Environmental and Economic Assessment of Ammonia as a Fuel for Ships
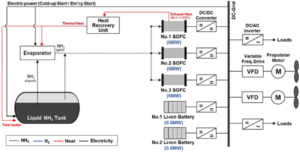
This month, the Korean Register published a comparative assessment of the environmental and economic merits of using ammonia as a maritime fuel. The work, written in collaboration with researchers at Pusan National University, is published in the open-access Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. It concludes that "ammonia can be a carbon-free fuel for ships," and presents "a meaningful approach toward solving GHG problems in the maritime industry."