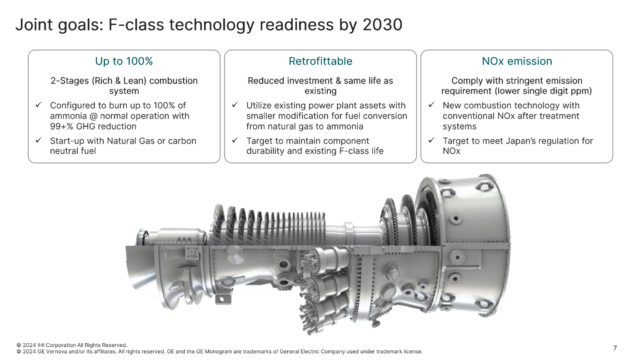
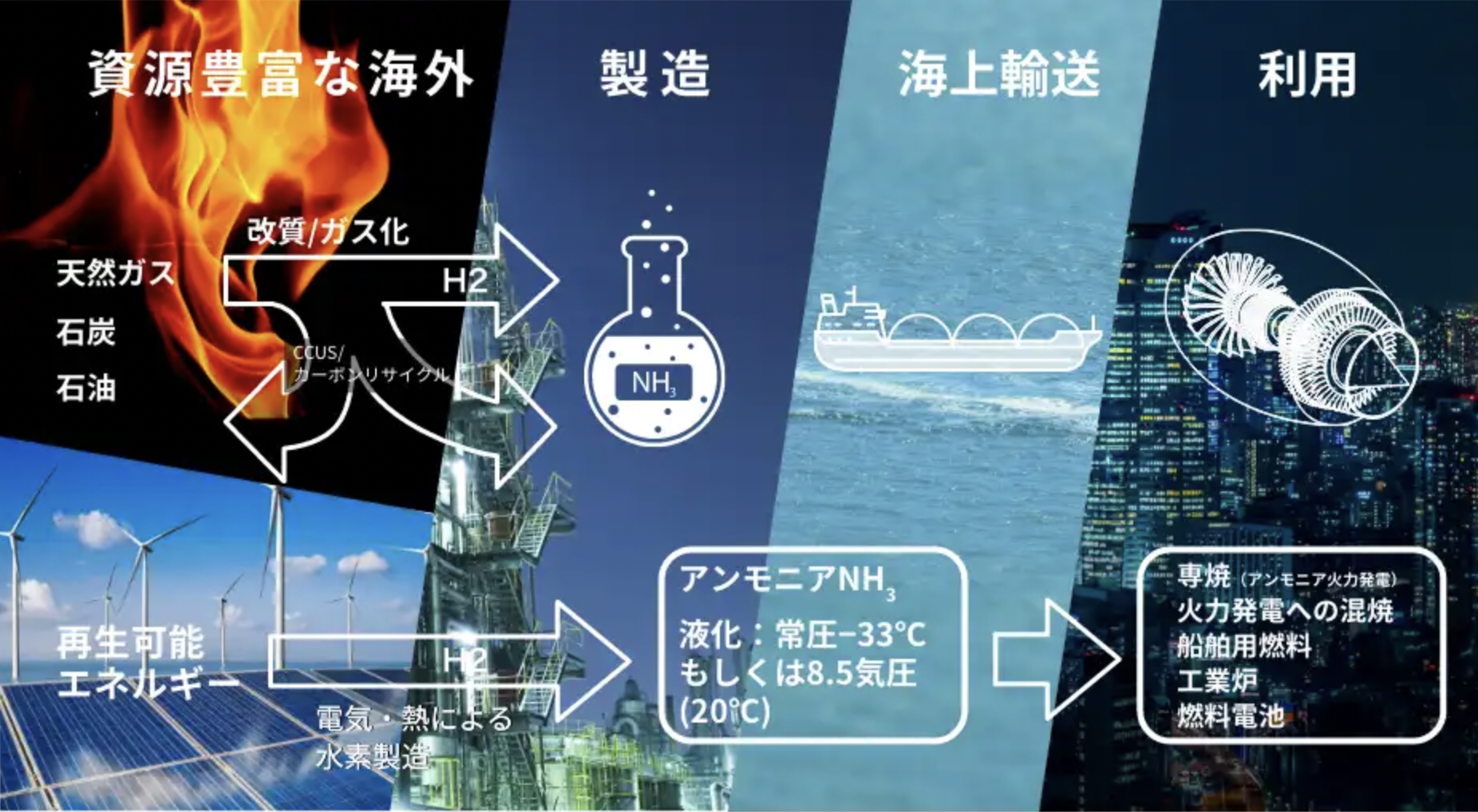
Approximately 40% of the world’s energy budget is consumed in the generation of electricity. This is by far the largest use of primary energy across major energy-consuming sectors (transportation, industry, etc.). What role ammonia will play in the electricity sector is therefore a question of considerable importance for the sustainable energy system of the future. One concept currently on the table is power-to-ammonia as a means of electricity storage, whereby electricity is used to produce hydrogen and the hydrogen is reacted with nitrogen to produce ammonia. The other, mirror-image, concept is to use ammonia, or hydrogen derived from ammonia, as a fuel that can be turned into electricity. This “back-end” use case is the focus of recent announcements from Mitsubishi Hitachi Power Systems (MHPS). According to an April 5 story in the Nikkei Sangyo, MHPS plans to put a “hydrogen-dedicated gas turbine . . . into practical use by 2030.” The company also stated that it has “started developing technology to extract hydrogen from ammonia,” citing ammonia’s ease “to store and transport.”