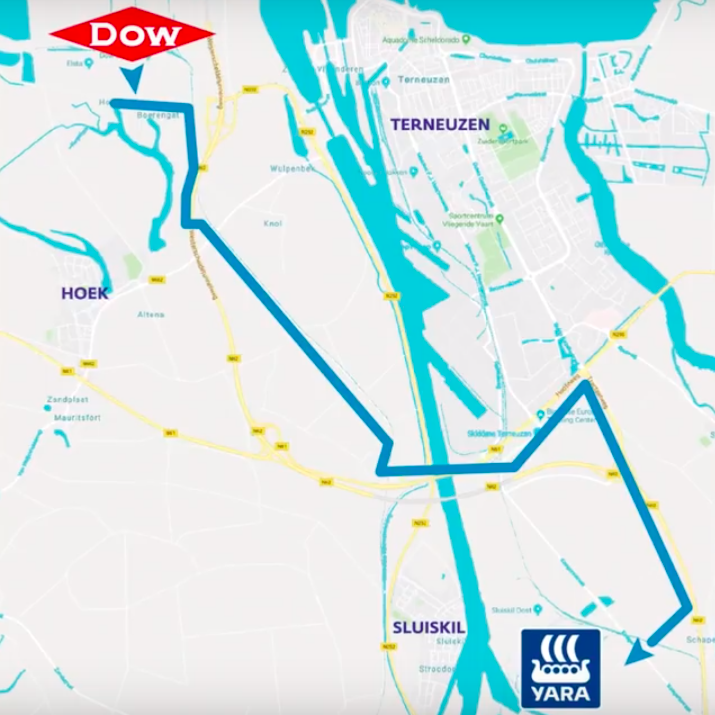
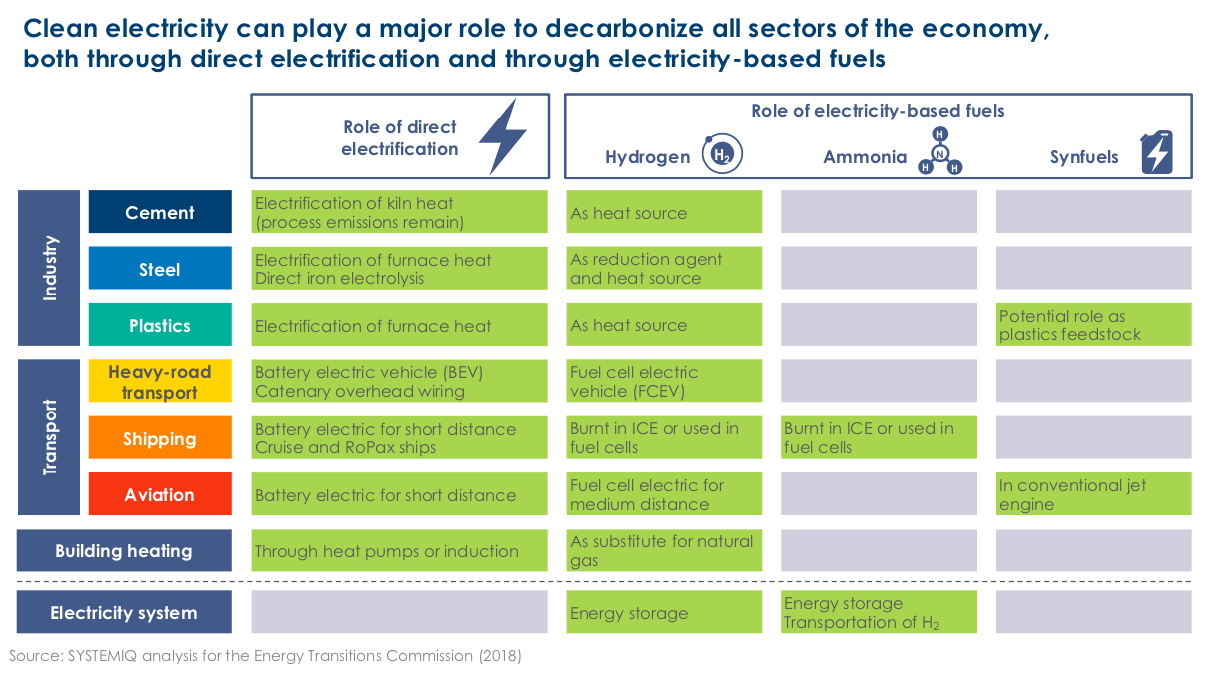
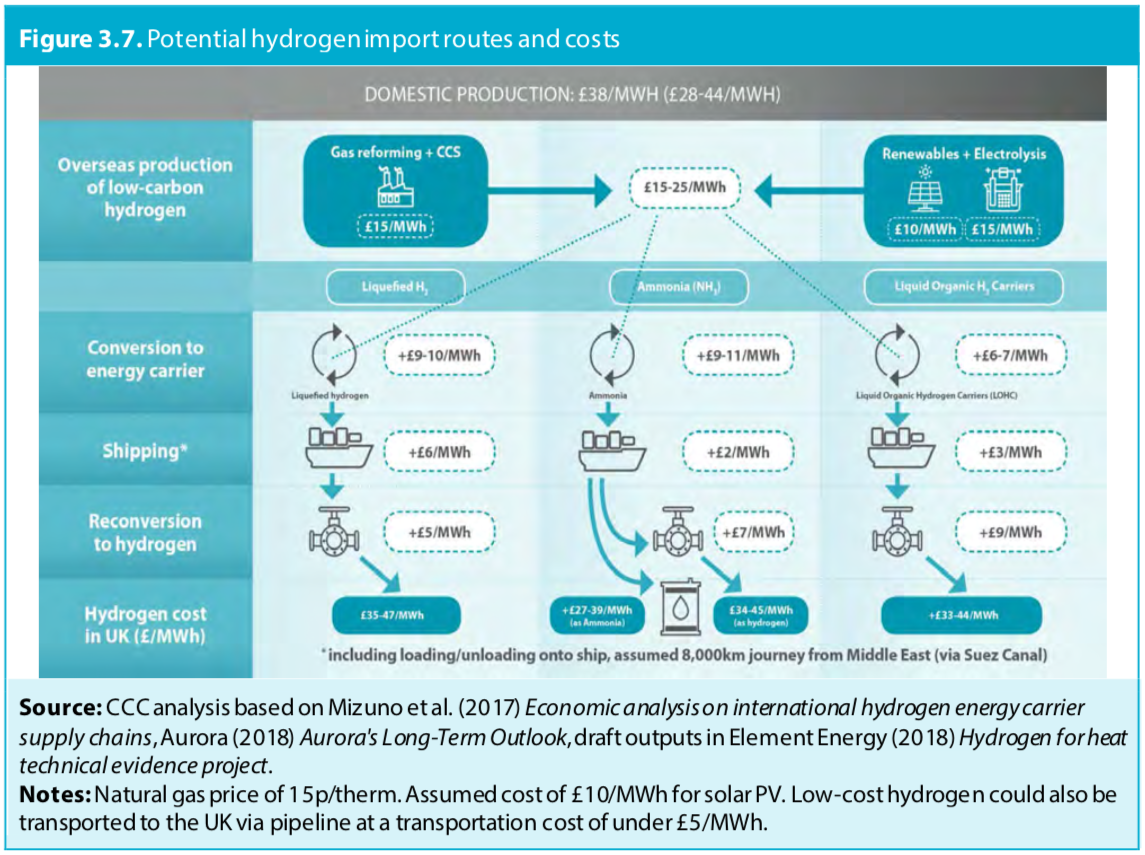
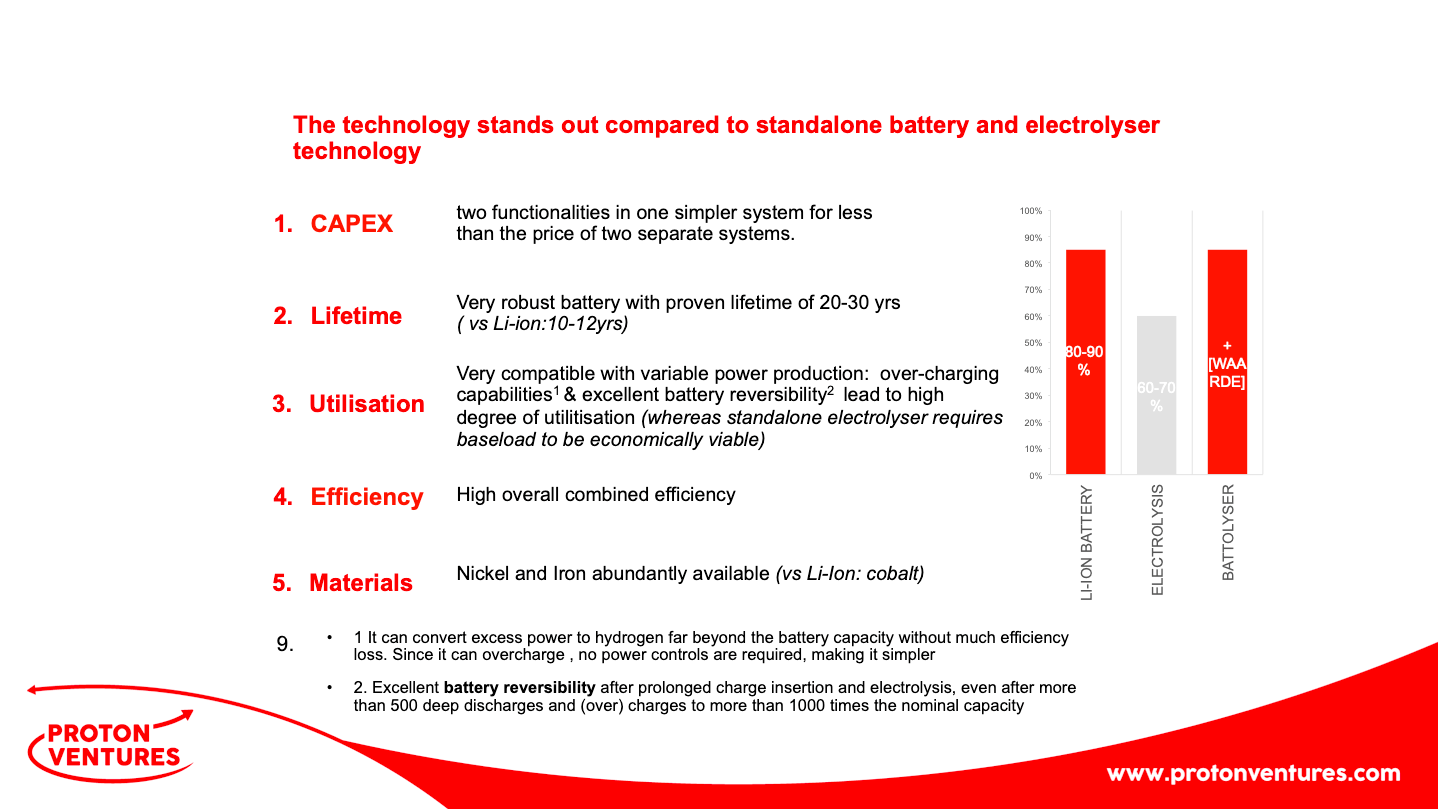
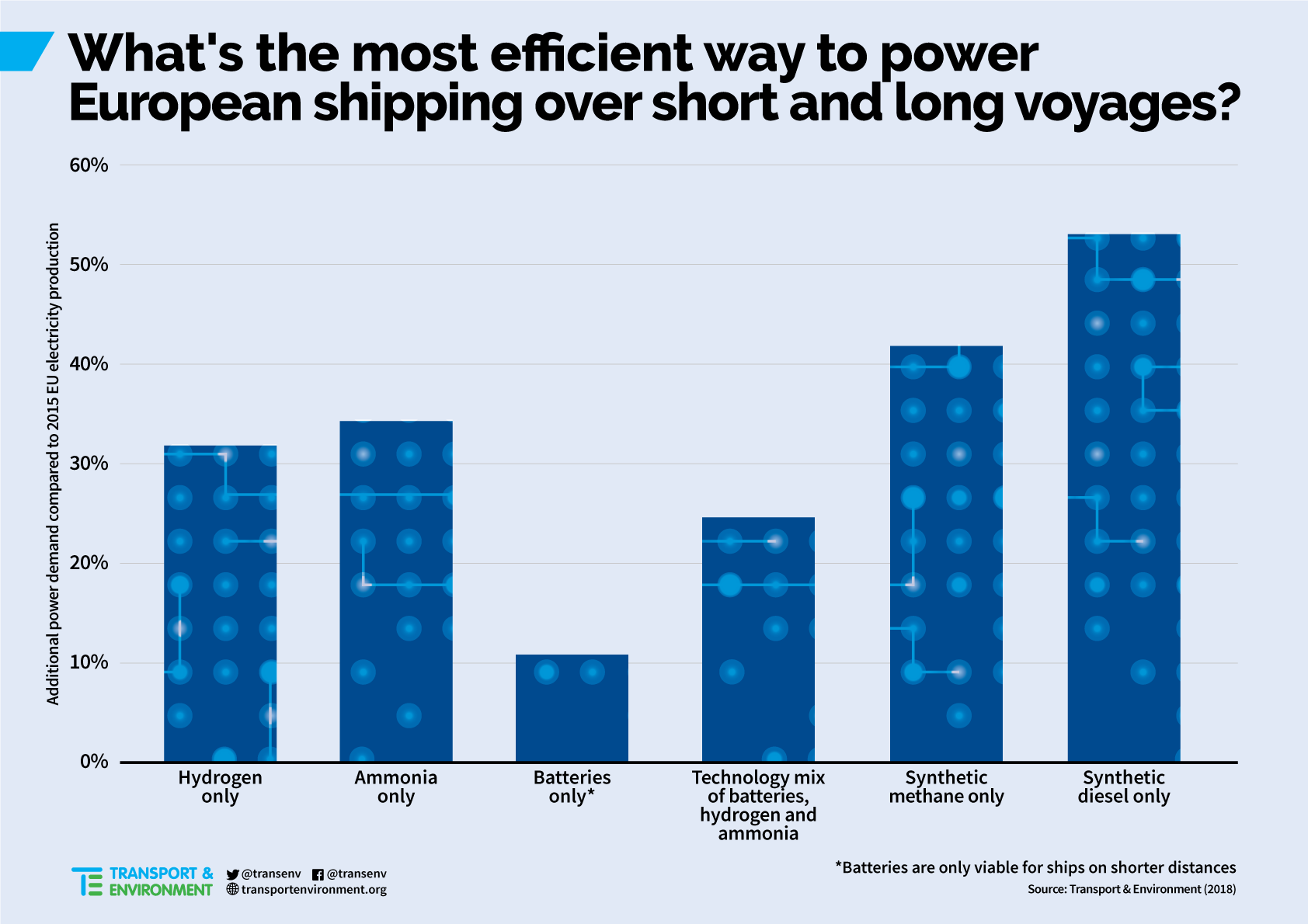
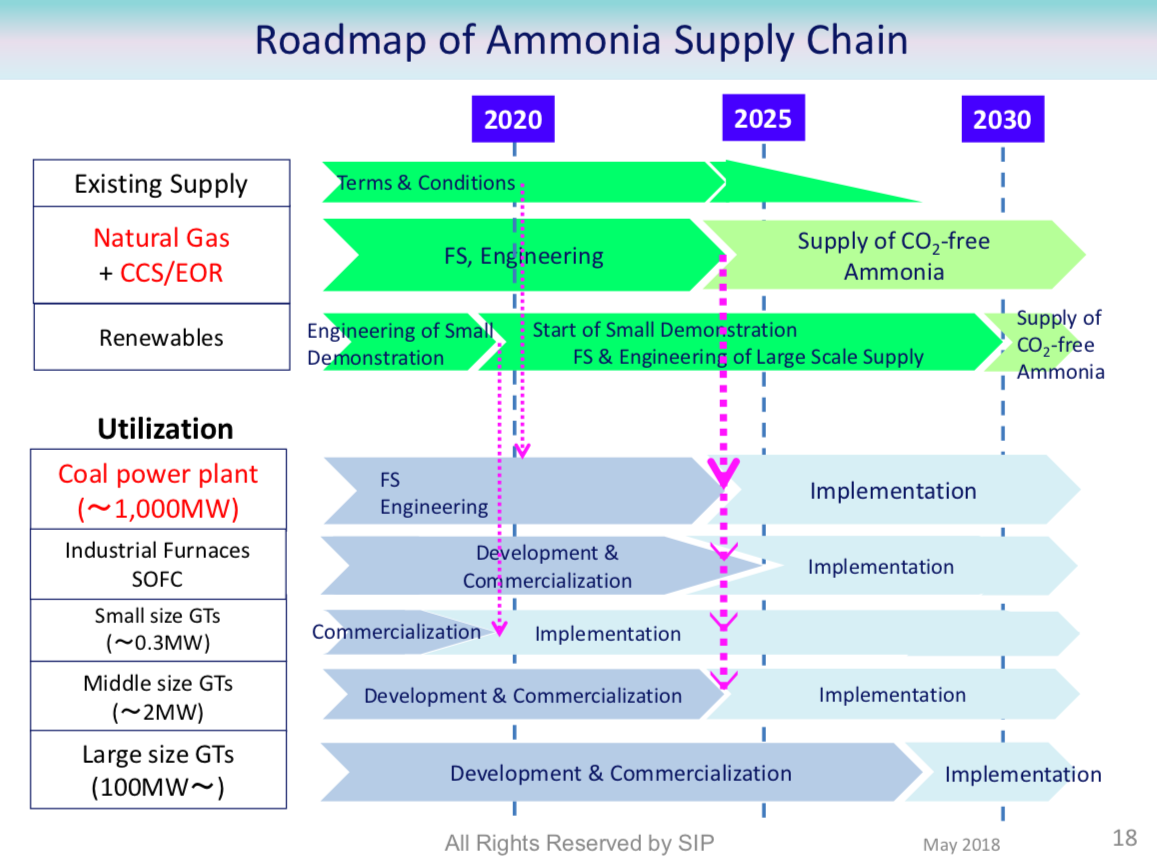
UK Department of Transport recommends launch of ammonia / hydrogen powered vessels within 5-15 years
In January 2019, the UK Department for Transport published a policy paper outlining its vision for the maritime sector over the coming decades. Among the many recommendations contained in Maritime 2050: navigating the future, is a medium-term objective to place "a group of hydrogen or ammonia powered domestic vessels in operation." The "strategic ambition" driving this recommendation is the expectation that "the UK will ... lead the way in taking action on clean maritime growth enjoying economic benefits from being an early adopter or fast mover." Moving forward, these recommendations will be developed into policy in the government's forthcoming Clean Maritime Plan, scheduled to be published in Spring 2019.