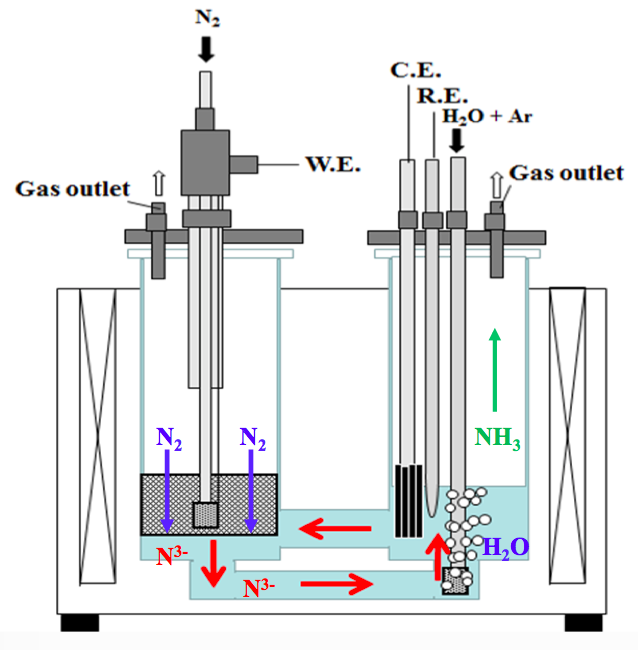
One of the many encouraging announcements at the recent Power-to-Ammonia conference in Rotterdam was the news that the Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) has extended funding for its electrochemical ammonia synthesis research program by another three years, pushing the project forward through 2019. KIER's research target for 2019 is significant: to demonstrate an ammonia production rate of 1x10-7 mol/s·cm2. If the KIER team can hit this target, not only would it be ten thousand times better than their 2012 results but, according to the numbers I'll provide below, it would be the closest an electrochemical ammonia synthesis technology has come to being commercially competitive.
Content Related to CERTH
Presentation
Progress in the Electrochemical Synthesis of Ammonia
Ammonia is one of the most important and widely produced chemicals worldwide with a key role in the growth of human population. Nowadays, the main route for ammonia synthesis is the Haber-Bosch process, developed one century ago. In this process, Fe-based catalysts are usually employed at temperatures between 400 and 500°C and pressures between 130 and 170 bar. As opposed to the industrial process, in nature, plants and bacteria have been producing ammonia for millions of years at mild conditions. Atmospheric nitrogen is reduced by solvated protons on the FeMo cofactor of the metalloenzyme nitrogenase. The natural method of nitrogen…