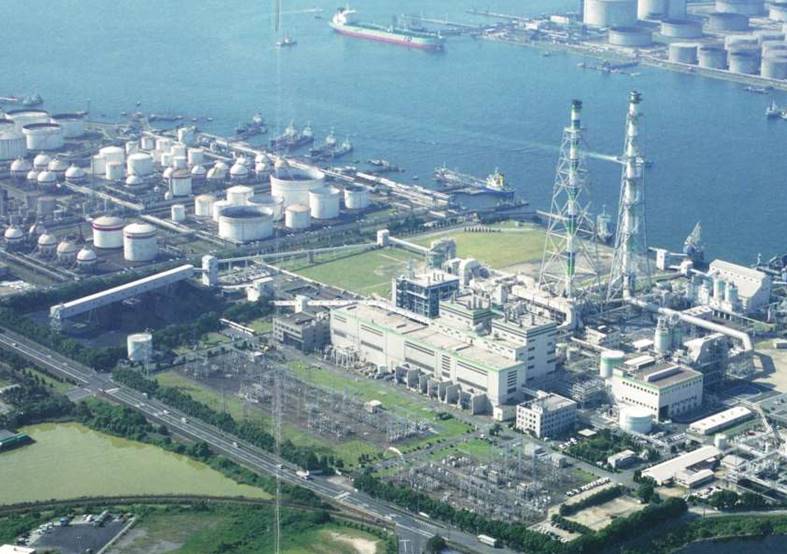
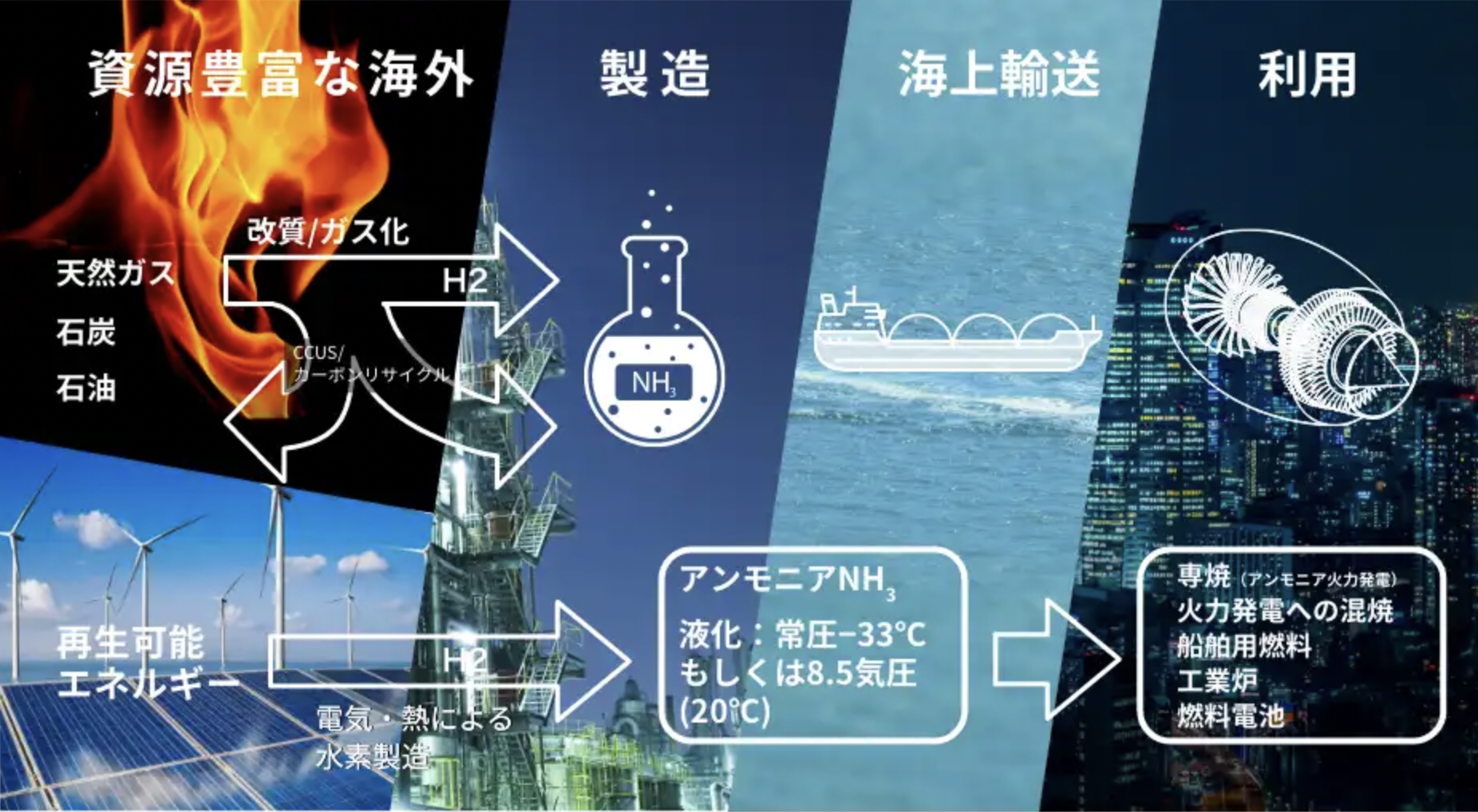
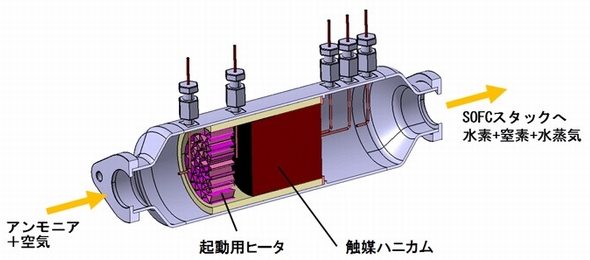
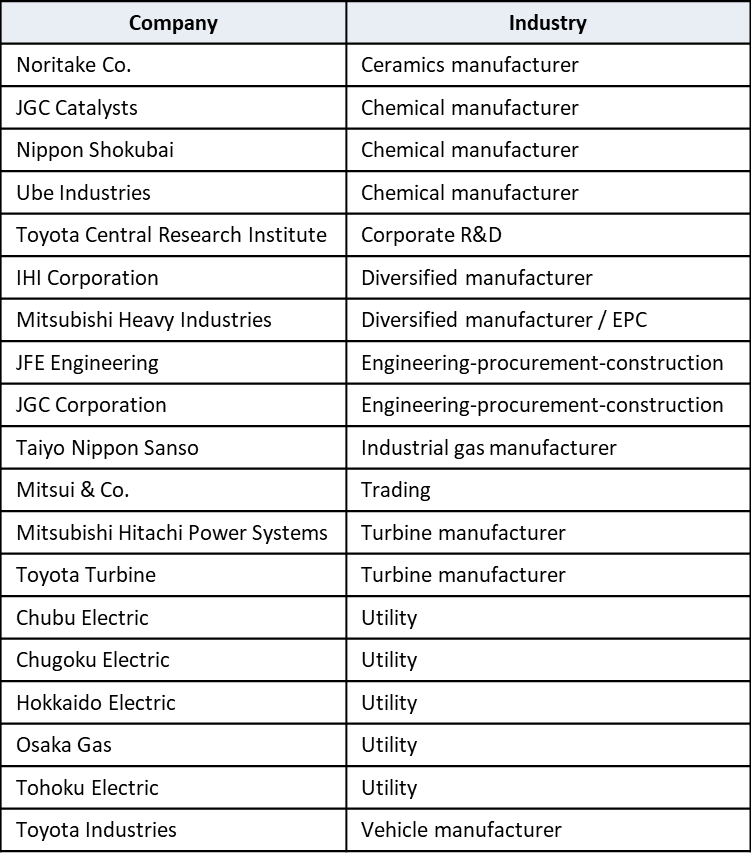
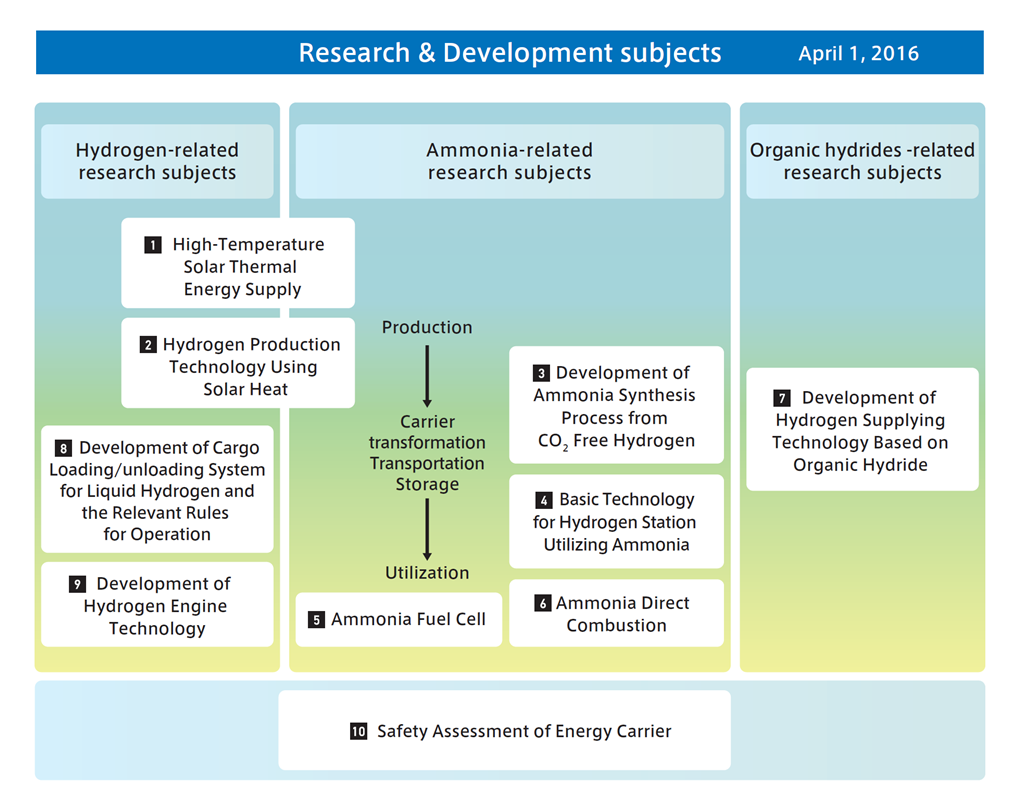
Japanese government funding via NEDO will support four critical ammonia energy projects, including JERA's new plan to demonstrate 50% ammonia-coal co-firing by 2030. Other projects include improved catalysts for ammonia production, low-temperature and low-pressure synthesis pathways, and developing 100% ammonia-fed boilers and gas turbines. In addition, a new cooperation agreement between ASEAN countries will see Japan support other members to adopt their ammonia energy solutions, particularly coal co-firing.
Content Related to Kyoto University
Article
The Ammonia Academic Wrap: "seamless" cracking, improving Haber Bosch, a novel green power-to-ammonia-to-power solution and a review into the use of ammonia as a fuel
Julian Atchison May 13, 2021
Welcome to the Ammonia Academic Wrap: a summary of all the latest papers, developments and emerging trends in the world of ammonia energy R&D. This week: "seamless" ammonia cracking tech from Northwestern, a new electrolysis catalyst, successful integration of ammonia synthesis and separation for improved efficiency, more research needed into transition metal catalysts for Haber Bosch, a novel, green power-to-ammonia to power system and a review on ammonia as a potential fuel.
Article
A Deep Dive into SIP “Energy Carriers” Ammonia Combustion Research (second half)
Bunro Shiozawa October 13, 2020
From 2014 to 2018 Bunro Shiozawa served as Deputy Program Director of the SIP “Energy Carriers” initiative in Japan. Over the last year he has published a ten-part series of articles that describe and reflect on the research supported by the initiative. Part 4 covers ammonia combustion technologies. The first half of the article was posted on September 23, 2020, in Shiozawa's English translation. The second half follows.
Article
Japan Advances SOFCs for the Built Environment
Stephen H. Crolius March 05, 2020
A steady stream of Japanese news reports over the last several months attest to the country’s progress in deploying fuel cells in the built environment. Dubbed “Ene-Farms,” the appliances function as micro-scale combined heat and power units, providing electricity as well as heat for domestic applications. Most of the Ene-Farms deployed so far feature proton-exchange membrane (PEM) technology (which requires high-purity hydrogen). However, two recent developments show that solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) technology (well suited for ammonia) could play a role, maybe even a large role, in Japan's Hydrogen Society.
Presentation
Activation By High Temperature Reduction of Ru Catalyst Supported on Rare Earth Oxide for Ammonia Synthesis
Ammonia is an important chemical feedstock, and more than 80% of the synthesized ammonia is used to produce fertilizer. Ammonia is also being considered as an energy carrier and hydrogen source (1) because it has a high energy density (12.8 GJ m-3) and a high hydrogen content (17.6 wt%), (2) because infrastructure for ammonia storage and transportation is already established, and (3) because carbon dioxide is not emitted when ammonia is decomposed to produce hydrogen. If ammonia could be efficiently produced from a renewable energy source, such as solar or wind energy, problems related to the global energy crisis could…
Presentation
Ammonia Decomposition and Separation Using Catalytic Membrane Reactors
Sai P. KatikaneniStephen N. PaglieriAadesh X. HaraleAqil JamalKoichi EguchiHiroki MuroyamaToshiaki Matsui
Hydrogen is the primary fuel source for fuel cells. However, the low volume density and difficulty in storing and transporting hydrogen are major obstacles for its practical utilization. Among various hydrogen carries, ammonia is one of the most promising candidates because of its high hydrogen density and boiling point and ease in liquefaction and transportation. The reaction temperature of ammonia cracking into nitrogen and hydrogen is about 500˚C or higher. The hydrogen can be effectively separated by the membrane based on Pd alloy about 500˚C. Currently, the extraction of hydrogen from ammonia is carried out by two step process involving…
Presentation
Carbon-Free H2 Production from NH3 Triggered at Ambient Temperature with Oxide Supported Ru Catalysts
Hydrogen produced from renewable energy has received a lot of attentions as a clean energy and development of a hydrogen storage and transportation system using hydrogen carrier has been greatly demanded. Among different kinds of hydrogen carrier, NH3 is regarded as one of the promising candidates, due to high energy density, high hydrogen capacity, and ease of liquification at room temperature. Furthermore, a carbon-free hydrogen storage and transportation system could be realized by using NH3 as hydrogen carrier. In this system, hydrogen produced from NH3 is used in engines, fuel cells, and turbines. However, use of NH3 as a hydrogen…
Presentation
Experimental and Computational Study for Reduction of NOx Emissions in the Ammonia / Methane Co-Combustion in a 10 KW Furnace
Ryuichi MuraiRyohei OmoriTakahiro KitanoHidetaka HigashinoNoriaki NakatsukaFumiteru AkamatsuYuya YoshizuruJun Hayashi
There are severe issues on increasing amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) emission in the world. Many studies are devoted to alternative fuels. One of promising candidates is the utilization of ammonia which is zero emission of CO2, a hydrogen energy carrier, and also can be burned directly as a fuel. For direct combustion of ammonia in industrial furnaces, there were two issues which were weaker radiative heat flux and a huge amount of NOx emission compared with the combustion of methane. We already have reported [1] the solution of the former issue by using the oxygen enriched combustion. The objective…
Presentation
Development of Catalytic Reactors and Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Systems for Utilization of Ammonia
Koichi EguchiYosuke TakahashiTakahiro MatsuoHayahide YamasakiHidehito KuboAkihiro OkabeTakenori Isomura
Hydrogen is the primary fuel source for fuel cells. However, the low volume density and difficulty in storage and transportation are major obstacles for the practical utilization. Among various hydrogen carriers, ammonia is one of the promising candidates because of its high hydrogen density and boiling point and ease in liquefaction and transportation. The reaction temperature of ammonia cracking to nitrogen and hydrogen, being about 600°C or higher, is close to the operating temperature of solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs). The integration of these two devices is beneficial in terms of heat and energy managements and will lead to the…
Article
Direct Ammonia Fuel Cells Take Another Step Forward in Japan
Stephen H. Crolius May 31, 2018
Japanese manufacturing concern IHI reported on May 16 that it had “successfully generated 1 kW class power” from a direct ammonia solid oxide fuel cell. This is the latest milestone for a technology that could play a major role in the roll-out of Japan’s Hydrogen Society.
Presentation
Development of Materials and Systems for Ammonia-Fueled Solid Oxide Fuel Cells
Koichi EguchiYosuke TakahashiHayahide YamasakiHidehito KuboAkihiro OkabeTakenori IsomuraTakahiro Matsuo
Hydrogen is the primary fuel source for fuel cells. However, the low volume density and difficulty in storage and transportation are major obstacles for the practical utilization. On-site generation of hydrogen from its carrier is an effective method for the fuel supply. Among various hydrogen carriers, ammonia is one of the promising candidates. Ammonia has high hydrogen density. The boiling point of ammonia is relatively high, leading to the ease in liquefaction and transportation. Hydrogen can be produced from ammonia with a mildly endothermic process. The reaction temperature of ammonia cracking is about 600˚C or higher which is close to…
Article
SIP "Energy Carriers" video: ammonia turbines, industrial furnaces, fuel cells
Trevor Brown October 13, 2017
To demonstrate the progress of the SIP "Energy Carriers" program, the Japan Science and Technology Agency last week released a video, embedded below, that shows three of its ammonia fuel research and development projects in operation. R&D is often an abstract idea: this video shows what it looks like to generate power from ammonia. As it turns out, fuel cells aren't hugely photogenic. Nonetheless, if a picture is worth a thousand words, this will be a long article.
Article
Development of Direct Ammonia Fuel Cells
Trevor Brown October 05, 2017
In the last 12 months ... Researchers from three continents have pushed the boundaries for direct ammonia fuel cells, setting records in power generation and continuous operation.
Article
Green Ammonia Consortium: Bright Prospects in Japan for Ammonia as an Energy Carrier
Stephen H. Crolius October 05, 2017
In the last 12 months ... In July 2017, 19 companies and three research institutions came together to form the Green Ammonia Consortium. Before this development, it was unclear whether ammonia would find a significant role in Japan’s hydrogen economy. In the wake of this announcement, however, ammonia seems to have claimed the leading position in the race among potential energy carriers.
Article
Major Development for Ammonia Energy in Japan
Stephen H. Crolius August 10, 2017
On July 25, the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) announced that a collection of companies and research institutions had come together to form a Green Ammonia Consortium. The 22-member group will take over responsibility for the ammonia aspect of the Cross-Ministerial Strategic Innovation Program (SIP) Energy Carriers agenda when the SIP is discontinued at the end of fiscal 2018. A JST press release states that the Consortium intends to develop a strategy for “forming [an] ammonia value chain,” promote demonstration projects that can further commercialization, and enable “Japanese industry to lead the world market.”
Article
Ammonia-Fueled Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Advance at Kyoto University
Stephen H. Crolius July 20, 2017
Earlier this month the Eguchi Laboratory at Kyoto University announced advances in ammonia-fueled solid oxide fuel cell technology. The lab was able to produce a functioning fuel cell with a power output of one kilowatt. The device attained “direct current power generation efficiency” in excess of 50% and reached 1,000 hours of continuous operation.
Article
New Ammonia-Reforming Catalyst System
Stephen H. Crolius May 05, 2017
On April 27 the on-line journal Science Advances published “Carbon-free H2 production from ammonia triggered at room temperature with an acidic RuO2/γ-Al2O3 catalyst.” The lead author, Katsutoshi Nagaoka, and his six co-authors are associated with the Department of Applied Chemistry at Oita University in Japan. The innovation featured in the paper could prove to be an important enabler of ammonia fuel in automotive applications.
Presentation
Research and Development of Ammonia-fueled SOFC Systems
Koichi EguchiAtthapon SrifaTakeou OkanishiHiroki MuroyamaToshiaki MatsuiMasashi KishimotoMotohiro SaitoHiroshi IwaiHideo YoshidaMasaki SaitoTakeshi KoideHiroyuki IwaiShinsuke SuzukiYosuke TakahashiToshitaka HoriuchiHayahide YamasakiShohei MatsumotoShuji YumotoHidehito KuboJun KawaharaAkihiro OkabeYuki KikkawaTakenori Isomura
Ammonia is a promising hydrogen carrier because of its high hydrogen density, low production cost, and ease in liquefaction and transport. Ammonia decomposes into nitrogen and hydrogen through a mildly endothermic process. The ammonia decomposition temperature is close to the operating conditions of solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs). Therefore, the integration of these two devices is beneficial in terms of efficient heat and energy managements and will lead to the development of simplified generation systems. We have investigated three types of ammonia-fueled SOFC systems. In one system, ammonia is directly supplied to the anode chamber. Ammonia decomposes into nitrogen and…
Presentation
Current progress in development of NH3-fueled solid-state fuel cell systems
Takeou OkanishiKaname OkuraJun YangHiroki MuroyamaToshiaki MatsuiMasashi KishimotoMotohiro SaitoHiroshi IwaiHideo YoshidaKoichi EguchiHiroyuki IwaiK. InaokaShinsuke SuzukiYosuke TakahashiToshitaka HoriuchiHayahide YamasakiHideyuki MatsumotoHidehito KuboJun KawaharaAkihiro OkabeYuki KikkawaT. NegishiS. Watanabe
Current progress in development of NH3-fueled solid-state fuel cell systems T. Okanishi*, K. Okura, J. Yang, H. Muroyama, T. Matsui, M. Kishimoto, M. Saito, H. Iwai, H. Yoshida, K. Eguchi, Kyoto University; H. Iwai, K. Inaoka, S. Suzuki, Y. Takahashi, Noritake; T. Horiuchi, H. Yamasaki, Nippon Shokubai; S. Matsumoto, H. Kubo, Toyota Industries; J. Kawahara, A. Okabe, Mitsui Chemical; Y. Kikkawa, T. Negishi, S. Watanabe, Tokuyama
Presentation
Research and development of NH3-fueled solid-state fuel cell systems
Hiroki MuroyamaJun YangKaname OkuraTakeou OkanishiToshiaki MatsuiMotohiro SaitoHiroshi IwaiHideo YoshidaKoichi Eguchi
Ammonia is a prospective carbon-free fuel source for fuel cell systems due to low production cost, ease in liquefaction at ambient temperatures, and high energy density. Furthermore, hydrogen and nitrogen originating from ammonia fuel are expected to have little negative effect on fuel cell performance, while hydrocarbon fuels draws some severe problems at electrodes, such as CO poisoning or carbon deposition in low- and high-temperature fuel cells, respectively. Several technologies can be considered for the ammonia utilization in fuel cell systems. For the utilization of ammonia fuel, we aim to develop a system combined with ammonia decomposition reactor and solid-state…