighted in Australia's Ammonia Industry
Last month the Commonwealth Bank of Australia (CBA) announced that it has “signed an AUD $400 million [USD $256 million] three-year bilateral sustainability-linked loan” with Australian conglomerate Wesfarmers. This represents at least the second occasion on which an ammonia producer has linked its cost of capital to progress in meeting sustainability goals. In July 2019, Yara announced that it had signed a USD $1.1 billion revolving credit facility with a group of 13 lenders whose margin “will be adjusted based on Yara’s progress to meet its carbon intensity target by 2025.”