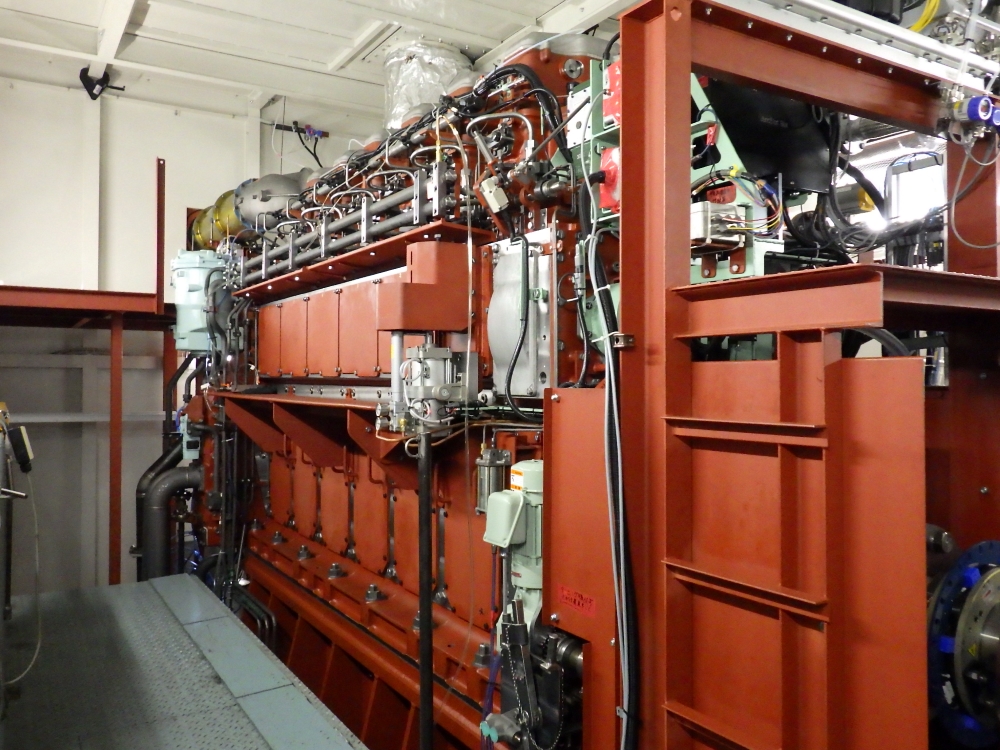
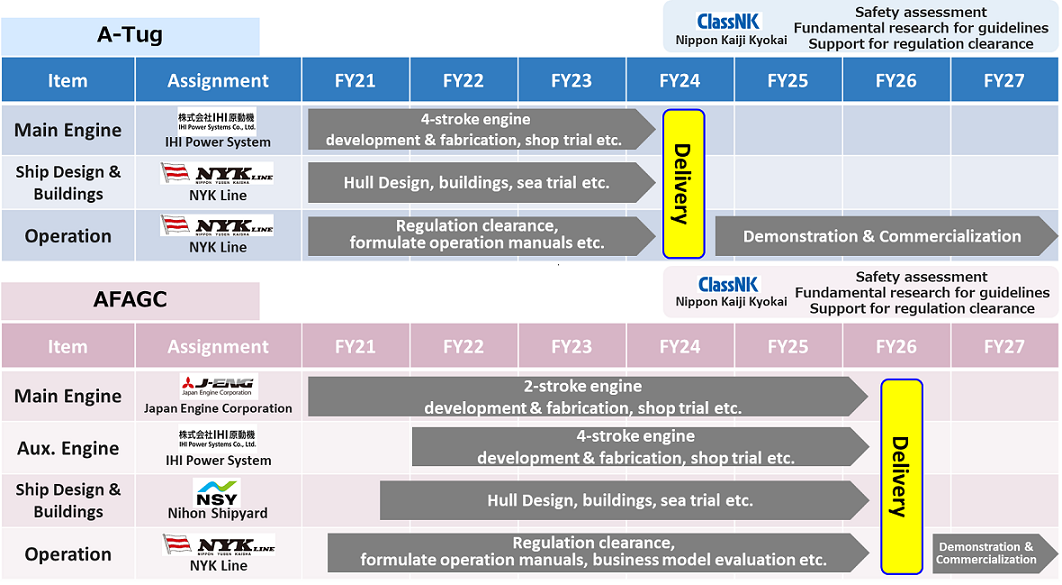
Japan Engine Corporation has announced commercial readiness for its new 2-stroke, dual-fuel engine. The first engine unit will be installed on an ammonia-fueled medium gas carrier next month, with the vessel scheduled to enter service in 2026.
Content Related to Japan Engine Corporation (J-ENG)
Article
J-ENG: testing complete, 2-stroke ammonia engine ready to roll out
Julian Atchison September 02, 2025
Article
Emission performance of ammonia-fueled, two-stroke marine engines
Kevin Rouwenhorst May 06, 2025
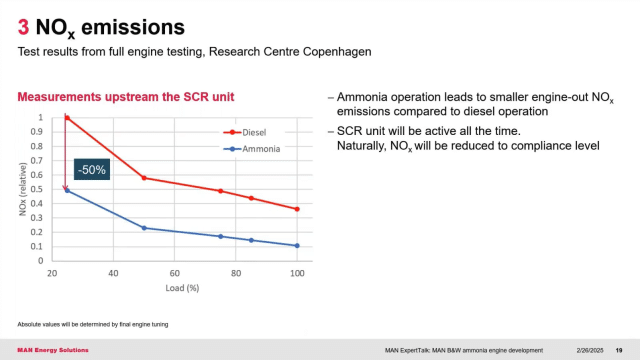
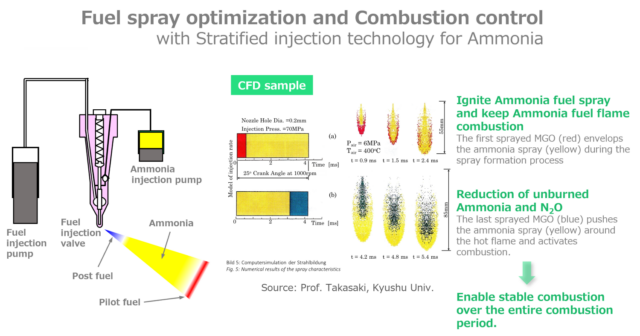
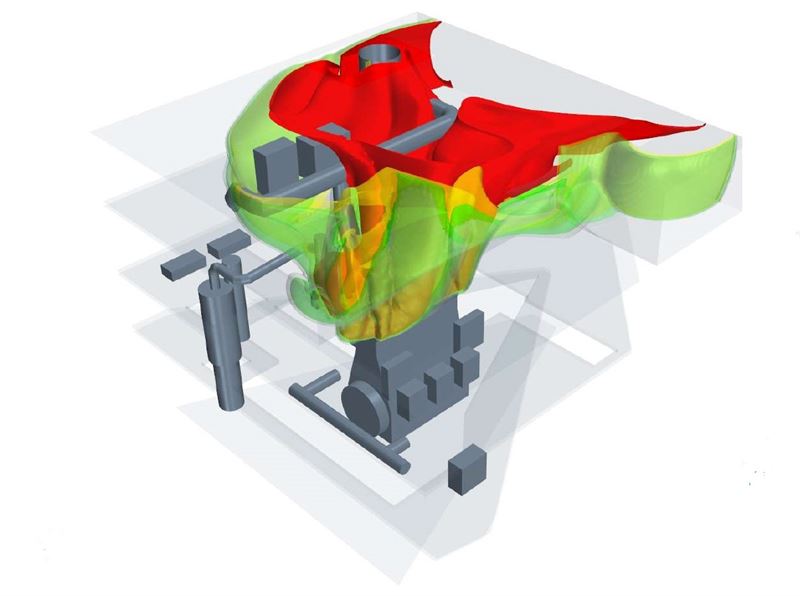
We explore recent, full-scale, dual-fuel engine testing results from leading maritime vendors such as MAN Energy Solutions and WinGD. Testing indicates negligible emissions of the potent GHG N2O (which can be fully eliminated with catalytic treatment), and significantly lower NOX emissions for engines running in ammonia mode, compared to running on fuel oil or diesel. Overall, compliance with IMO Tier II and III emission limits is well within reach for the first generation of ammonia-fueled maritime engines.
Article
Government support for ammonia-powered shipping in Japan, Korea
Julian Atchison January 28, 2025
In Japan, the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism, in cooperation with the Ministry of the Environment will invest $212 million in the domestic manufacture of ammonia engines, fuel tanks and components. In Korea, the national Export-Import Bank has committed to supporting ammonia-fueled newbuilds.
Article
J-ENG completes testing for its first ammonia-fueled marine engine
Julian Atchison November 29, 2024
Japan Engine Corporation (J-ENG) announced that it has completed test operations on its low-speed, 2-stroke engine, with installation and subsequent trial operations due to begin in April 2025. Installation will be onboard one of the first ammonia-fueled vessels to hit the water: the NYK-led midsized gas carrier project.
Article
NYK's ammonia-powered gas carrier to hit the water in late 2026
Julian Atchison February 14, 2024
An NYK-led consortium, which includes Japan Engine Corporation, IHI Power Systems and Nihon Shipyard, has announced that a construction contract has been signed with Japan Marine United to build its 40,000 m3 ammonia-fueled medium gas carrier (AFMGC) in Ariake. The vessel is due to be delivered in November 2026.
Article
Maritime updates: modeling engine room fuel leaks, testing a new fuel supply system
Julian Atchison June 04, 2023
ABS has used computational fluid dynamics to model ammonia dispersion patterns in a ship’s engine room, with the aim of producing a fast, real-time response system for ammonia leaks. In Japan, a fuel supply system for large-scale, low-speed, two-stroke marine engines is undergoing final verification testing. Mitsubishi Shipbuilding aims to become a key technology provider of such systems, and in the ammonia maritime fuel space.
Article
IHI, NYK Line report successful marine engine testing in Japan
Julian Atchison May 23, 2023
Successful testing has been completed at IHI’s facilities in Ota, Japan. A four-stroke marine engine - fully integrated with exhaust gas aftertreatment and fuel supply systems - produced stable operations running on up to 80% ammonia fuel. Emissions of dinitrogen monoxide (N2O) and ammonia slip were reported as “virtually zero”.
Article
Wärtsilä & Møkster join forces, Japanese maritime consortium takes next steps
Julian Atchison November 01, 2021
Wärtsilä and Simon Møkster Shipping will explore the feasibility of using ammonia as the main fuel in dual fuel engines. Currently Møkster's fleet operates on LNG. In Japan, NYK Line, Japan Engine Corporation, IHI Power Systems, Nihon Shipyards and ClassNK will all collaborate on a demonstration project of ammonia-powered vessels in Japan. First announced in 2020 with three vessel concepts, two of the three vessel designs now have a commercialisation schedule fully defined (the A Tug and the AFAGC).
Article
The maritime sector's ammonia learning curve: moving from scenario analysis to product development
Trevor Brown October 25, 2019
ANNUAL REVIEW 2019: The maritime industry is learning about ammonia fast. It is searching for a new bunker fuel, and ammonia is one of the few options that can realistically deliver a 50% reduction in the sector's GHG emissions by 2050. The IMO declared this target in April 2018 and, in last year's Annual Review, I wrote about all the reports that were published demonstrating that ammonia could deliver this outcome. In the last 12 months, by contrast, we have moved quickly beyond analysis and into engineering design, technology testing, and product development.
Article
Maritime ammonia engines in Japan; ammonia shipbuilding in South Korea
Trevor Brown September 27, 2019
This week, Japan Engine Corporation (J-ENG) announced the launch of a new R&D program, in collaboration with the National Maritime Research Institute, that focuses on engine development for "combustion of carbon-free fuel (e.g. hydrogen and ammonia)." Five hundred miles across the Sea of Japan, DSME has completed a techno-economic feasibility study comparing three fuels: HFO (with scrubber), LNG, and ammonia. The results of this study will be presented at the Ammonia Energy Conference, in Orlando, FL, on November 13. DSME is one of the three big shipbuilders in South Korea, and its business case for ammonia is strong enough that now "DSME is planning to expand our technology and business to NH3 engineering and systems for commercial ships."