Content Related to Enaex
Article
Orica and Fertiberia demonstrate low-carbon blasting agent in Spain
Julian Atchison June 18, 2024
Orica and Fertiberia have conducted a test blast of their low-carbon Technical Ammonium Nitrate product in Spain. To manufacture the TAN blasting agent, Orica used low-carbon ammonium nitrate produced by Fertiberia in Puertollano, Spain.
Article
Enaex, NYK to explore ammonia marine fuel supply in Chile
Julian Atchison March 13, 2024
Enaex and NYK Bulk & Project Carriers will explore the feasibility of supplying renewable ammonia fuel in Mejillones, northern Chile. NYK Bulk and Chilean national copper company Codelco have already signed an MoU to build a fleet of 10-15 ammonia-fueled vessels to transport copper concentrate from Mejillones to key Asian markets.
Article
HyEx: ammonia from the Chilean desert
Kevin Rouwenhorst March 08, 2023
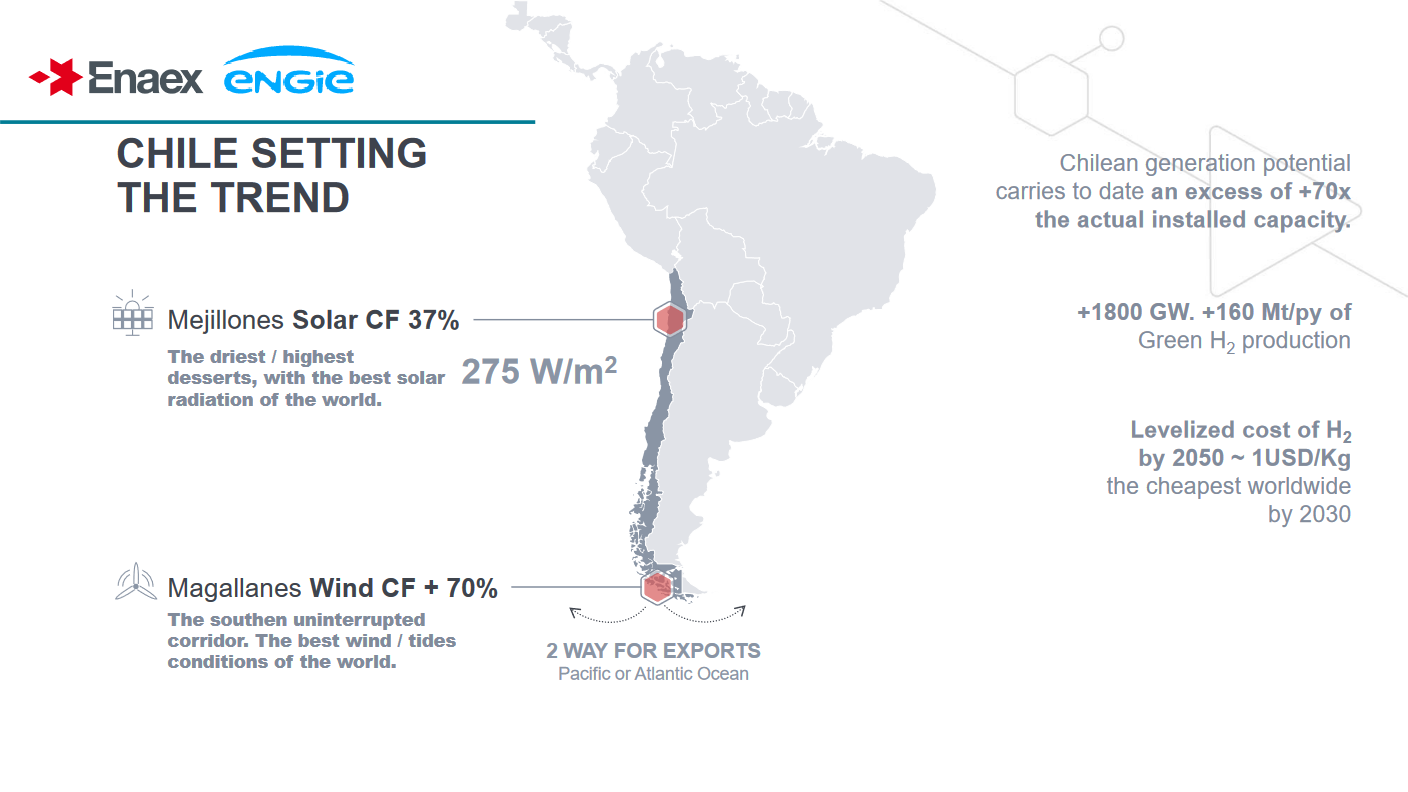
In our latest episode of Ammonia Project Features, Asunción Borras (Engie) and Pablo Wallach (Enaex) presented the HyEx project. Although a historical exporter of nitrogen fertilizers, Chile is now a major importer of ammonia, particularly as a feedstock for manufacturing mining explosives. Solar PV generating potential in Chile’s Atacama desert is among the world’s best, and the HyEx project will leverage this to produce renewable ammonia. By 2030, HyEx could produce enough ammonia to completely replace Enaex’s current ammonia imports, with volume left for exports or other applications.
Article
Japanese giants explore renewable ammonia production in Chile
Julian Atchison February 06, 2023
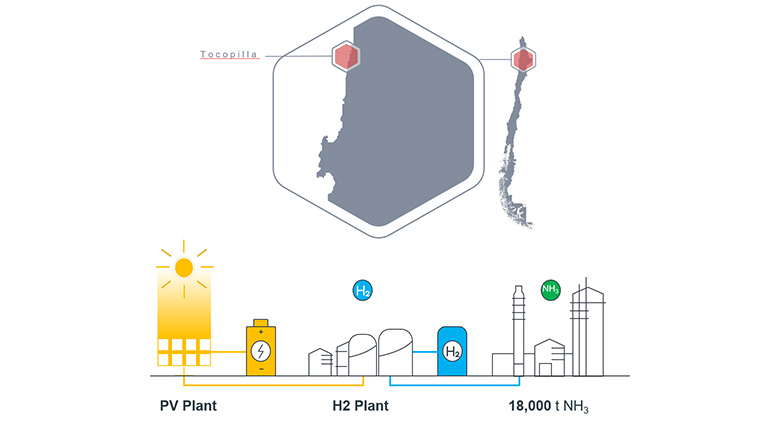
As part of the HyEx project, Mitsui & Co., Toyo Engineering and Enaex will develop a solar-powered, 18,000 tonnes-per-year renewable ammonia plant in Tocopilla, northern Chile. Just outside of Tocopilla, Sumitomo and Chilean transmission utility Colbún have teamed up to explore renewable ammonia production & export. The pair will also assess million-tonne-per-year production in Chile’s south. Also in South America, Proton Ventures have contracted Fitchner to assess the feasibility of planned renewable production projects.
Webinar
HyEx: decarbonizing the Chilean mining industry with renewable ammonia
Meet Engie and Enaex, partners in the HyEx project in Antofagasta (Chile), where Engie will produce renewable hydrogen and Enaex will produce green ammonia to feed subsequent production of mining explosives.
Article
Technology status: ammonia production from electrolysis-based hydrogen
Kevin Rouwenhorst January 31, 2023
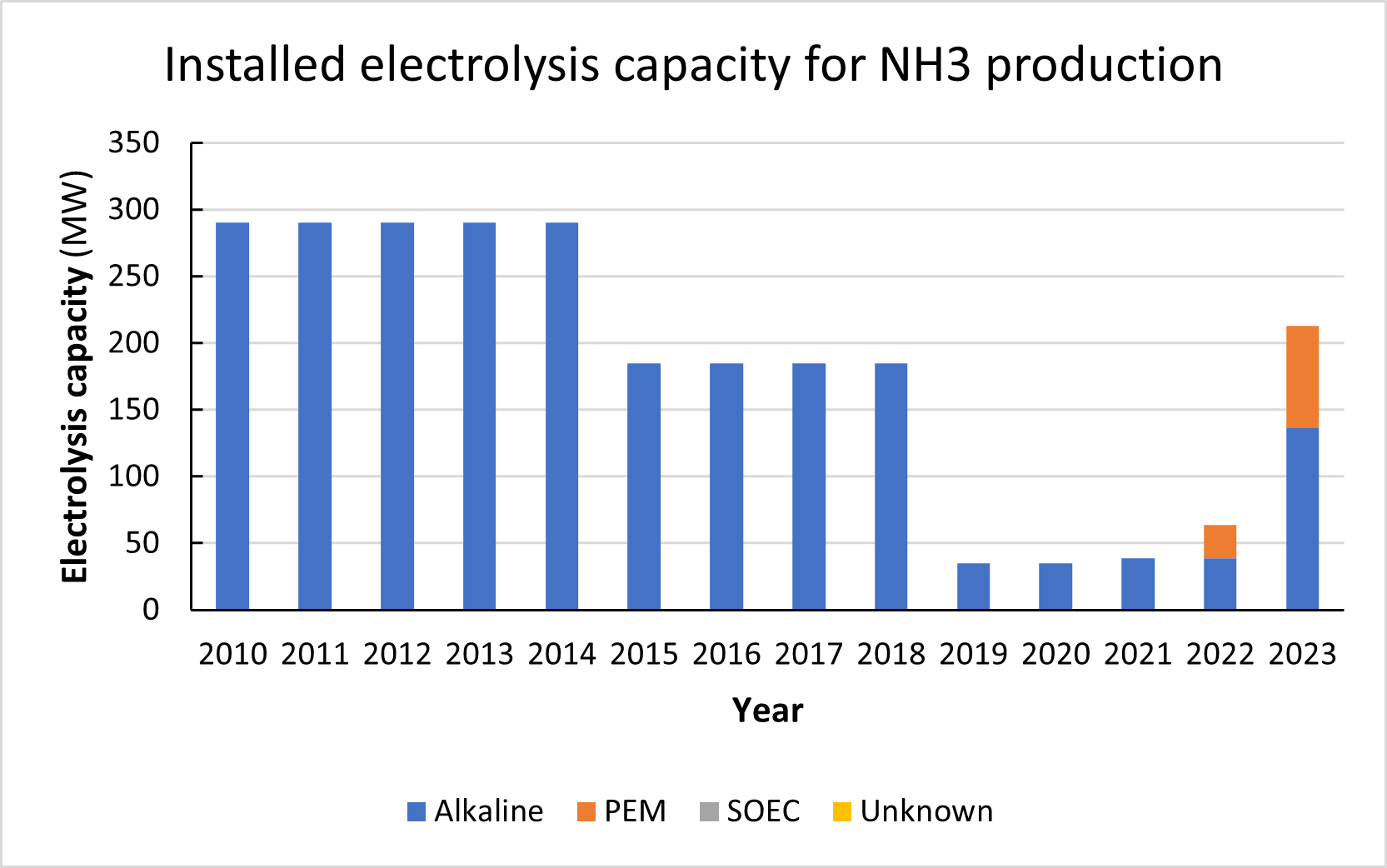
Electrolysis-based ammonia production peaked worldwide around 1970, before the economies of scale and cheap gas feedstock led to its decline. With decarbonization and climate-neutral industrial processes now a critical priority, electrolysis-based ammonia production has re-emerged as a long-term solution. From a base of 10,000 tonnes per year worldwide production in 2020, as much as 100 million tonnes per year of electrolysis-based ammonia could be produced by the end of this decade, driven by a dramatic roll-out of renewable energy generation and installed electrolyzer capacity.
Article
Progress on renewable conversion project in Australia
Julian Atchison October 19, 2022
Fortescue Future Industries and Incitec Pivot will progress plans to convert the Gibson Island ammonia production facility to run on renewable hydrogen feedstock. A grant from Australian government body ARENA will help FEED work begin immediately, with FID expected around 2025. We also explore more renewable project updates from Peru and Chile.
Article
Renewable ammonia in Colombia
Julian Atchison May 11, 2022
Colombian fertiliser producer Monómeros has signed an MoU with local power utility APBAQ to develop a renewable ammonia project near the city of Barranquilla, on Colombia’s Caribbean coast. The project will be powered by a 350 MW offshore wind farm being developed by Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners.
Article
Chilean government awards $50 million for key green projects
Julian Atchison January 18, 2022
CORFO - Chile's state-owned economic development agency - announced that US$50 million would be spread across six key green hydrogen projects, with the aim of attracting foreign investment and fast-tracking the start of green hydrogen production. Of particular interest to our readers is the HyEx project in Antofagasta, where explosives manufacturer Enaex have agreed to off take green hydrogen from ENGIE's to-be-built plant to produce green ammonia (and ultimately ammonium nitrate explosives for use in the mining industry).
Article
The mining industry: a driving force behind green ammonia
Trevor Brown November 01, 2019
ANNUAL REVIEW 2019: Ammonia is too often assumed to be only a fertilizer. This assumption overlooks other important uses for the chemical, large and small, in every corner of our economy. Some of the recent green ammonia announcements suggest that these other industries might, in fact, present better economic fundamentals for green ammonia investments than the fertilizer industry. Alternatively, these companies might have set their sights on becoming first movers in developing the commodities of the future. Time will tell but, if the last 12 months is any guide, the mining industry could be a force for change in the ammonia industry.
Article
Green Ammonia Plants in Chile, Australia, New Zealand
Trevor Brown October 04, 2019
Green ammonia plants are being announced quicker than I can report. Here is a summary of four new projects that propose to use electrolyzers, fed by renewable power, to produce hydrogen for ammonia production. These are big companies, operating in regions with excellent renewable resources, making significant investments in their future. In Chile, it is Enaex, a major ammonium nitrate manufacturer, supplying explosives to the mining industry. In Australia, it is Incitec Pivot, "the second largest supplier of explosives products and services in the world," and Wesfarmers, "the largest Australian company by revenue," according to Wikipedia. In New Zealand, it is Ballance-Agri Nutrients, a big farmers' co-operative and the country's sole fertilizer producer. Each aims to make its business "future-proof." The transition from fossil ammonia to renewable ammonia is underway.