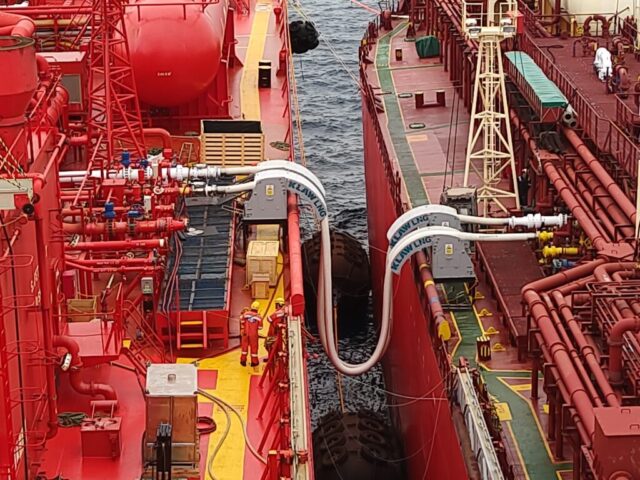
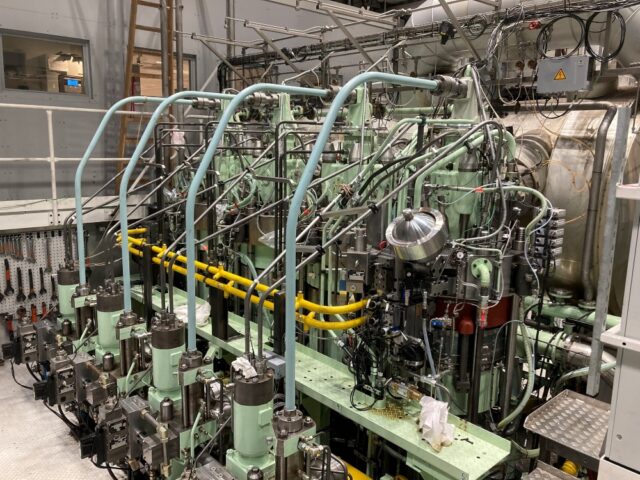
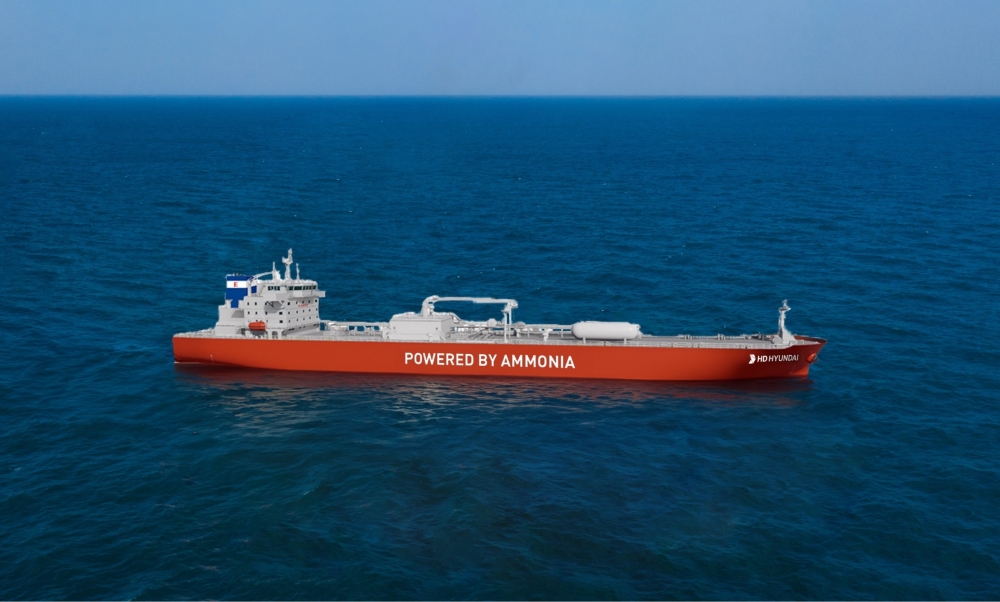
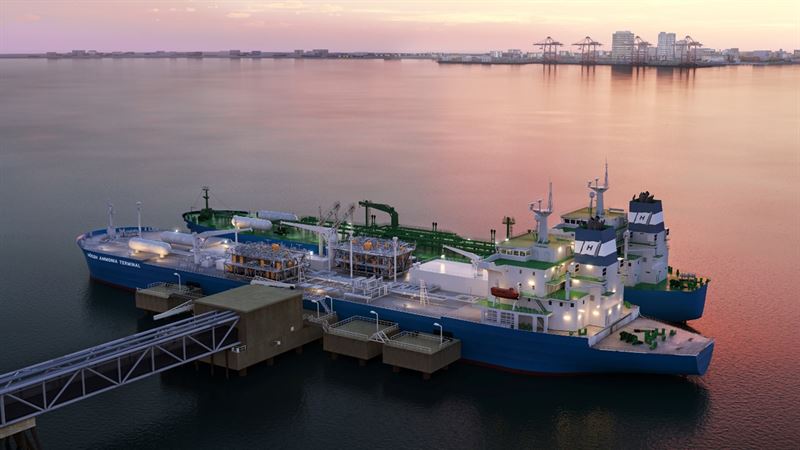
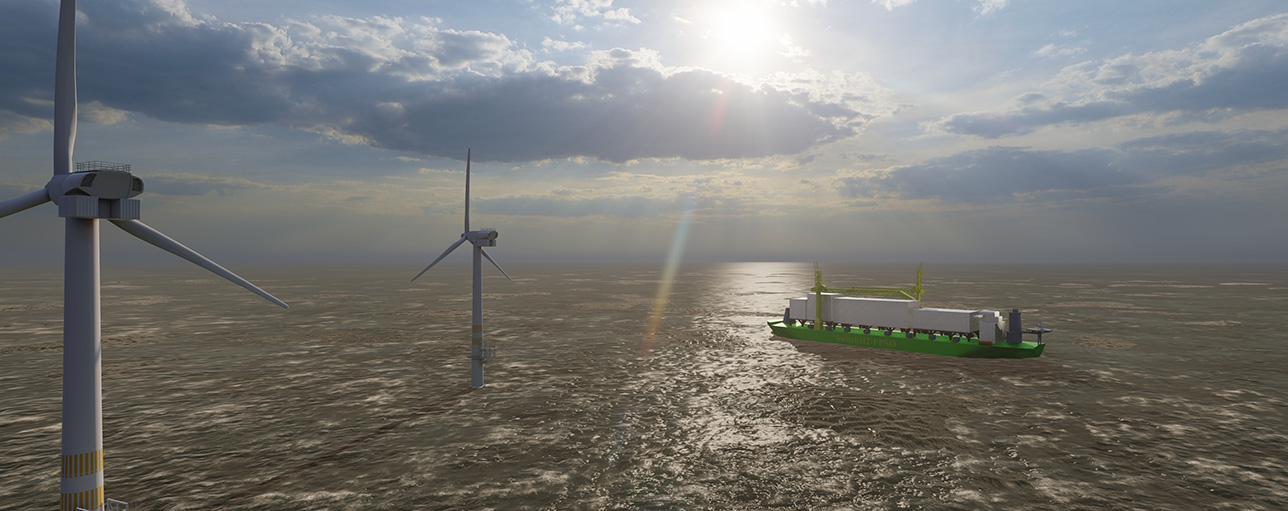
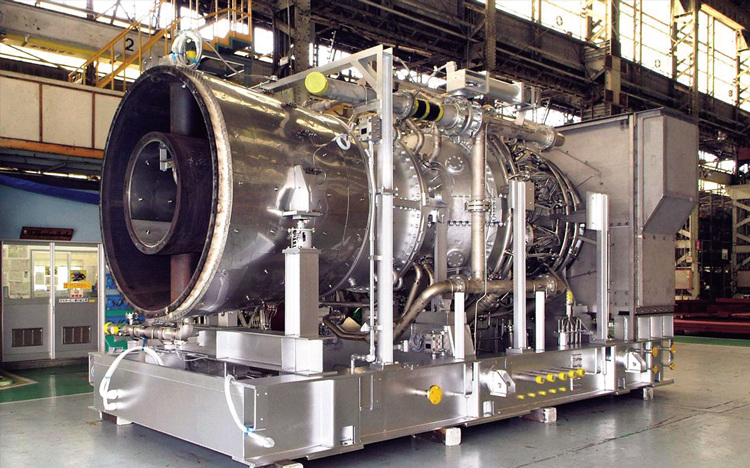
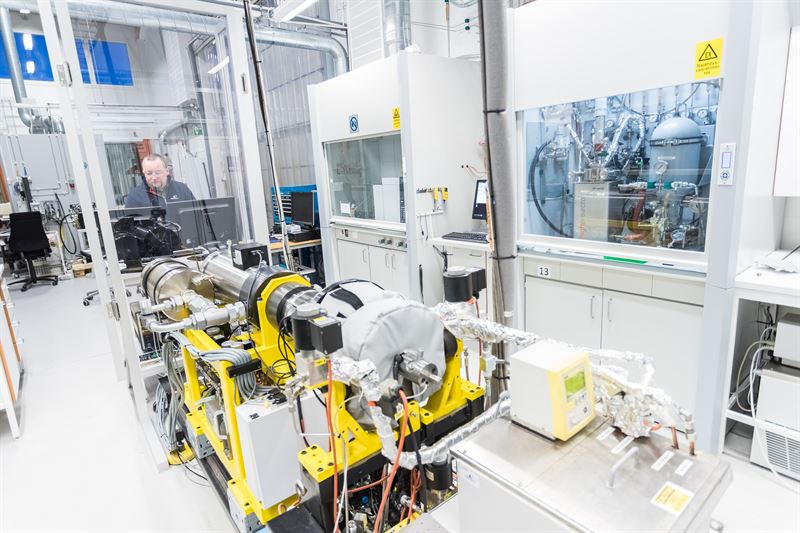
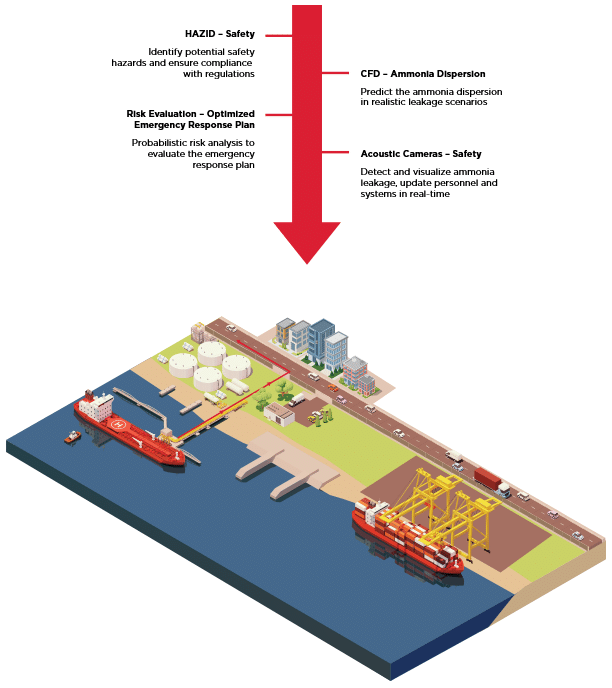
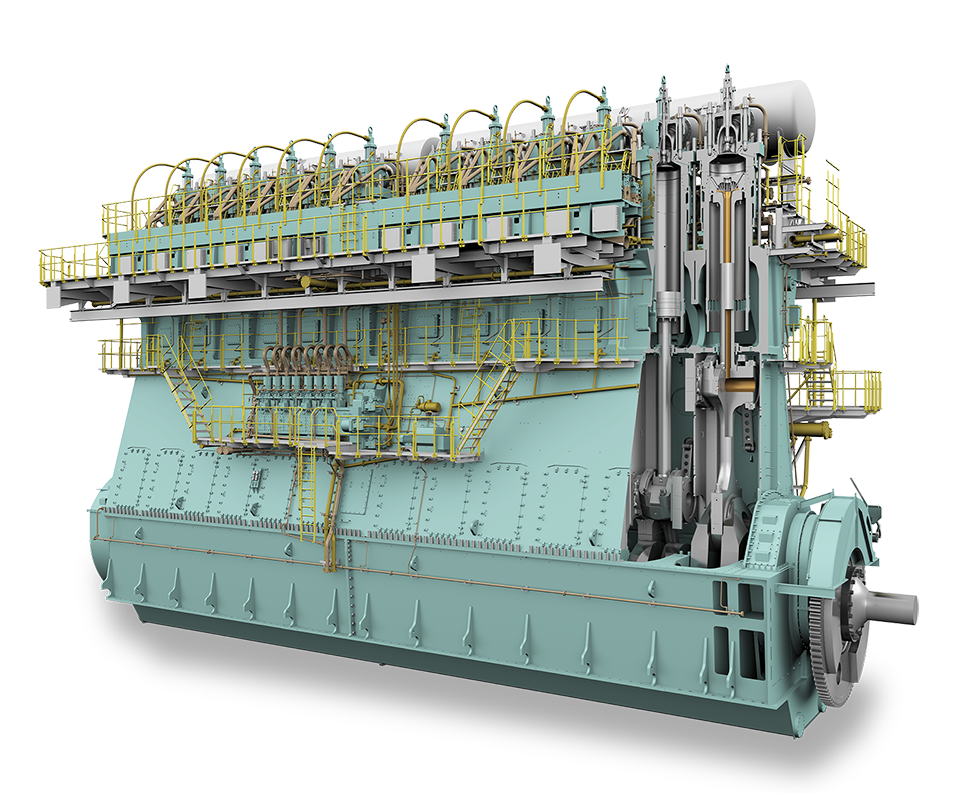
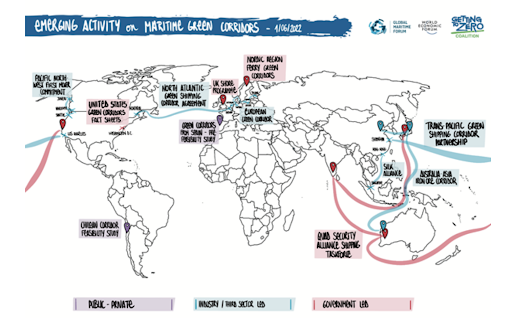
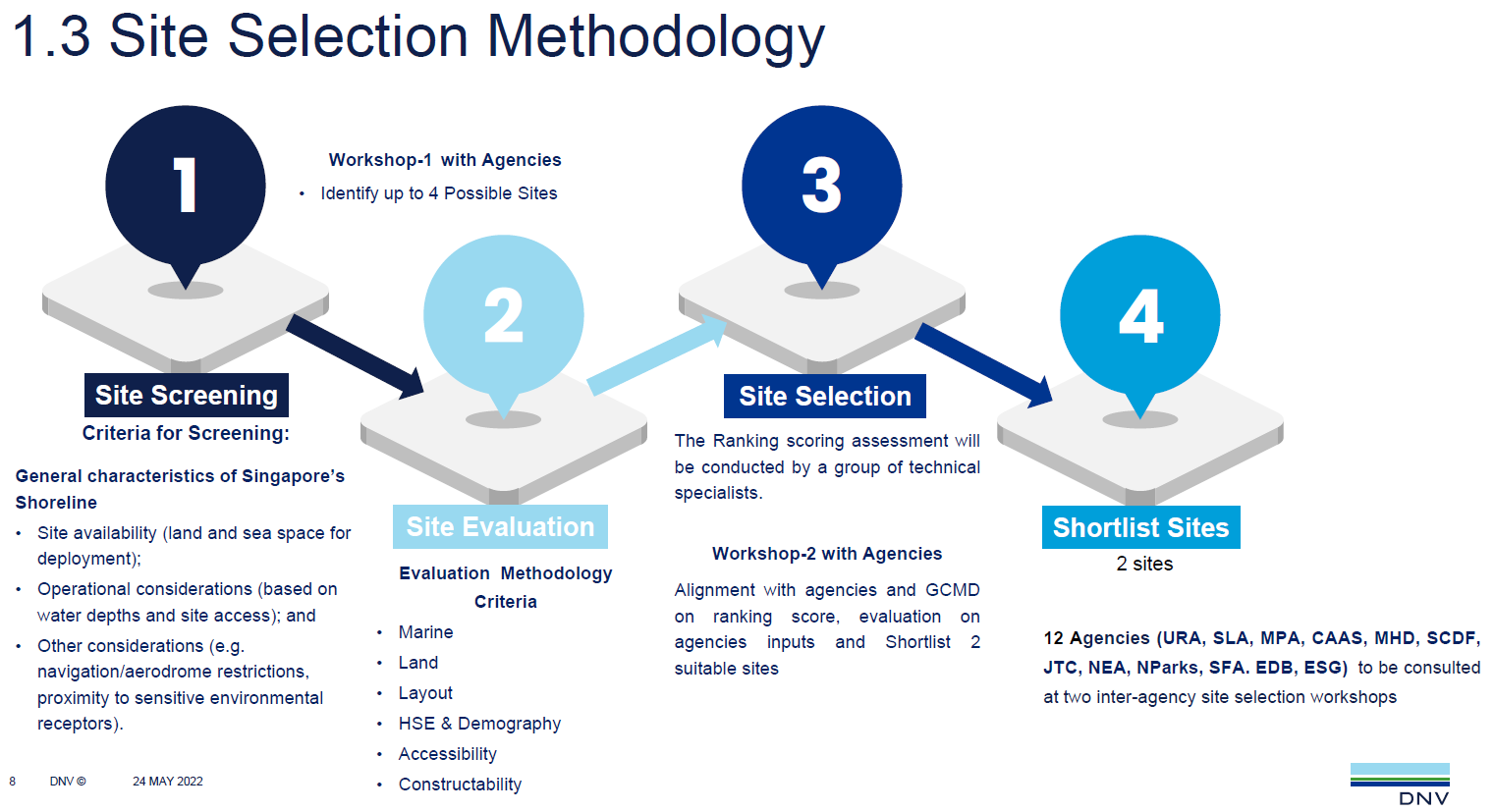
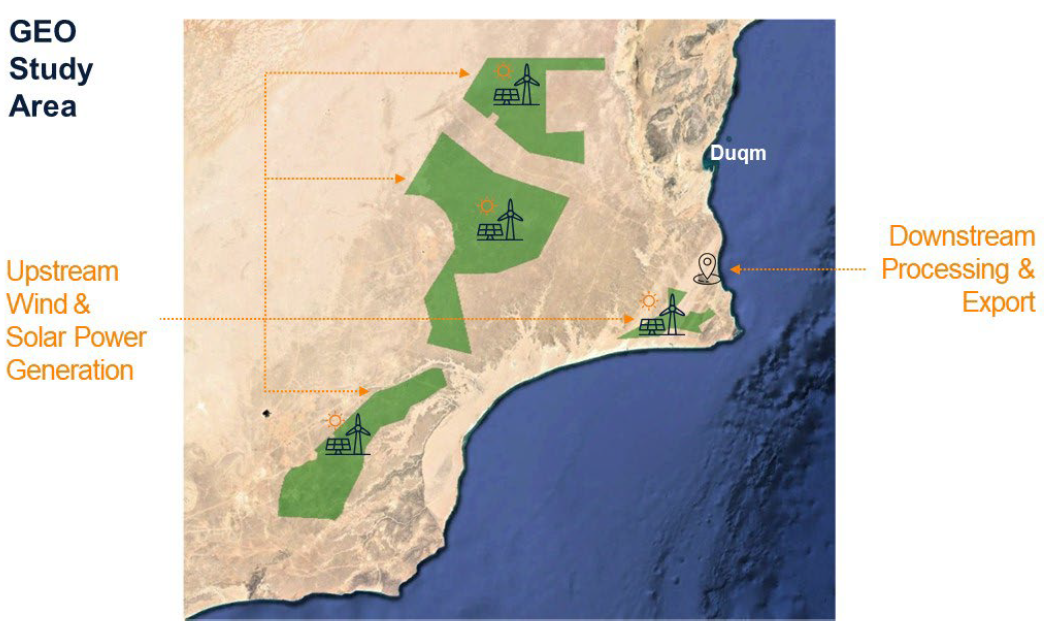
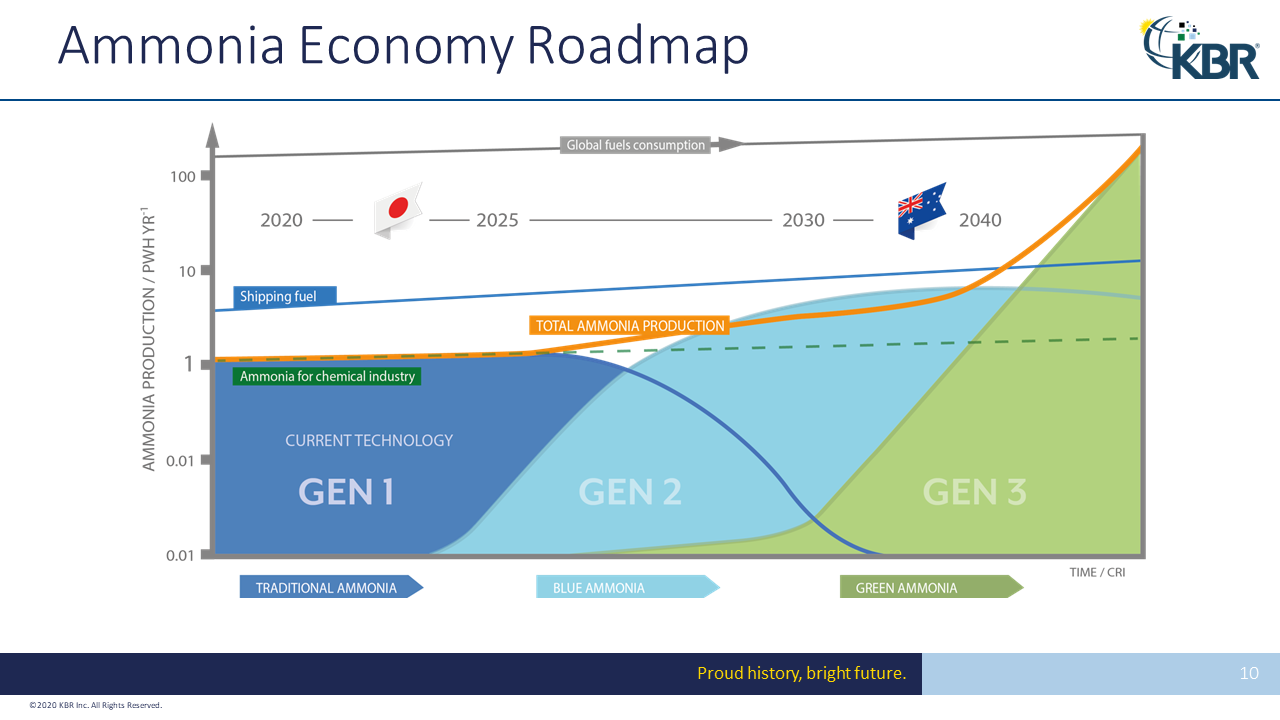
Despite the successes and progress made in 2025, the year remains a missed opportunity for ammonia energy. The first complete supply chains for renewable ammonia are emerging, and some 600,000 tons of annual production capacity is set to be online in northeast China early next year. Maritime engines, cracking, and power & heat technology solutions also made their mark, moving from feasibility into deployment. But disappointing outcomes at the IMO and government support that failed to spark market development remains an issue, with plenty of critical, detail-heavy work ahead of us in 2026.