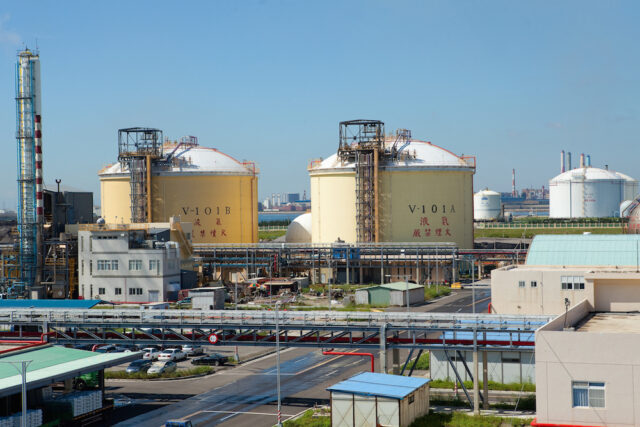
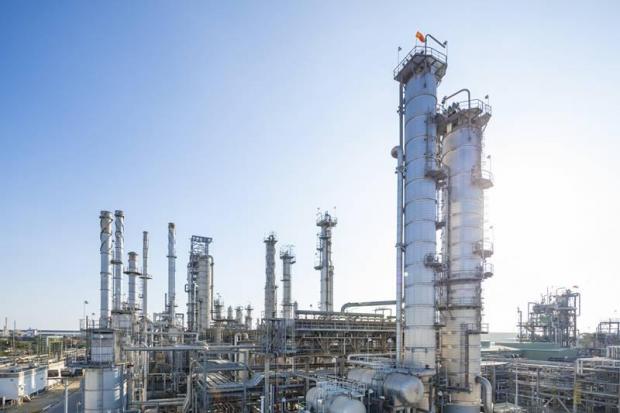
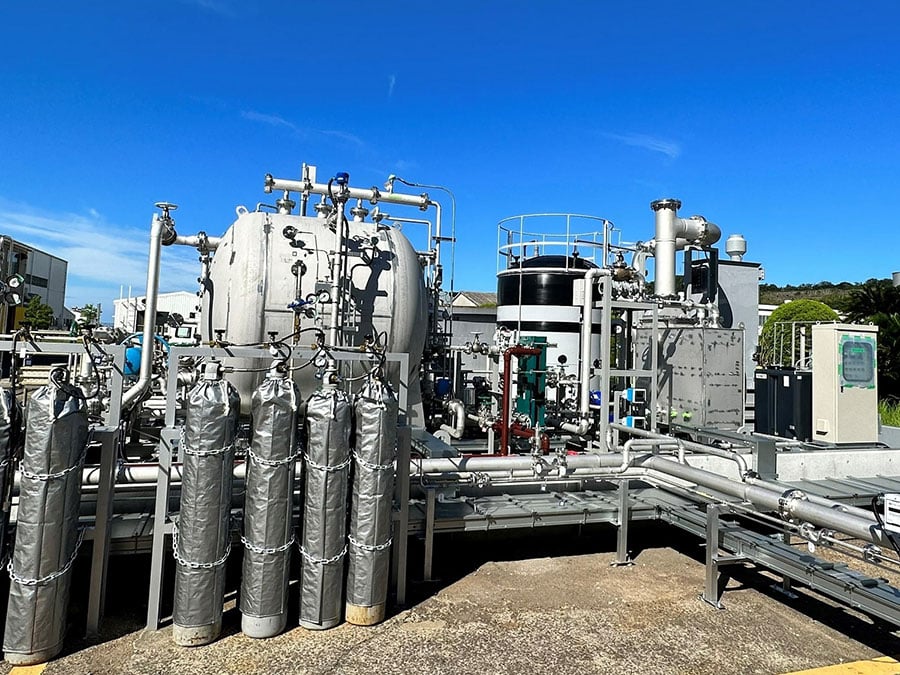
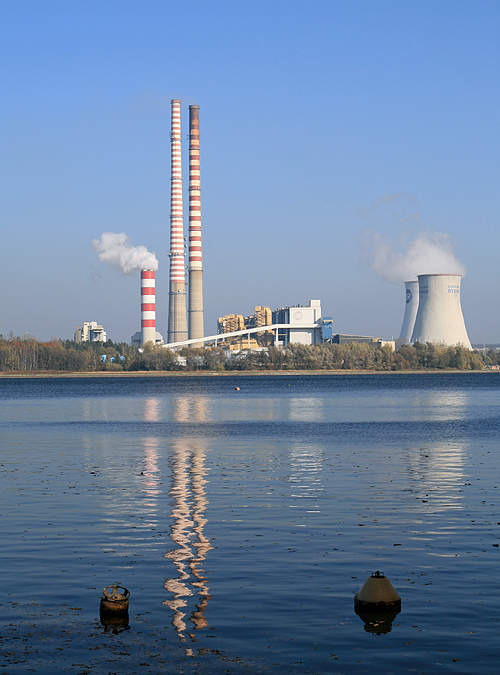
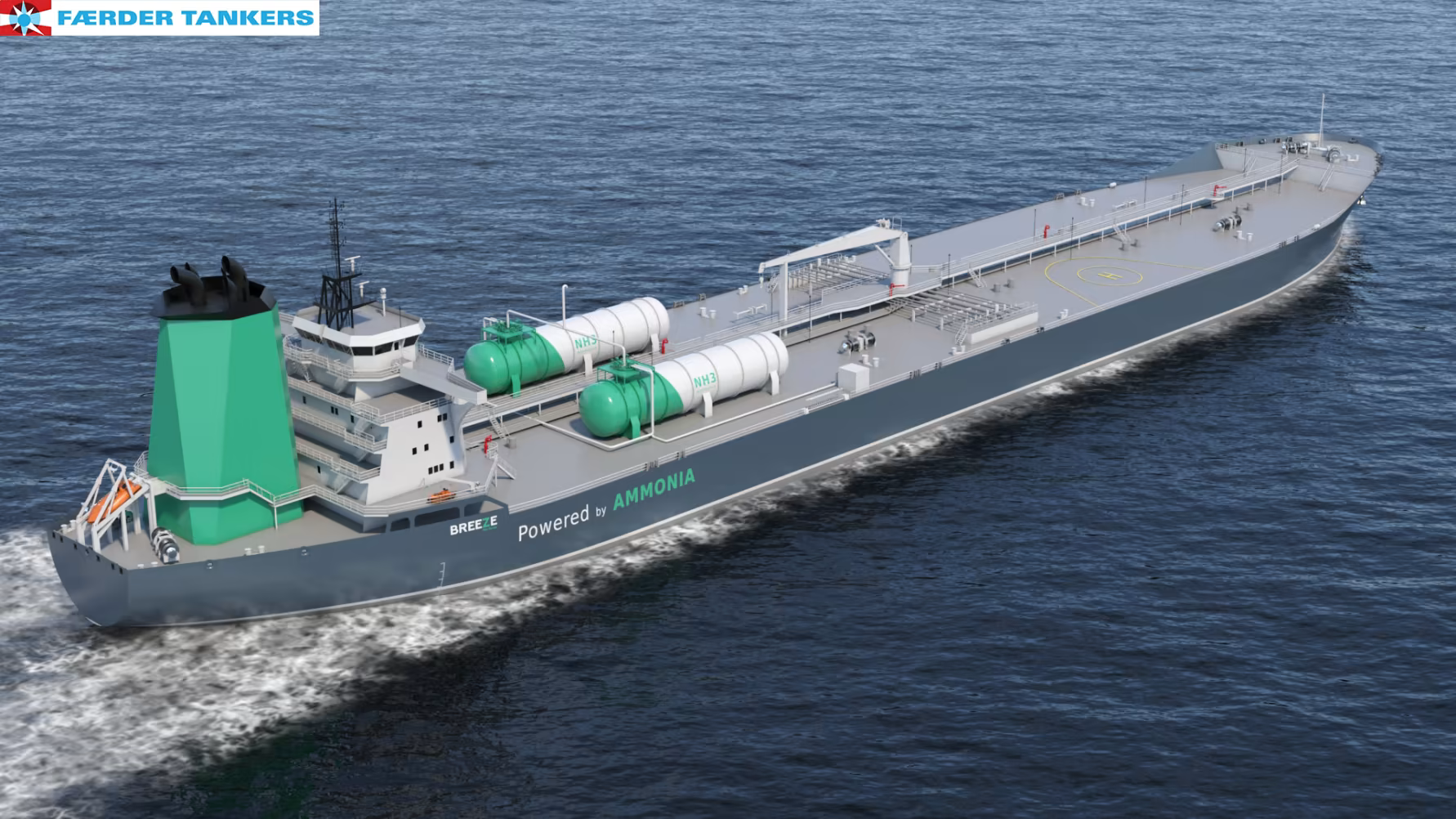
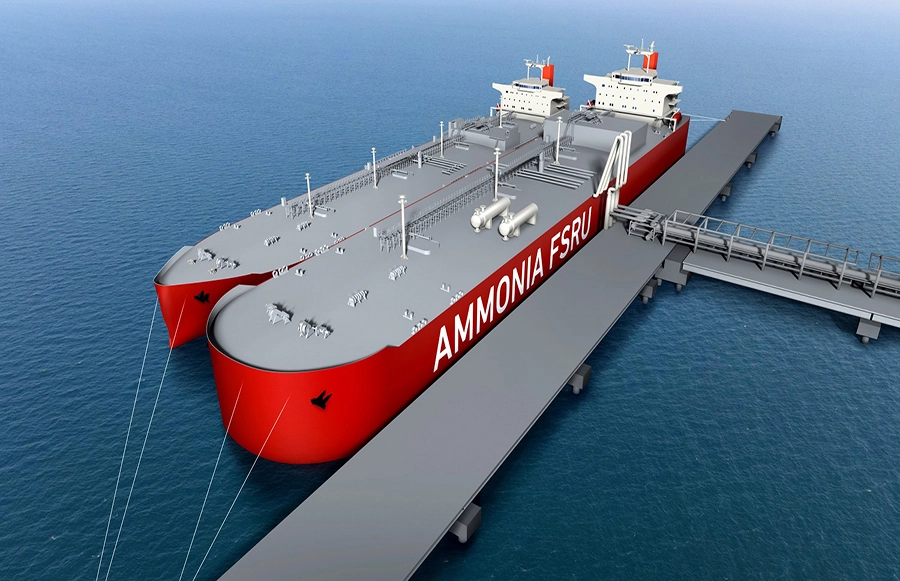
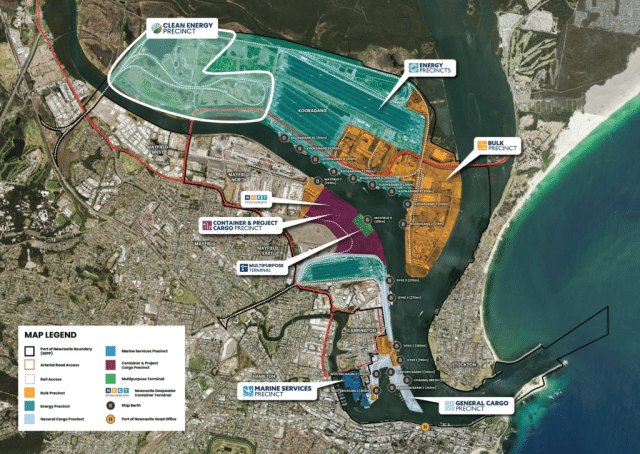
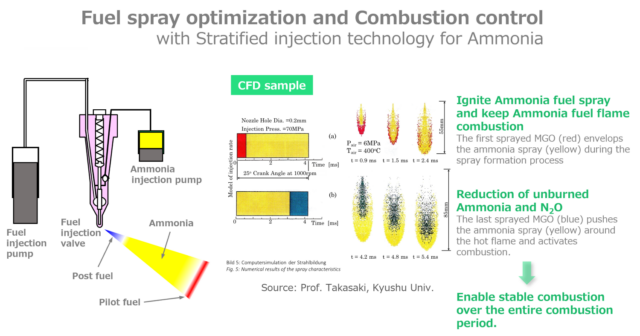
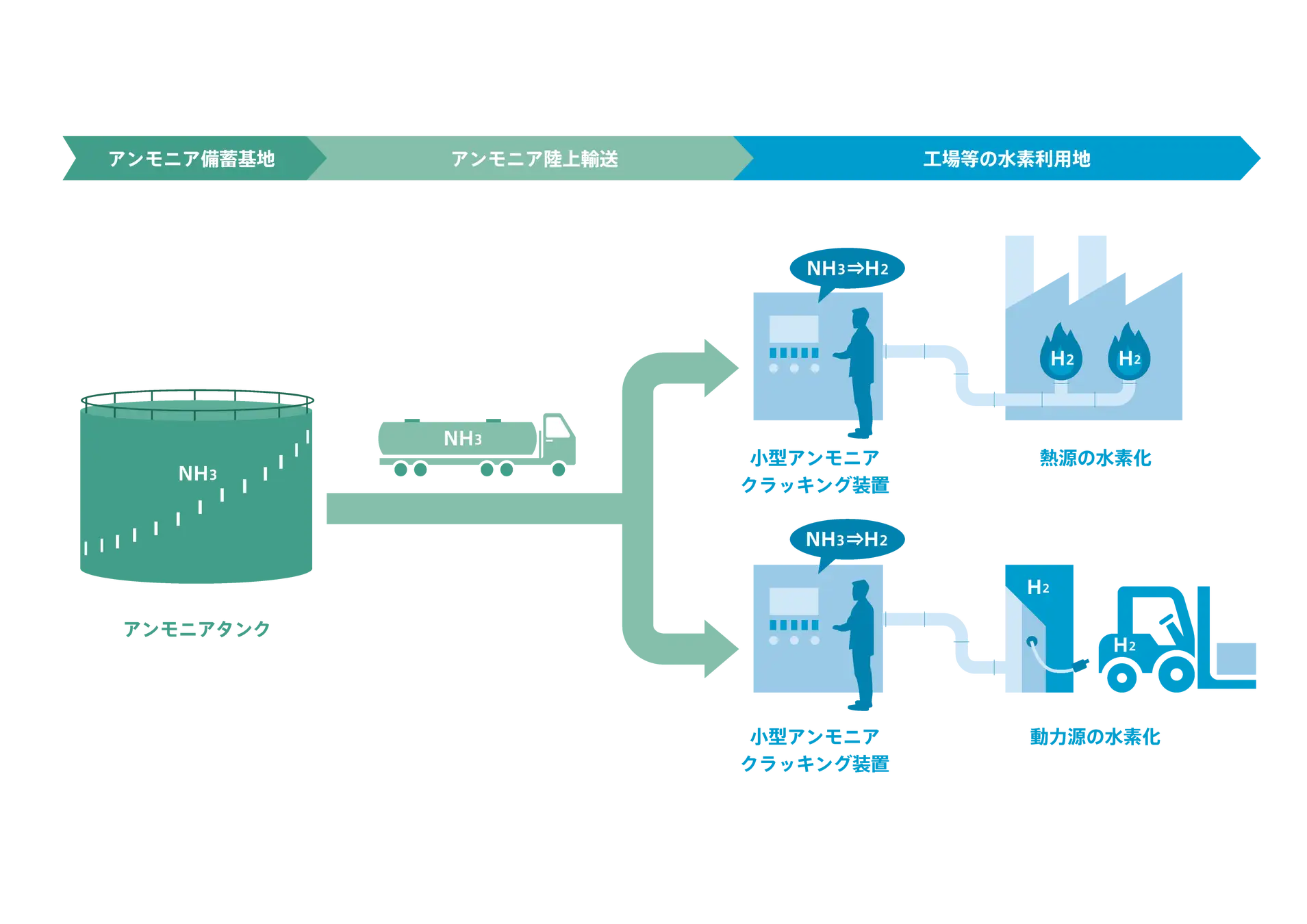
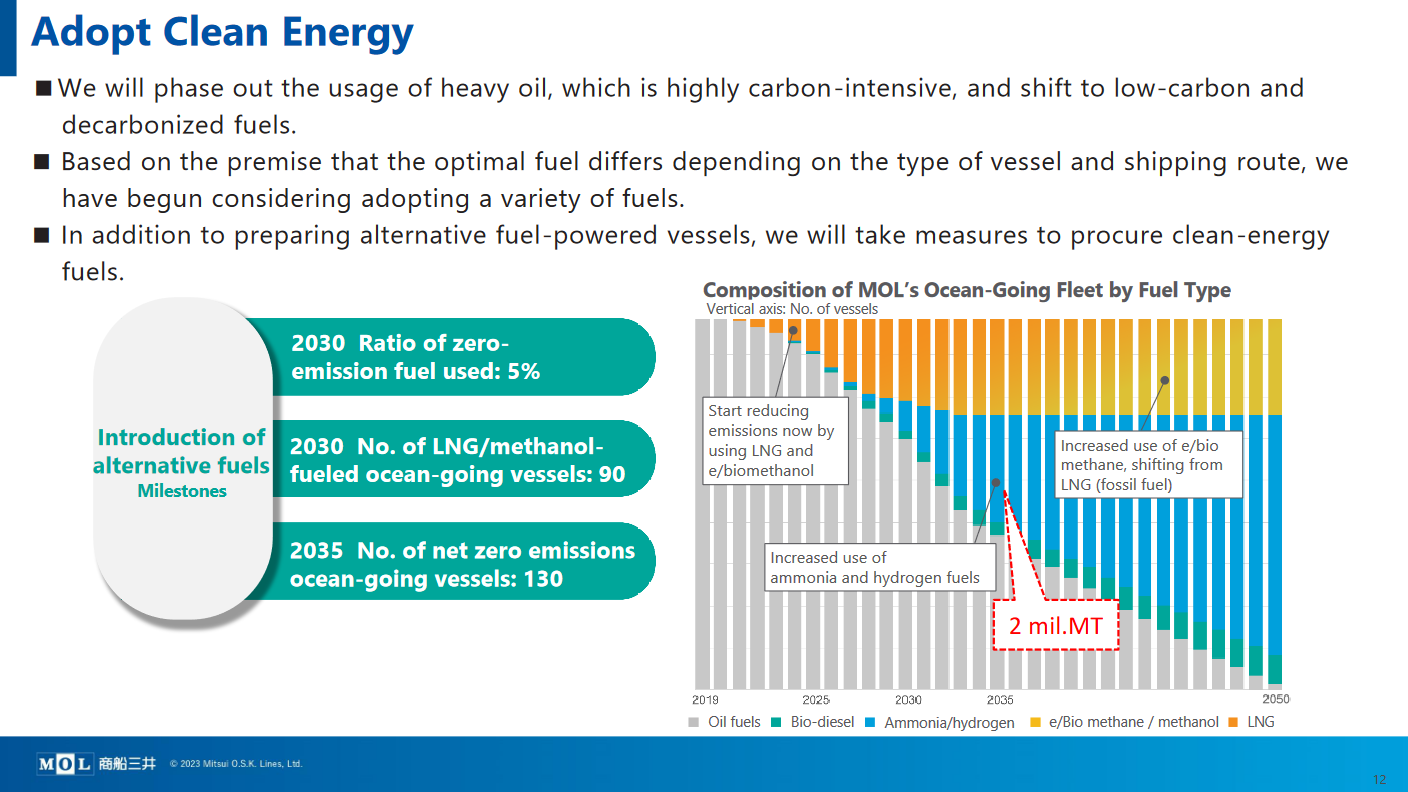
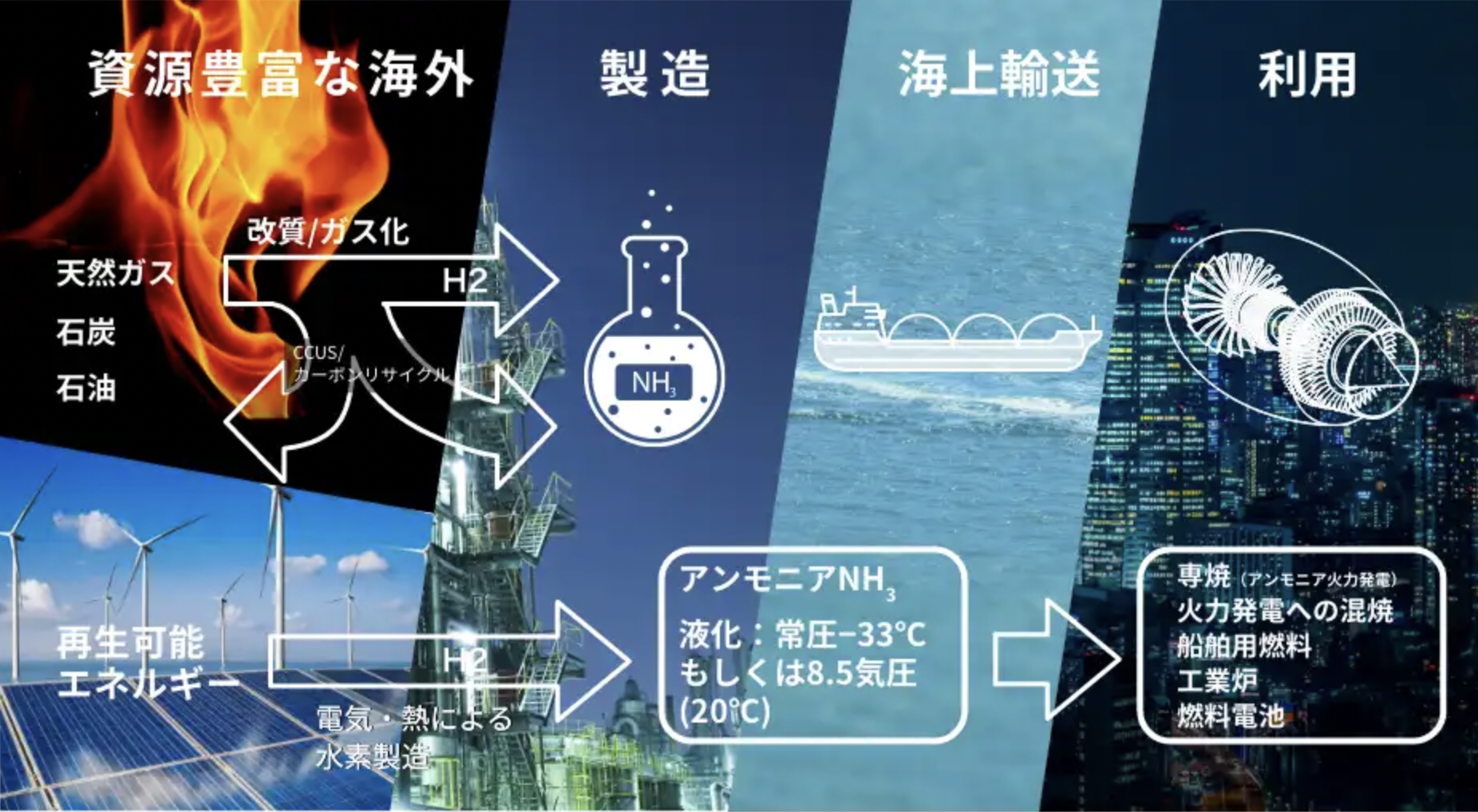
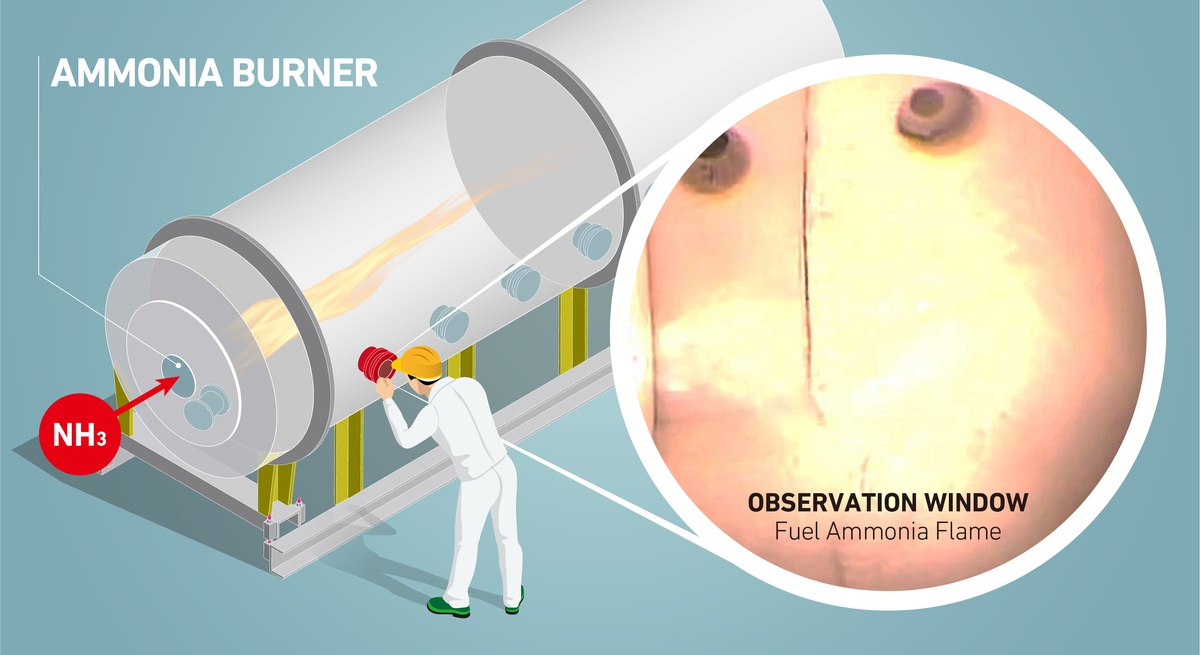
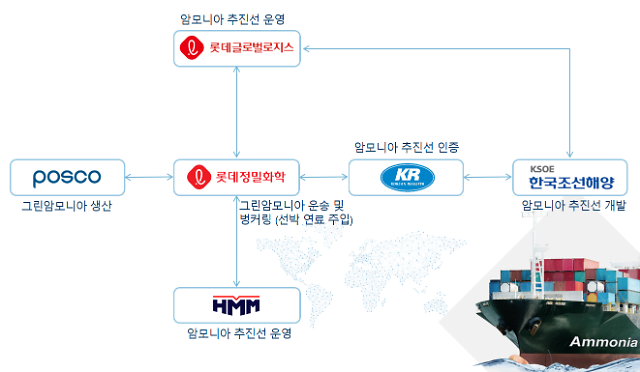
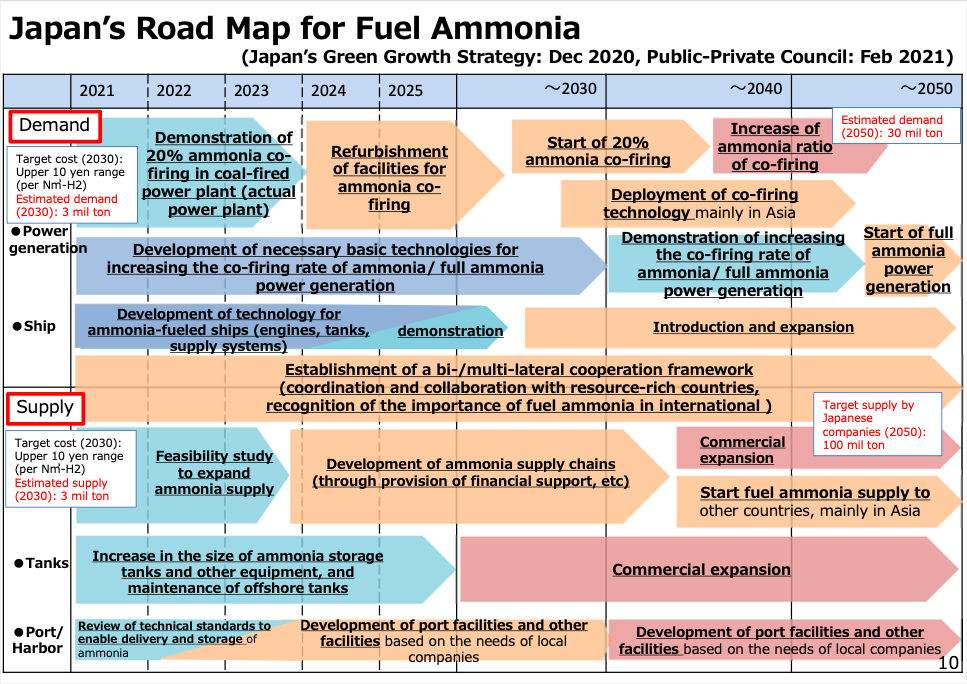
This month, the Japanese Ministry for Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI) began promoting an updated Road Map for Fuel Ammonia, focused on the use of ammonia in thermal power plants and as a shipping fuel. By 2030, Japan expects to import 3 million tons of clean ammonia, with demand rising to 30 million tons by 2050. To secure these volumes, Japanese companies are now making investments up and down the supply chain. These are ambitious numbers, matching Japan’s recent commitment to reach net-zero emissions, but still they miss the big picture. The broader economic opportunity arrives when Japanese companies export their fuel ammonia technologies, decarbonizing coal-fired power plants across Asia, and then supply the fuel to these newly sustainable shipping and electricity sectors. By 2050, the METI Road Map expects Japanese trading companies to supply the wider region with 100 million tons per year of clean ammonia.