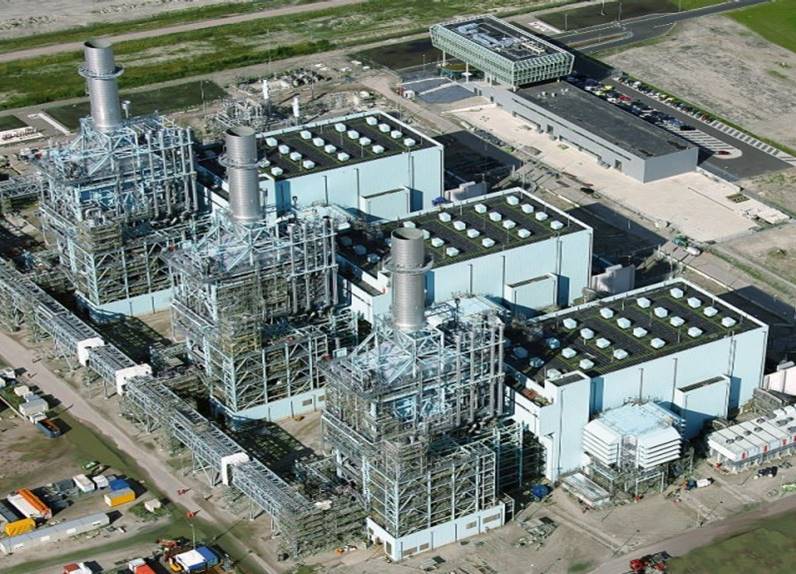
The kernel of the story is this: Battolyser B.V. is taking a step forward with the battolyser, its eponymous energy storage technology. On June 12, Battolyser’s joint venture partners Delft University of Technology (TU Delft) and Proton Ventures announced that they had secured a €480,000 grant from Waddenfonds, a Dutch public-sector funding agency, to build a 15 kW/60 kWh version of the battolyser. The installation will take place at Nuon’s Magnum generating station at Eemshaven in the Netherlands. The move makes tangible the vision of the battolyser as an integral part of an energy supply system with a robust quota of renewably generated electricity. The battolyser is a battery that stores electricity in the conventional galvanic manner until it is fully charged. At that point, the device uses any additional electricity supplied for the electrolysis of water and evolution of hydrogen. If the device is integrated with hydrogen buffer storage and an ammonia production train, the result will be a versatile and highly scalable energy storage system that can provide highly responsive grid support on all time scales from seconds to months. (Ammonia Energy last posted on the battolyser on March 1, 2018.)
Content Related to Institute for Sustainable Process Technology
Article
Power-to-Ammonia: the Economic Viability of Ammonia Energy
Trevor Brown October 05, 2017
In the last 12 months ... The extensive Power-to-Ammonia feasibility study demonstrated that ammonia energy could be economically viable in different business cases. The report was a collaborative effort by large European corporations - power companies, electricity distributors, chemical producers, engineering firms - and it has already resulted in plans for one 440 MW power plant to be converted to carbon-free fuel by 2023.
Article
Ammonia for grid-scale power: Nuon, Gasunie, and Statoil
Trevor Brown July 12, 2017
A new collaboration was announced last week, between Dutch power company Nuon, European natural gas pipeline operator Gasunie, and Norwegian oil major Statoil. The joint venture will look at converting one of the Magnum power plant's three 440 MW gasifiers, with hopes to have it running on hydrogen fuel by 2023. This is the continuation of the Power to Ammonia project and, although ammonia is not expected to be used in this particular stage of the project, converting Magnum to hydrogen fuel represents the "intermediate step" to demonstrate that "where hydrogen could be produced using natural gas by 2023, from the year 2030 it could be possible to produce it with sustainably produced ammonia ... Ammonia then effectively serves as a storage medium for hydrogen, making Magnum a super battery."
Article
Report from the European Conference: Renewable Ammonia cost-competitive with Natural Gas Ammonia
Trevor Brown June 23, 2017
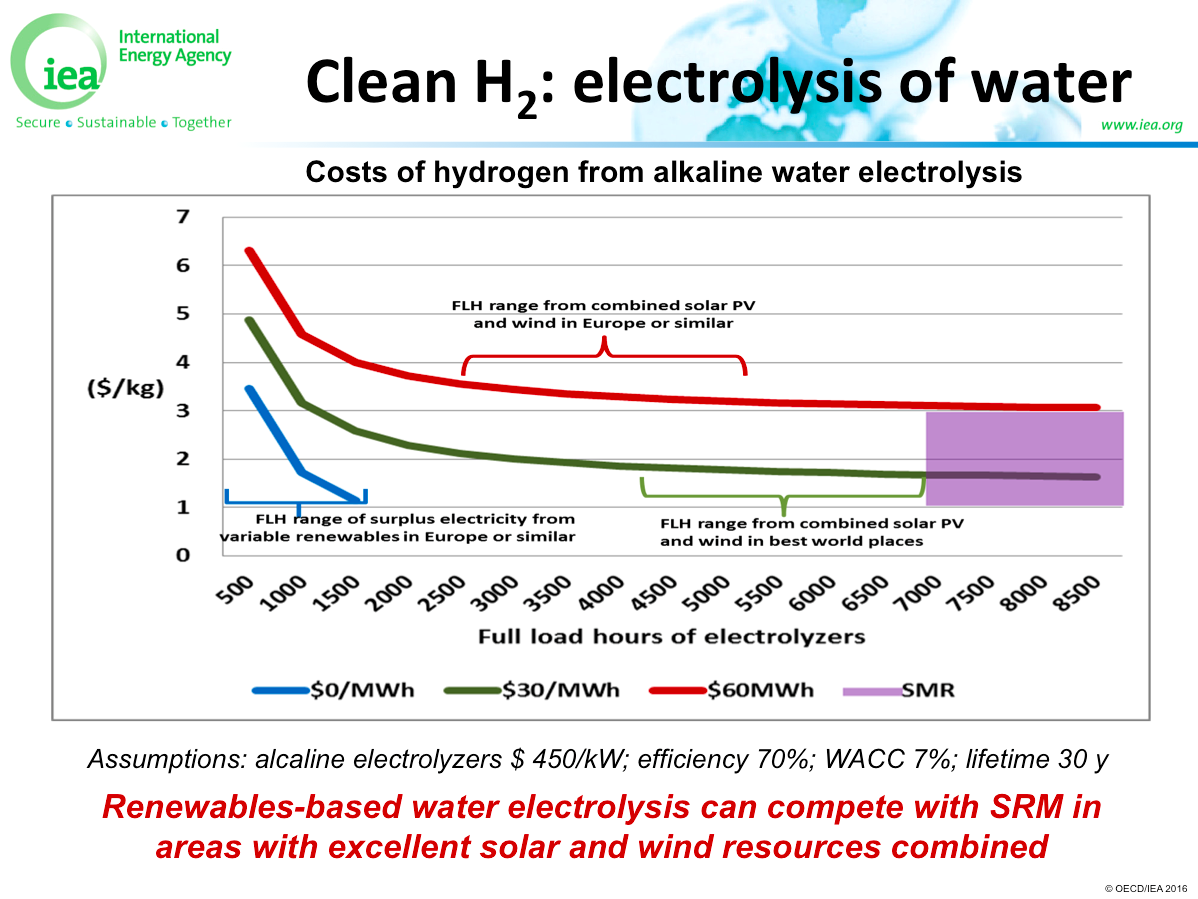
The viability of producing ammonia using renewable energy was one of the recurring themes of the recent Power to Ammonia conference in Rotterdam. Specifically, what cost reductions or market mechanisms would be necessary so that renewable ammonia - produced using electrolytic hydrogen in a Haber-Bosch plant - would be competitive with normal, "brown" ammonia, made from fossil fuels. A number of major industry participants addressed this theme at the conference, including Yara and OCI Nitrogen, but it was the closing speech, from the International Energy Agency (IEA), that provided the key data to demonstrate that, because costs have already come down so far, renewable ammonia is cost-competitive in certain regions today.
Article
Power to Ammonia: alternative synthesis technologies
Trevor Brown June 01, 2017
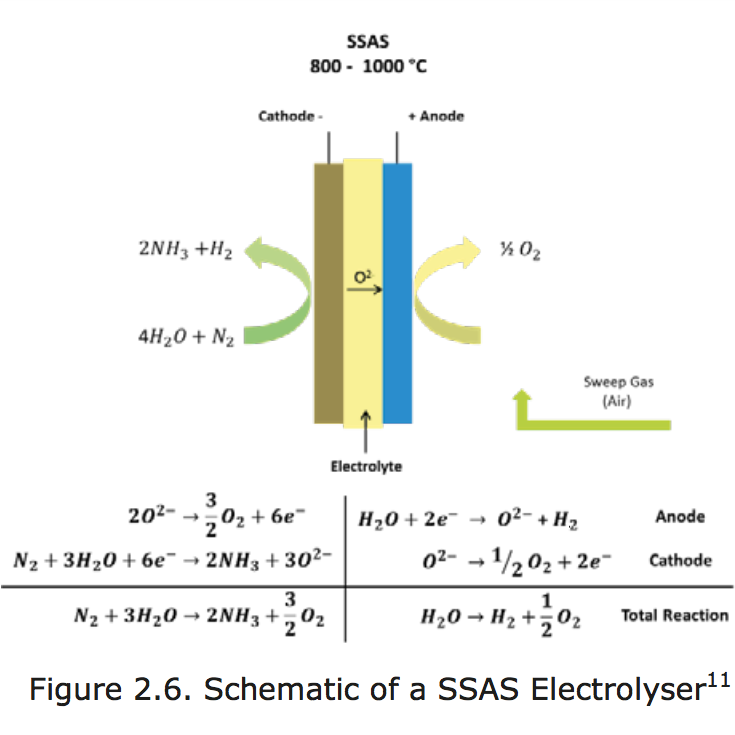
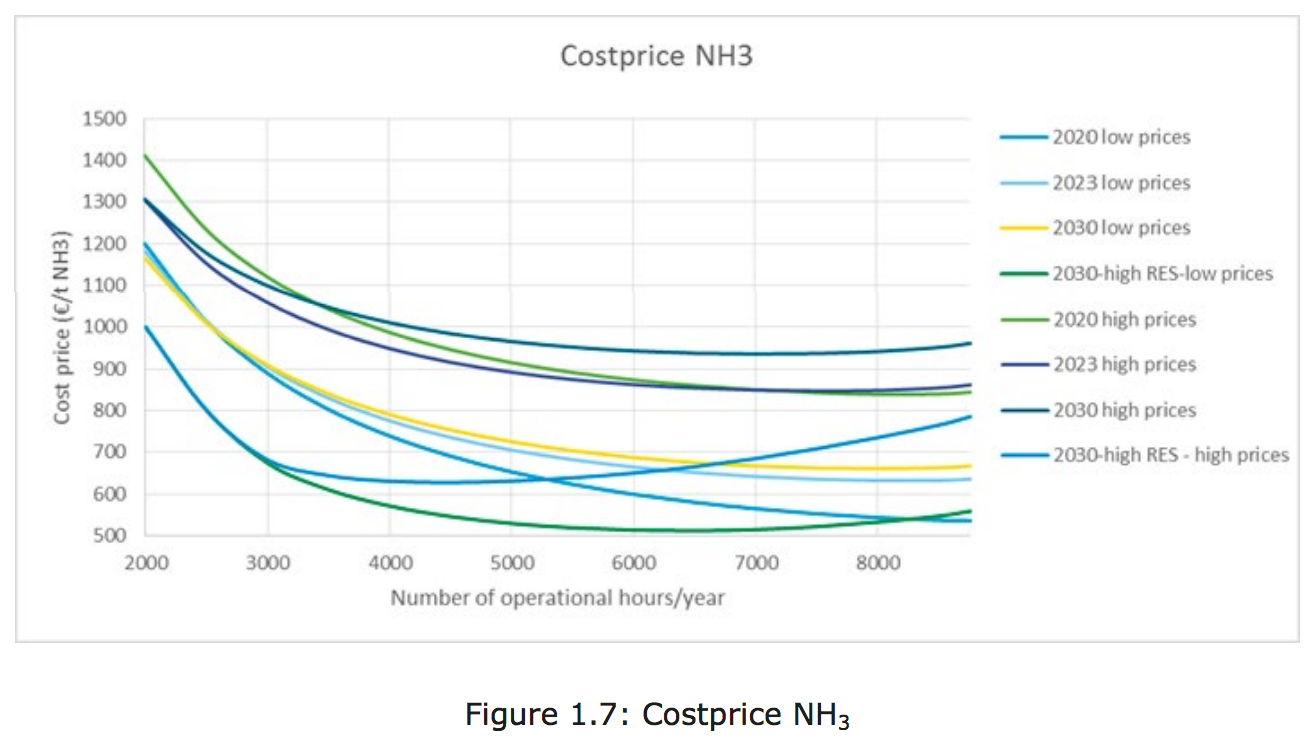
The Institute for Sustainable Process Technology (ISPT) recently published a detailed analysis of three business cases for producing renewable ammonia from electricity: Power to Ammonia. The feasibility study concludes that, in the near term, ammonia production using clean electricity will likely rely on a combination of two old-established, proven technologies: electrolysis and Haber-Bosch (E-HB). To reach this conclusion, however, the study also assessed a range of alternative technologies, which I summarize in this article.
Article
Power to Ammonia: The OCI Nitrogen - Geleen case
Trevor Brown May 18, 2017
The Power-to-Ammonia feasibility study includes an assessment of the costs and benefits of producing ammonia from renewable energy at OCI Nitrogen's existing production site in Geleen. Of all the companies who joined forces in the Power-to-Ammonia project, OCI is the only ammonia producer. Its business case for making carbon-free ammonia is especially interesting therefore: not just because of the company's deep understanding of the ammonia market and available technologies, but also because it faces corporate exposure to the financial, operational, and social risks of relying upon a fossil-fueled technology in a carbon constrained future.
Article
Power to Ammonia: the Eemshaven case
Trevor Brown April 28, 2017
The Institute for Sustainable Process Technology recently published a feasibility study, Power to Ammonia, looking at the possibility of producing and using ammonia in the renewable power sector. This project is based in The Netherlands and is led by a powerful industrial consortium. I wrote about the feasibility study last month, but it deserves closer attention because it examines three entirely separate business cases for integrating ammonia into a renewable energy economy, centered on three site-specific participants in the study: Nuon at Eemshaven, Stedin at Goeree-Overflakkee, and OCI Nitrogen at Geleen. Over the next few years, the group intends to build pilot projects to develop and demonstrate the necessary technologies. Next month, however, these projects will be an important part of the Power-to-Ammonia Conference, in Rotterdam on May 18-19. This article is the first in a series of three that aims to introduce each business case.
Article
Power to Ammonia feasibility study
Trevor Brown March 31, 2017
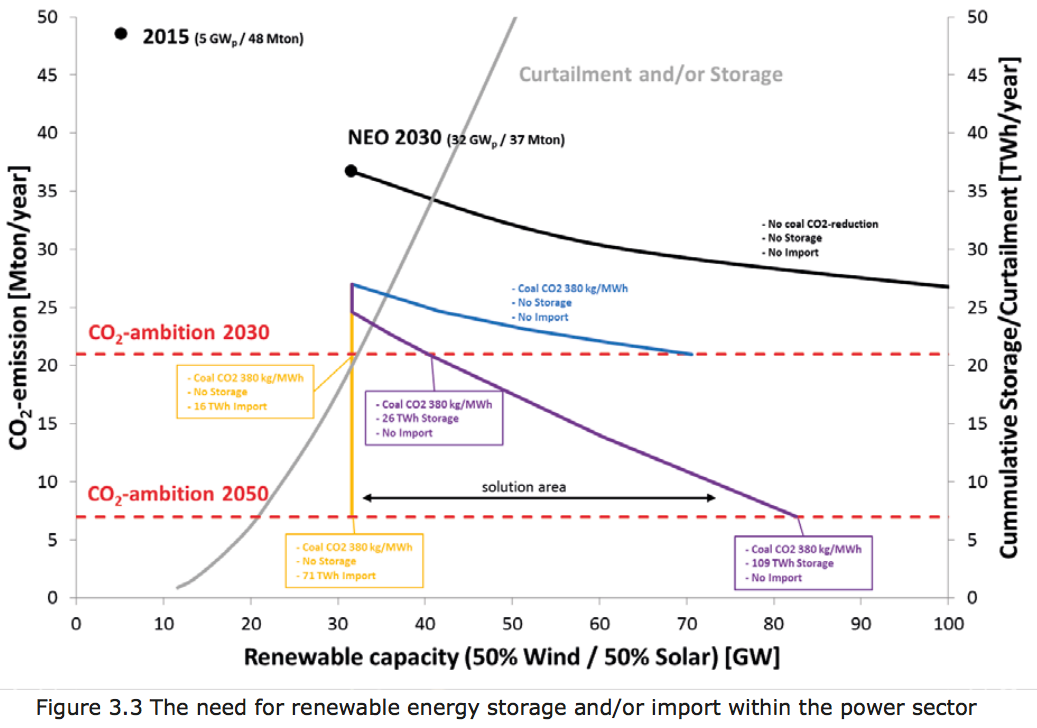
The Institute for Sustainable Process Technology has just published a feasibility study that represents a major step toward commercializing renewable ammonia. It examines the "value chains and business cases to produce CO2-free ammonia," analysing the potential for commercial deployment at three companies with existing sites in The Netherlands: Nuon at Eemshaven, Stedin at Goeree-Overflakkee, and OCI Nitrogen at Geleen. The project is called Power to Ammonia.
Article
Nuon's Power-to-Ammonia update, and the first European ammonia fuel conference in 2017
Trevor Brown December 02, 2016
An article in the latest issue of Dutch-language magazine NPT Proces Technologie provides a detailed update on the Nuon project, about which we wrote a few months ago. Nuon's Power-to-Ammonia project looks at grid-scale storage of "seasonal surplus" electricity from wind and solar in the form of ammonia. Proton Ventures, the originators of the Power-to-Ammonia concept in The Netherlands, have also been sharing details of the project in recent conference presentations - and announced that they will be hosting the first European ammonia fuel conference, in Rotterdam, in May 2017.
Article
Nuon - Power to Ammonia
Stephen H. Crolius September 19, 2016
In March 2016 the Dutch utility Nuon announced that it will study the possibility of storing "seasonal surplus" electricity from wind and solar in the form of ammonia. The study by Nuon and Delft University of Technology (TU Delft) is part of the project "Power to Ammonia." The study will be conducted at Nuon's Magnum power station.