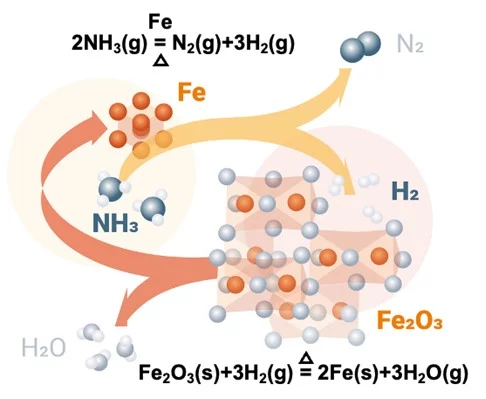
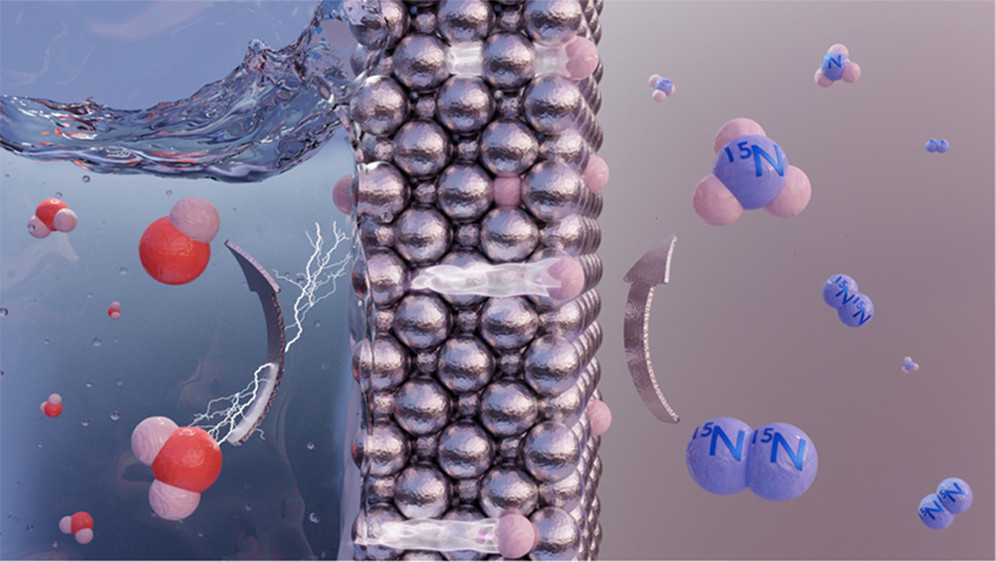
We look at four new developments this week:
1. A team from DTU Energy and the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics have uncovered a new class of alternative catalysts for mild condition ammonia synthesis. The ternary ruthenium complex hydrides Li4RuH6 and Ba2RuH6 avoid the energy-intensive pathway of nitrogen dissociation in a "synergistic" manner.
2. A team from the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials reported a highly selective (95%) plasma ammonia synthesis method.
3. A team from Delft University of Technology has presented an present an "unconventional electrochemical design" that physically separates hydrogen and dinitrogen activation sites.
4. A team at the Max Planck Institute for Coal Research has demonstrated a new mechanochemical ammonia synthesis system that operates at room temperature and pressures as low as 1 bar.