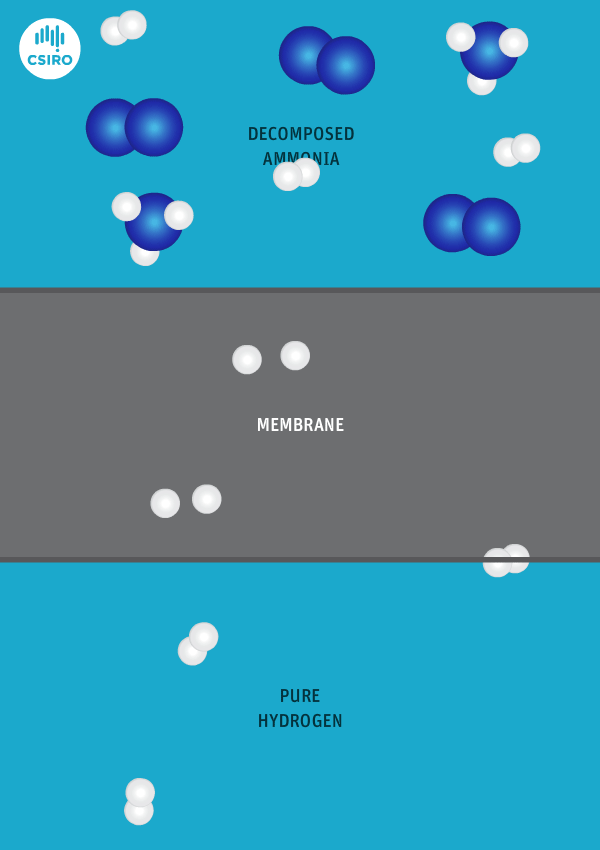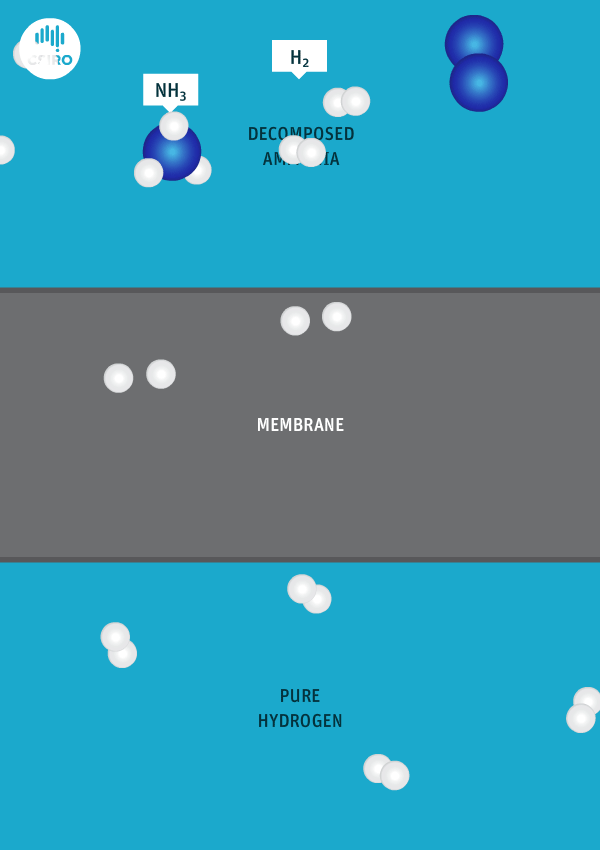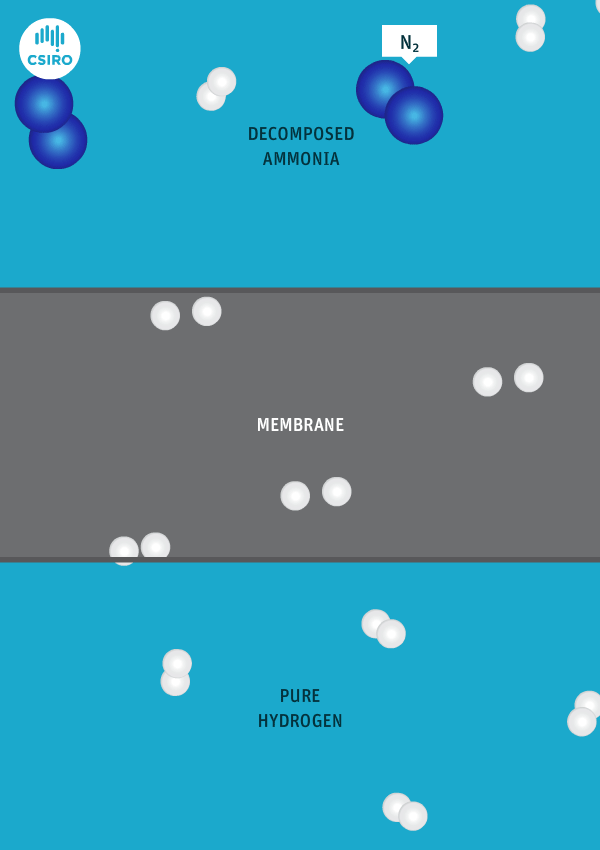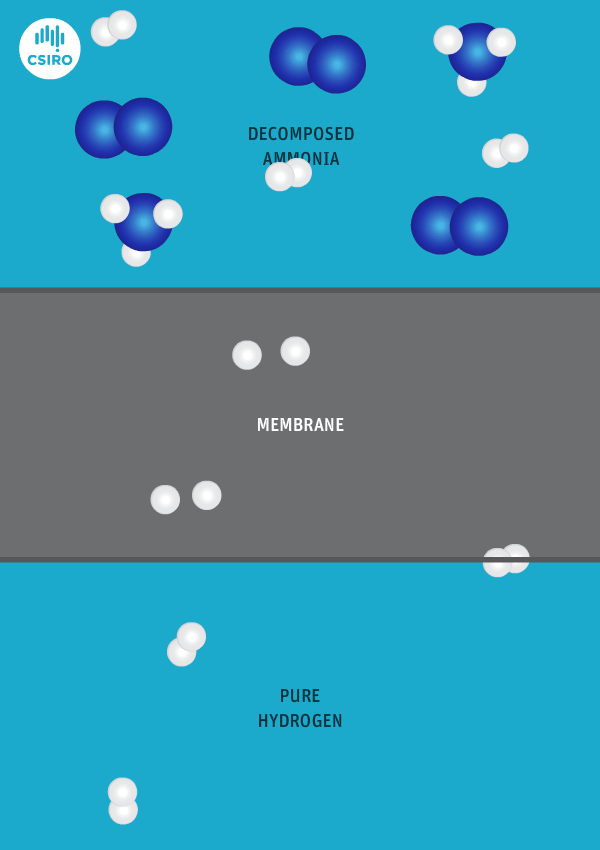
Current global ammonia production is mostly based on gas-fed, two-stage reforming processs. Decarbonization of this existing production capacity – as well as new newbuild low-emission capacity also based on gas – can utilize an industrially-proven suite of alternative technologies and processes, including autothermal reforming, and partial oxidation combined with CCS. This article discusses some of the technologies available from various tech providers, and reference projects in operation.