Content by Author
Showcasing ammonia energy developments in China
The recent Symposium on Ammonia Energy in Shanghai showcased the latest ammonia energy R&D, including cutting-edge work on catalysts, direct ammonia combustion, large-scale co-firing and industrial ceramics production.
The 3rd Symposium on Ammonia Energy: Shanghai, Sept 22-26
Learn more about the 3rd Symposium on Ammonia Energy, to be held in Shanghai from 22-26 September this year. The AEA is a proud supporter of the event, which will showcase the latest R&D in ammonia energy. Hear from a program of global researchers, take part in industry collaboration workshops, and get the chance to explore local R&D in a series of site visits.
Ammonia as a Marine Fuel
Ammonia-Hydrogen Power for Combustion Engines
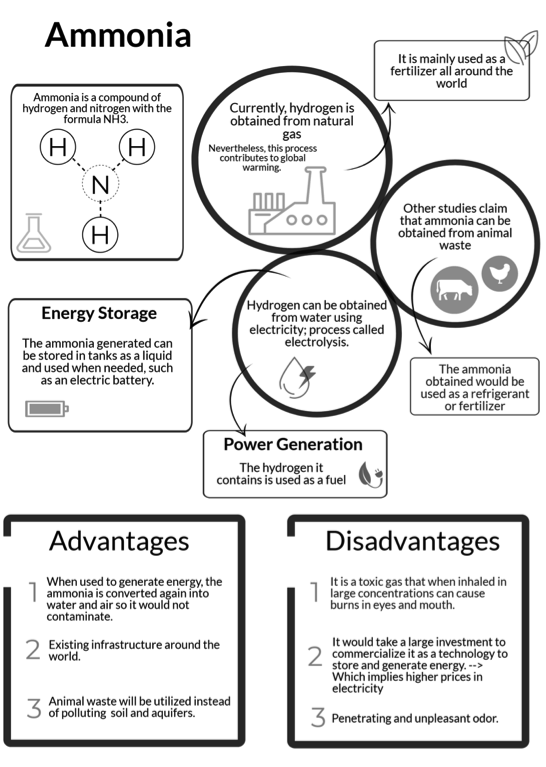
Importance of Public Perception towards an Ammonia Economy
During development of the technical aspects of any energy project, a social perspective needs to be considered. Public opinion is going to be a fundamental parameter to determine the role of renewables in the future, with decarbonisation meaning innovation towards a comprehensive plan that involves not only technology but also psychology and how these two can benefit from each other. Due to the importance of understanding public perception of ammonia, Cardiff University conducted a study focused on the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico, which currently presents high revenues in agriculture and depends on ammonia as a fertiliser. An analysis of stakeholder’s perception of ammonia was carried out to understand the different barriers and drivers of each established group.
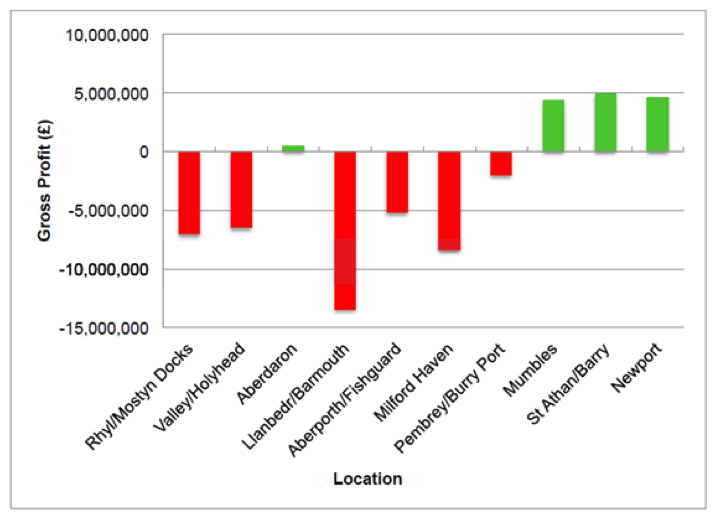
Sustainable Energy for Wales: Tidal and Wind with Ammonia Storage
As part of the sustainable agenda of the UK, the government, research institutions and various enterprises have looked for options to reduce the carbon footprint of the country while ensuring energy independence for several years. As a response, one of the alternatives has been to introduce the use of marine energy via the implementation of a barrage in the Severn Estuary or the development and implementation of Tidal Lagoons located around the Welsh coast. From these alternatives, the tidal lagoon concept seems to be most feasible. Hybrid tidal and wind energy systems will produce vast amounts of energy during off-peak hours that will require the use of energy storage technologies - the size of each proposed tidal lagoon ranges close to ~1.5 GW. Currently, companies involved in the development of these complexes are thinking of batteries, pumped hydro, and ammonia as the potential candidates to provide storage for these vast amounts of energy.