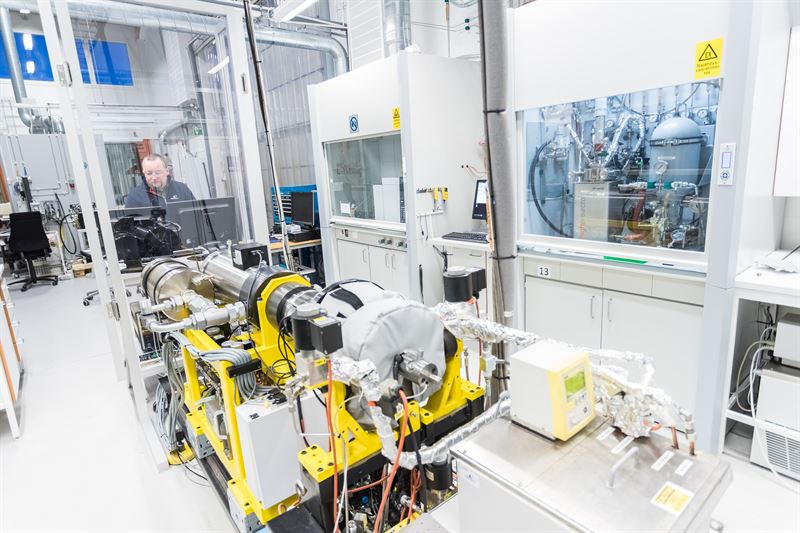
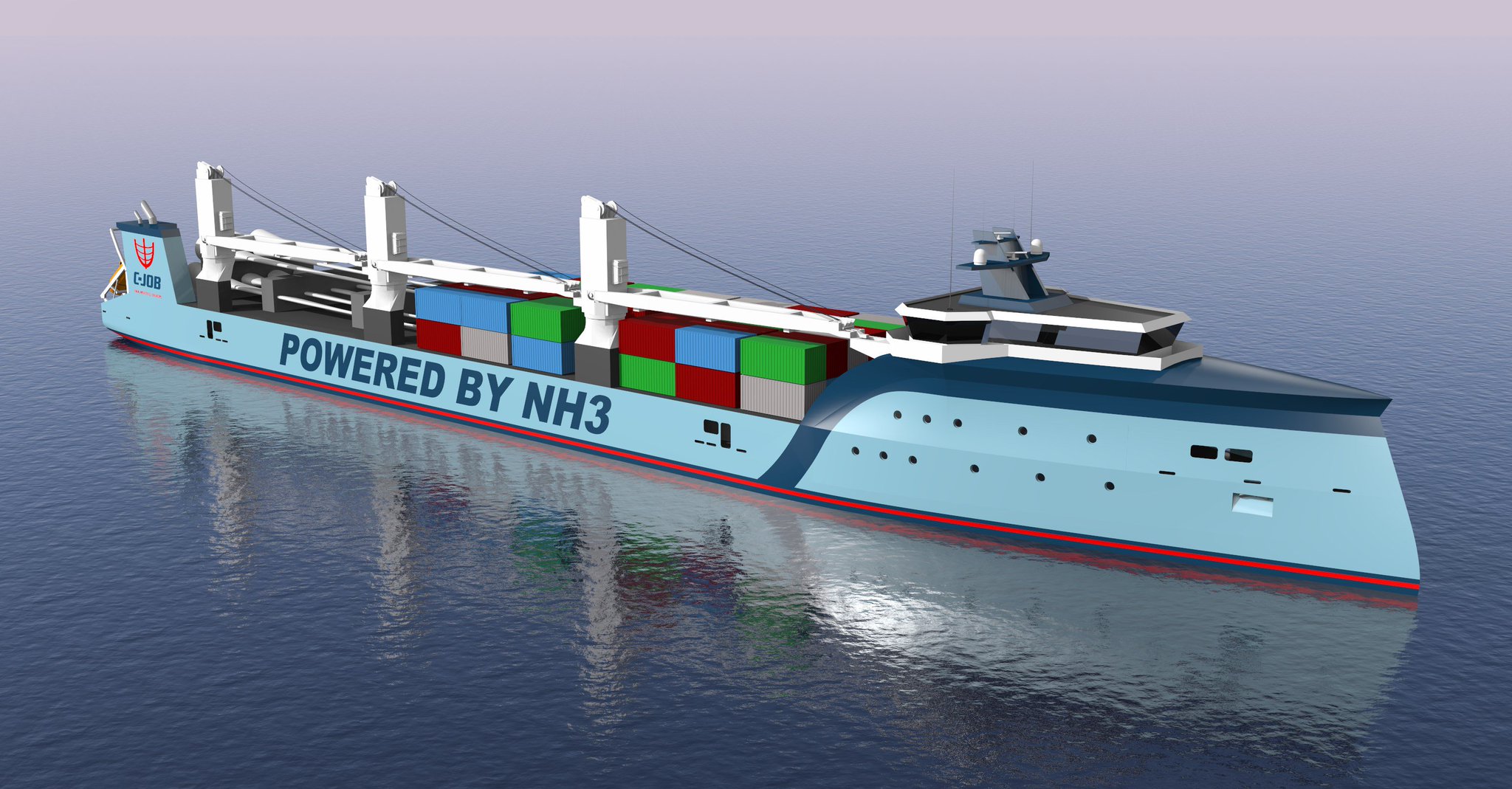
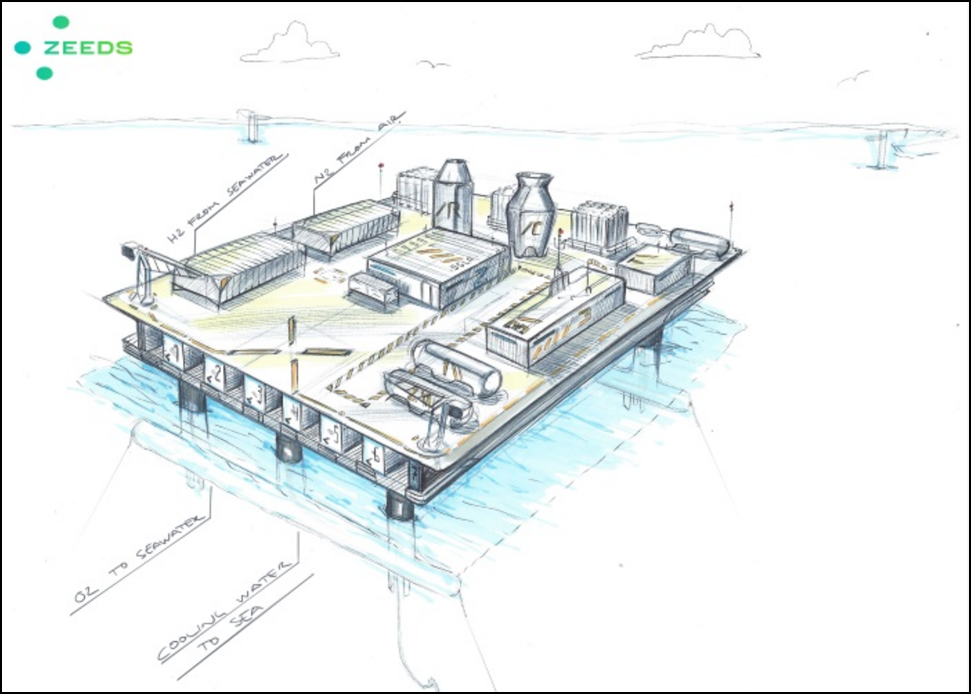
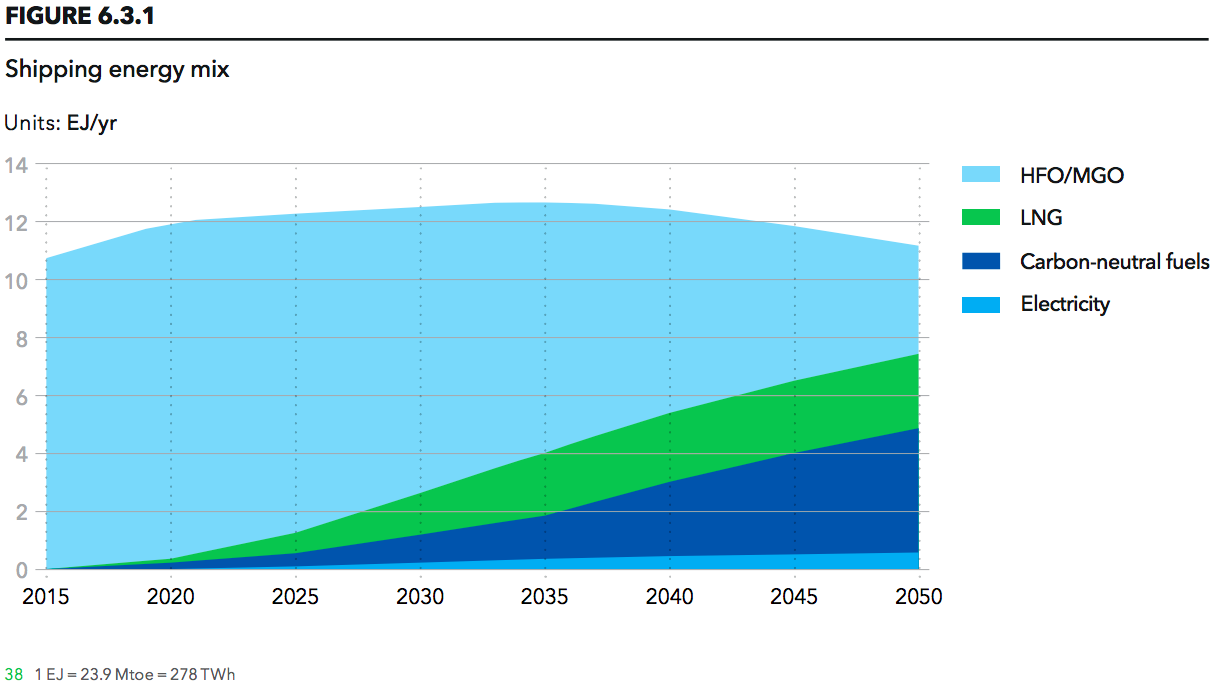
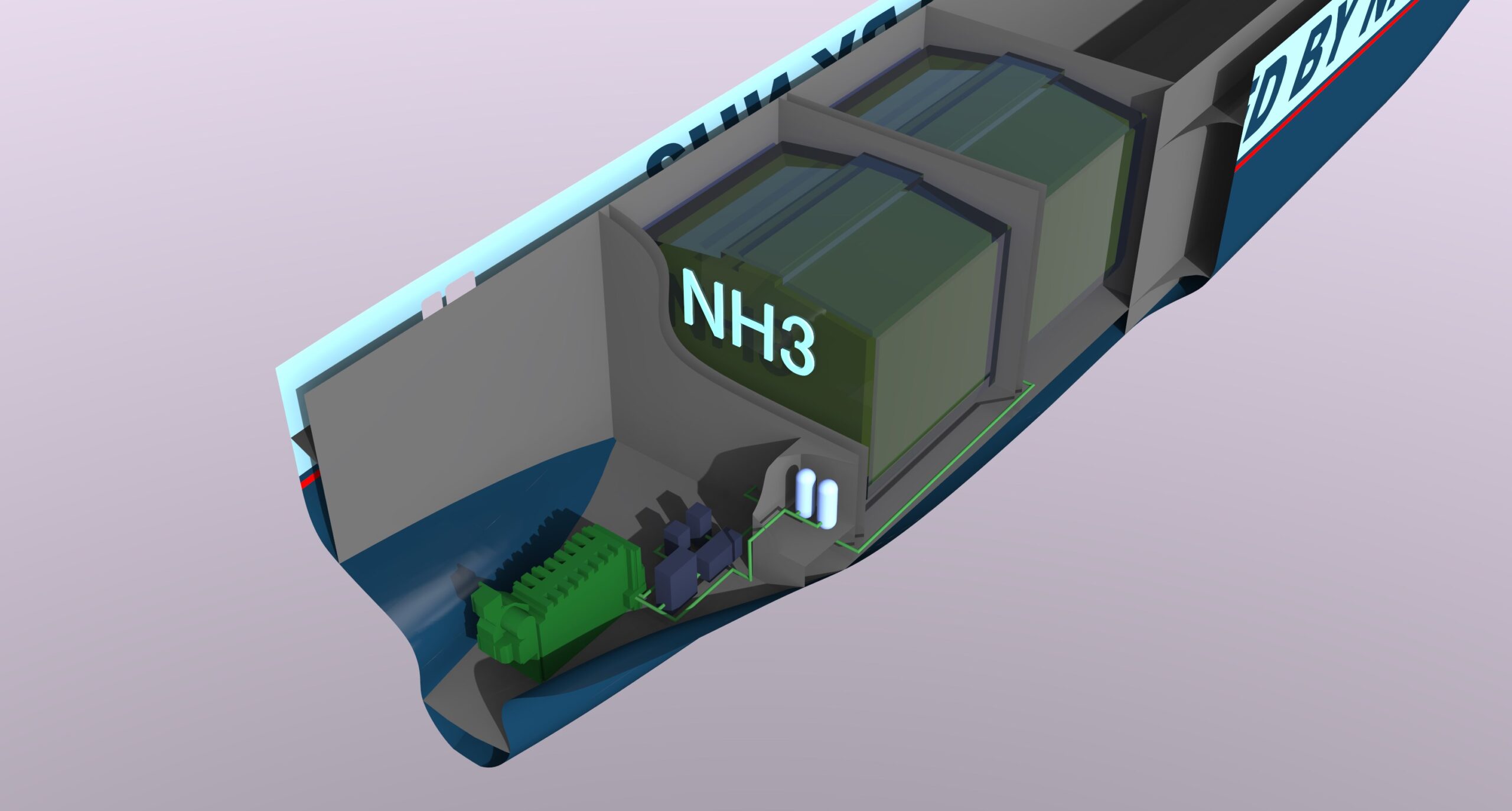
Last week, I wrote about a crucial new report that discusses four fuel technologies: batteries, hydrogen, ammonia, and nuclear. These could reduce the shipping sector's emissions in line with targets set in the IMO's Initial GHG Strategy. The report, Reducing CO2 Emissions to Zero, concludes that "all industry stakeholders ... need to get on with the job of developing zero CO2 fuels." This call to action should be consequential: it comes from the International Chamber of Shipping, an influential industry group that represents "more than 80% of the world merchant fleet." This week, I provide an example of the kind of research required, with an update on a project that aims to demonstrate "the technical feasibility and cost effectiveness of an ammonia tanker fueled by its own cargo." Although this project is still in its early days, I want to highlight three aspects that I believe will be crucial to its success. First, the work is being done by a consortium, bringing together many industry stakeholders, each with its own expertise and commercial interests. Second, the scope of research extends beyond conventional engine configurations to include not just new fuels but also new technology combinations; in other words, rather than assess new fuels in old engines, it aims to develop optimized propulsion designs for zero-emission fuels. And, third, its consideration of ammonia as a fuel begins with a comprehensive safety analysis.