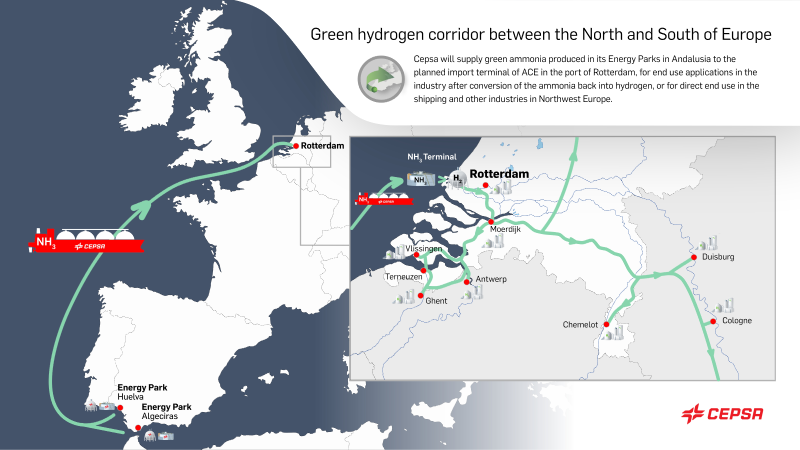
Trammo will purchase & sell up to 100,000 tonnes per year of renewable ammonia from Iberdrola in Spain, starting in 2026. The agreement kickstarts a green hydrogen corridor linking southern and northern Europe, with Trammo to focus on ammonia sales to industrial customers.
Content Related to Gasunie
Article
Cepsa: renewable ammonia in Spain
Julian Atchison February 27, 2023
Spanish energy & chemicals giant Cepsa has announced two new, significant ammonia partnerships this week. Cepsa will supply renewable ammonia imports to ACE Terminal in Rotterdam from 2027, realizing the vision for a green maritime corridor between the Netherlands and the Mediterranean. And, together with Fertiberia, Cepsa will develop a 1 GW renewable hydrogen plant near the La Rábida energy park. The plant will produce hydrogen feedstock for Fertiberia’s Palos de la Frontera ammonia & fertiliser manufacturing complex, and Cepsa’s own industrial needs in the area.
Article
Air Products and Gunvor to develop new import terminal in Rotterdam
Julian Atchison July 06, 2022
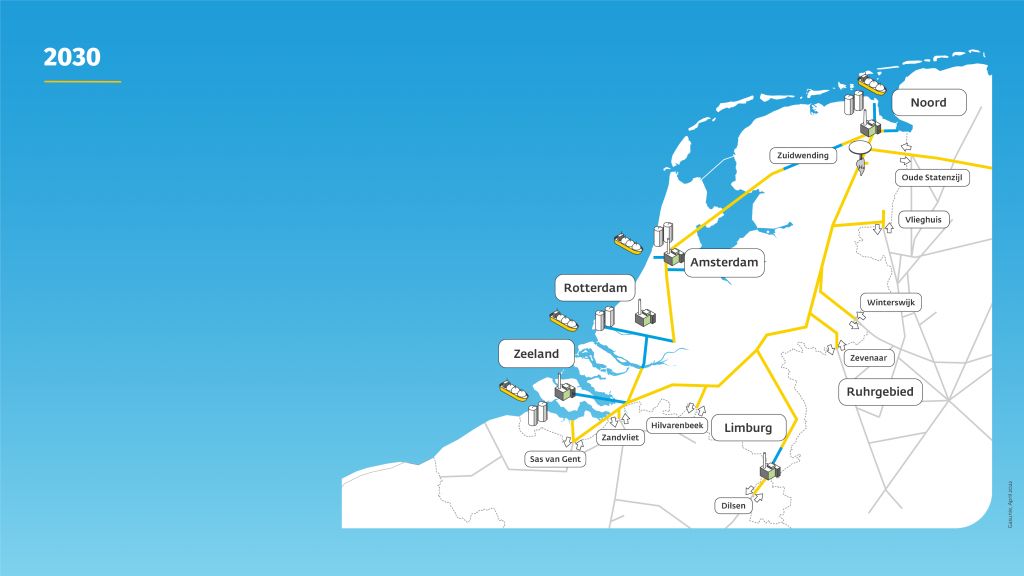
Air Products and Gunvor will jointly develop a renewable ammonia import terminal at Gunvor Petroleum’s existing refinery & distribution facilities in Rotterdam Europoort. The partners expect to be providing hydrogen to the Netherlands in 2026, with the new terminal receiving imports of renewable ammonia from Air Products production projects around the world. The new project is now the third ammonia import terminal under development at the Port of Rotterdam, and comes the same week as Dutch gas network operator Gasunie announced that it had started construction of a national hydrogen distribution network in the Netherlands.
Article
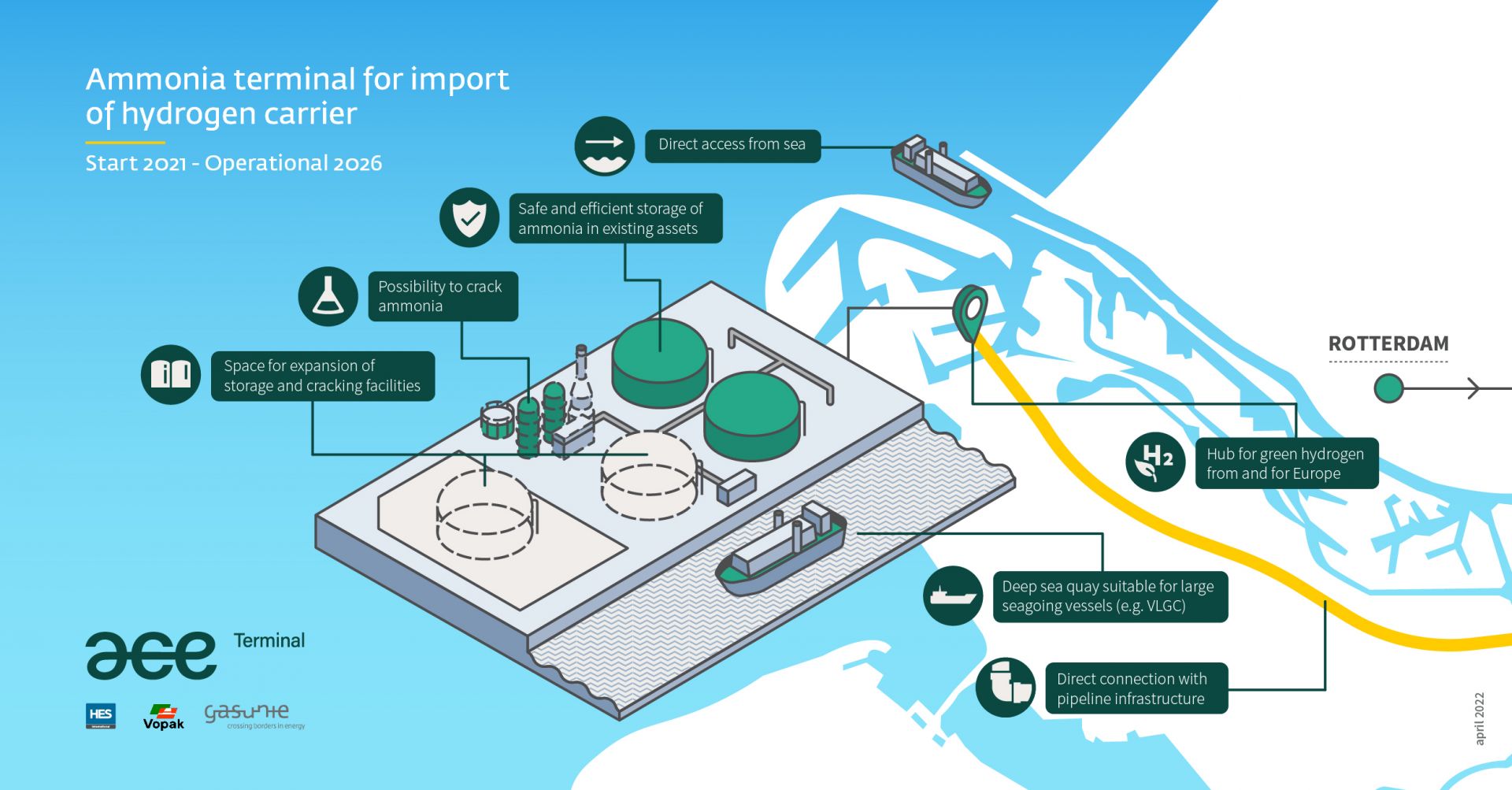
ACE Terminal: importing ammonia to Rotterdam from 2026
Julian Atchison April 13, 2022
Gasunie, HES International and Vopak will develop an import terminal for ammonia on Rotterdam’s Maasvlakte, with operations to begin in 2026 under the name ACE Terminal. While green imports are the long-term focus, blue ammonia imports are possible in the initial phase. The design will leverage existing ammonia infrastructure on Maasvlakte. New build features include a deep-sea berth for large vessels and possibly an ammonia cracker.
Article
The fertilizer industry is learning to love green ammonia
Trevor Brown October 25, 2019
ANNUAL REVIEW 2019: Green ammonia is no longer a lonely venture for Yara, which used to appear alone among fertilizer producers in its desire to reduce carbon dioxide emissions from ammonia plants. While dozens of green ammonia demonstration projects and prototype technologies have been demonstrated in recent years, this progress was mostly achieved by energy companies and technology start-ups - and Yara. In the last year, however, fertilizer producers on five continents have begun feasibility studies, launched pilot demonstrations, or simply gone ahead and re-engineered their ammonia plants to replace fossil fuel inputs with renewable hydrogen.
Article
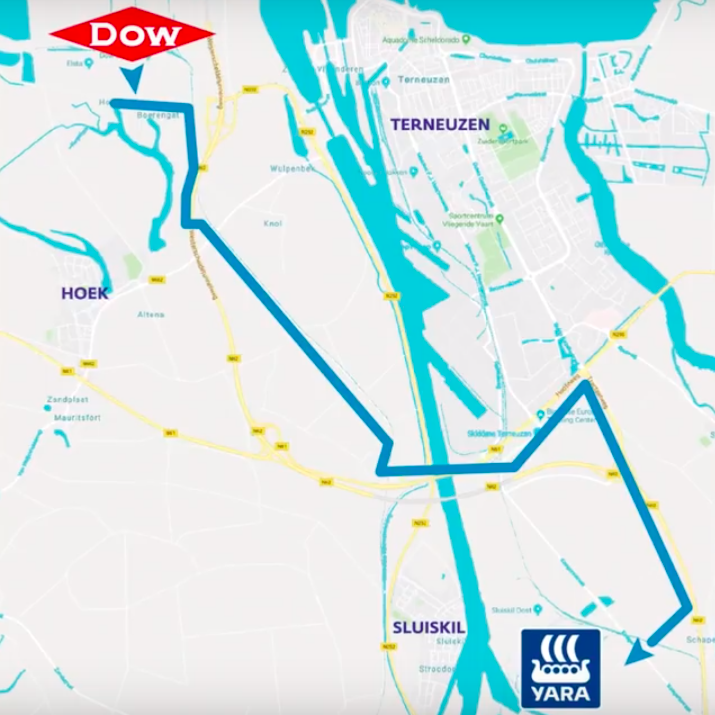
Ammonia plant revamp to decarbonize: Yara Sluiskil
Trevor Brown February 01, 2019
Last year, Yara Sluiskil, in the Netherlands, upgraded its existing ammonia plant by introducing a hydrogen pipeline connection, thereby reducing its reliance on fossil fuels. The pipeline was commissioned in October 2018 and now "ensures the efficient and safe transport of hydrogen," which was previously a waste-product at Dow's nearby ethylene cracker. Already, the project "delivers a CO2 saving of 10,000 tons" and a decrease in energy consumption of "0.15 petajoules (PJ) per year." This is, perhaps, the first ammonia plant decarbonization revamp, and it shows that it is both possible and affordable to reduce emissions from existing ammonia plants today.
Article
Power-to-Ammonia: the Economic Viability of Ammonia Energy
Trevor Brown October 05, 2017
In the last 12 months ... The extensive Power-to-Ammonia feasibility study demonstrated that ammonia energy could be economically viable in different business cases. The report was a collaborative effort by large European corporations - power companies, electricity distributors, chemical producers, engineering firms - and it has already resulted in plans for one 440 MW power plant to be converted to carbon-free fuel by 2023.
Article
Ammonia for grid-scale power: Nuon, Gasunie, and Statoil
Trevor Brown July 12, 2017
A new collaboration was announced last week, between Dutch power company Nuon, European natural gas pipeline operator Gasunie, and Norwegian oil major Statoil. The joint venture will look at converting one of the Magnum power plant's three 440 MW gasifiers, with hopes to have it running on hydrogen fuel by 2023. This is the continuation of the Power to Ammonia project and, although ammonia is not expected to be used in this particular stage of the project, converting Magnum to hydrogen fuel represents the "intermediate step" to demonstrate that "where hydrogen could be produced using natural gas by 2023, from the year 2030 it could be possible to produce it with sustainably produced ammonia ... Ammonia then effectively serves as a storage medium for hydrogen, making Magnum a super battery."