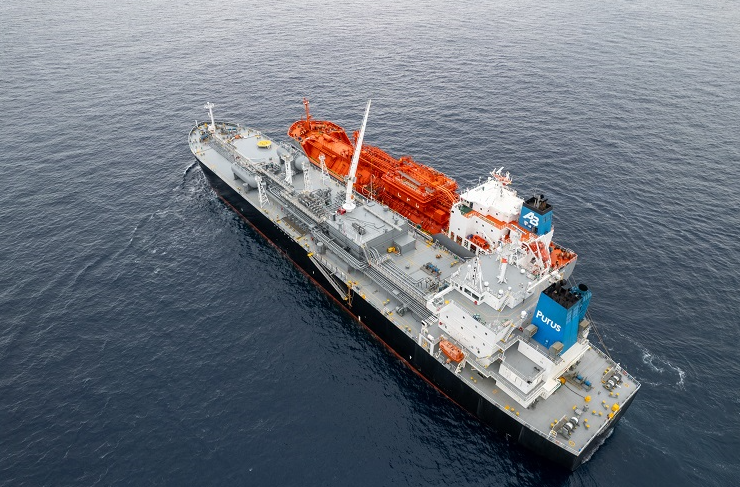
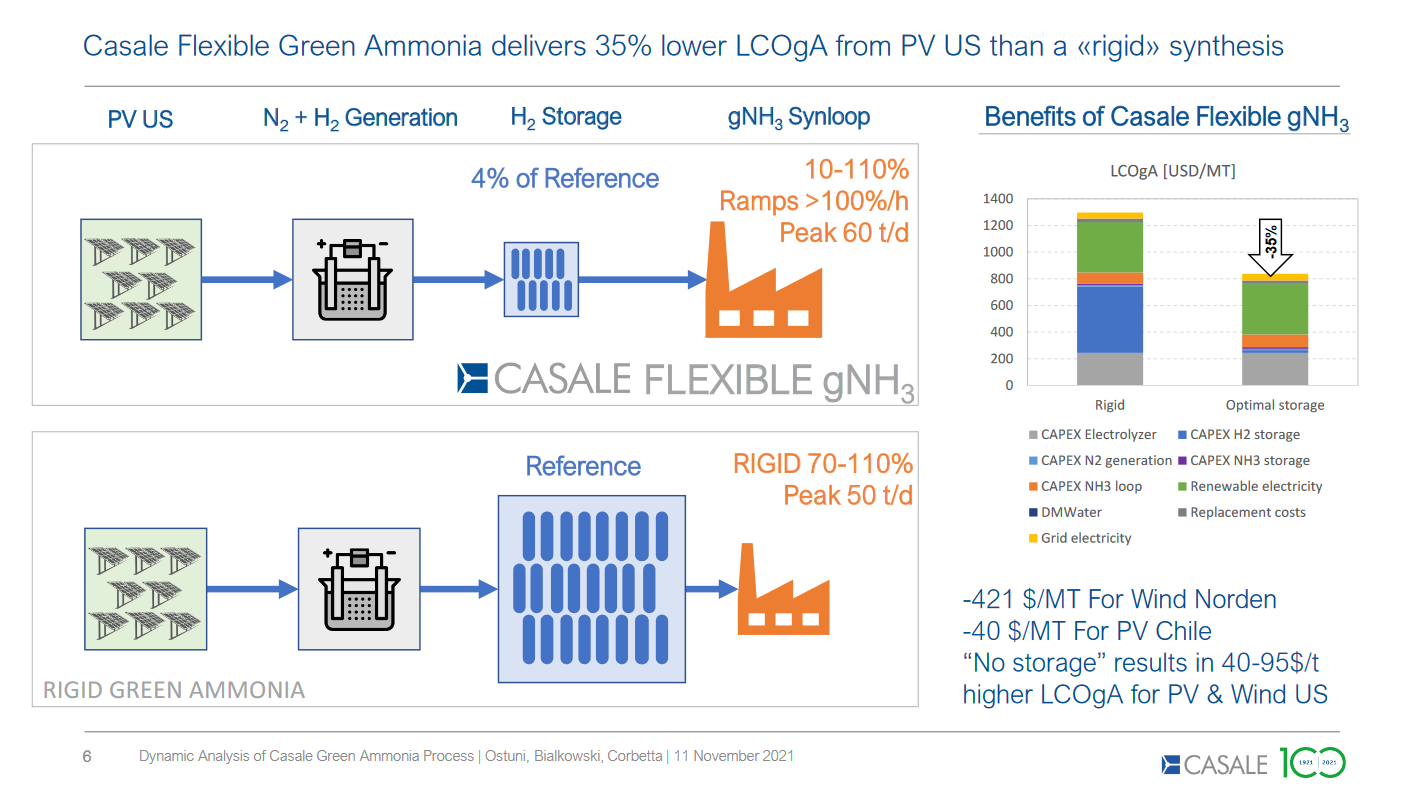
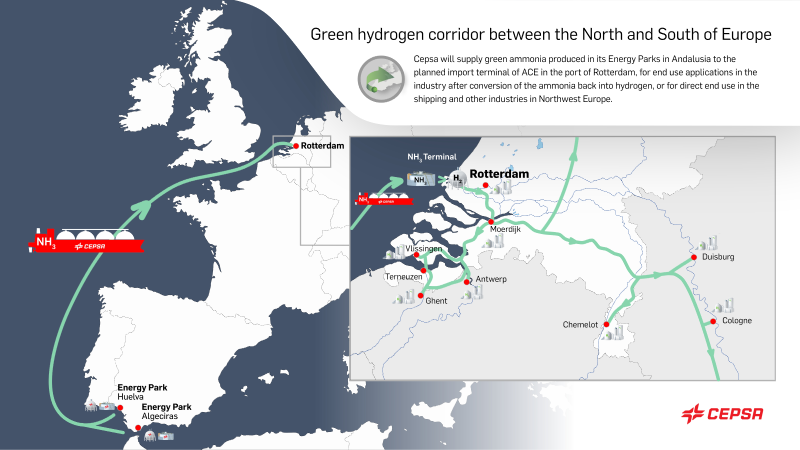
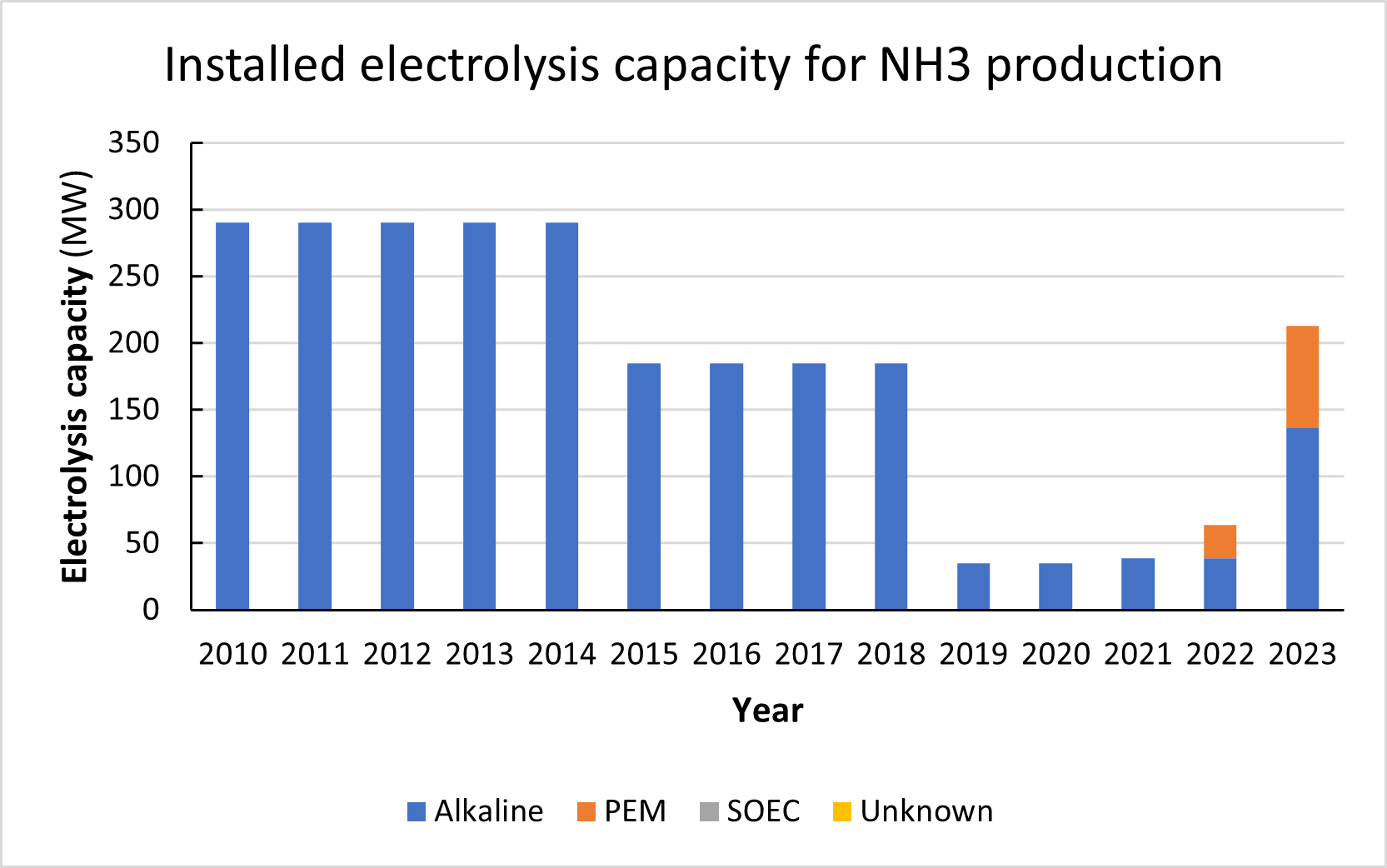
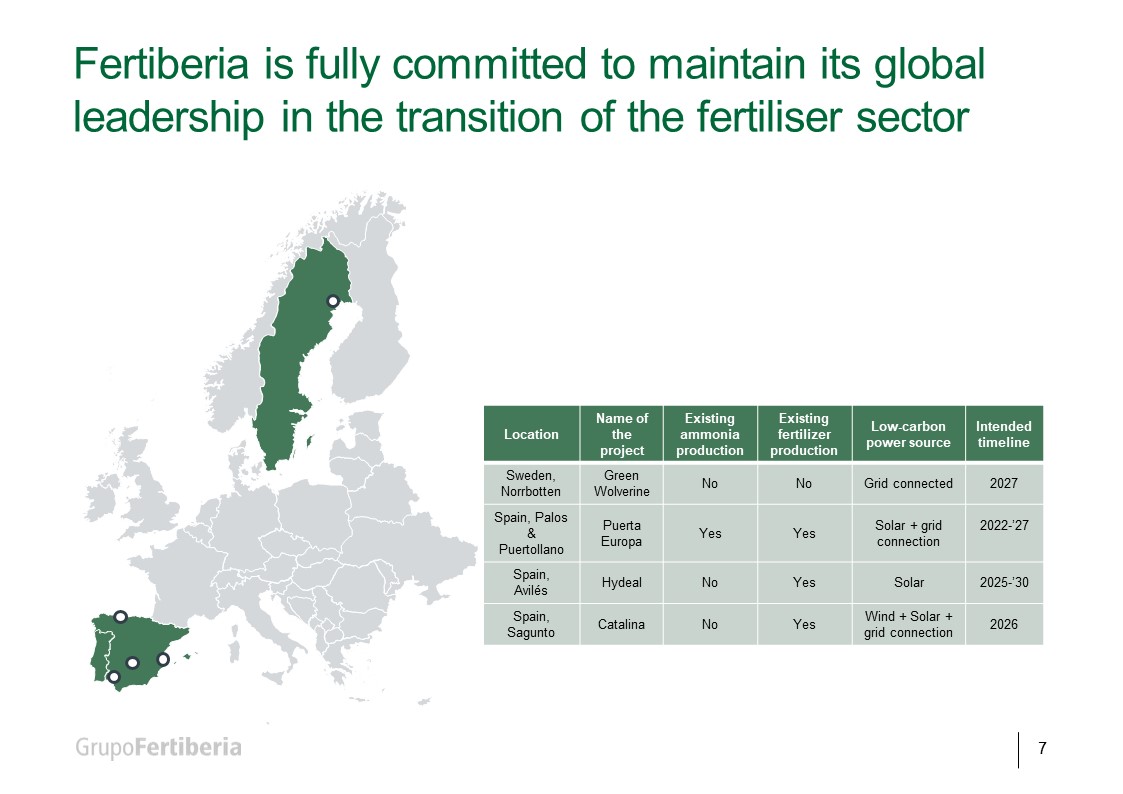
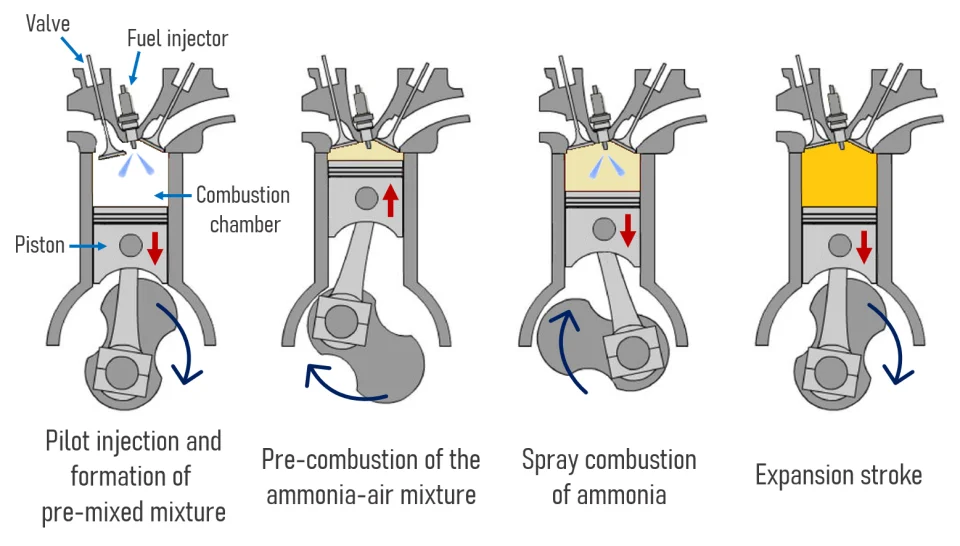
Trafigura reports its first successful ship-to-ship transfer of ammonia has taken place in the Straits of Gibraltar. Around 6,000 tons of ammonia being shipped from CF Industries’ Donaldsonville complex in Louisiana was transferred between gas carriers, before being delivered to Fertiberia in Spain for the production of feritliser.