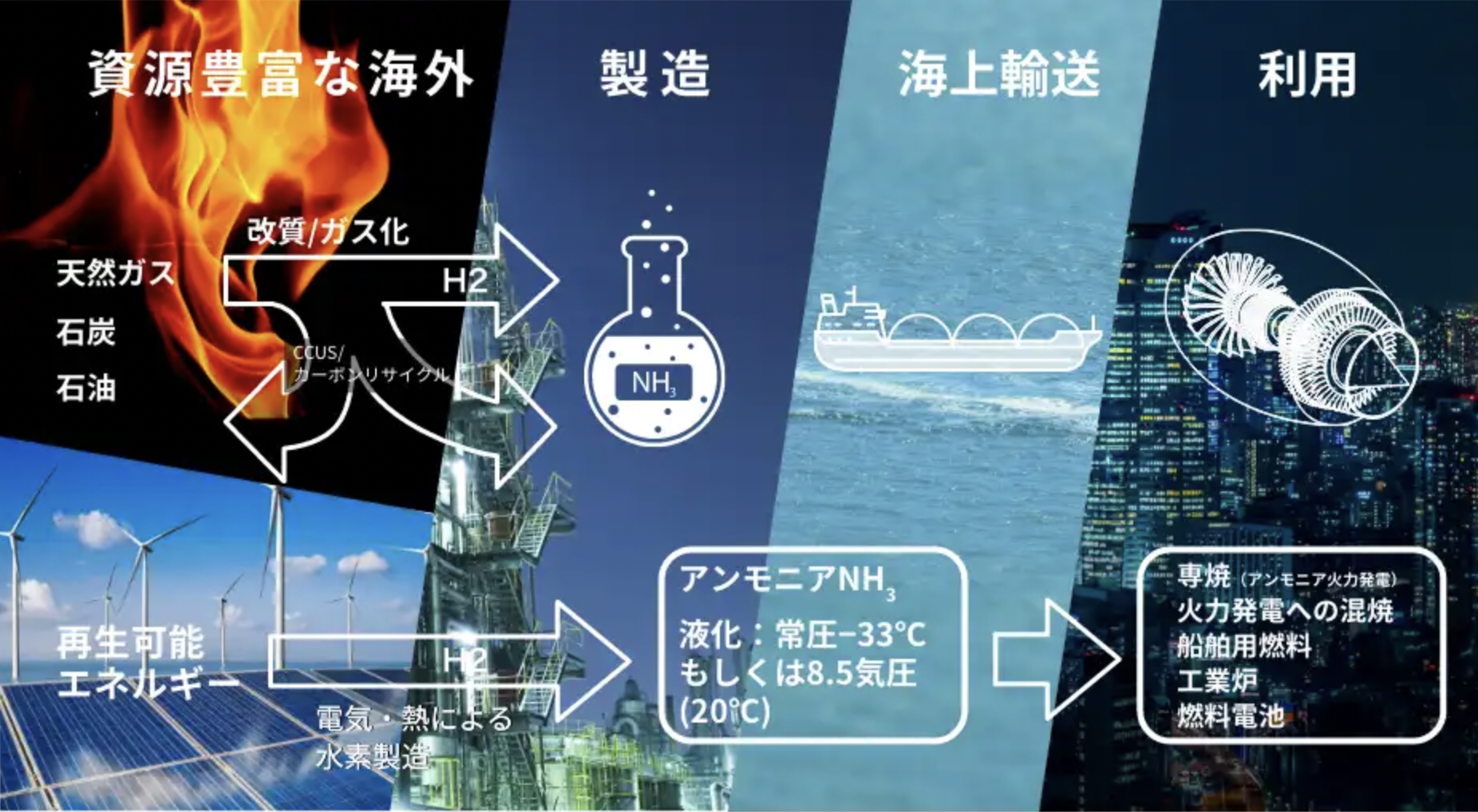
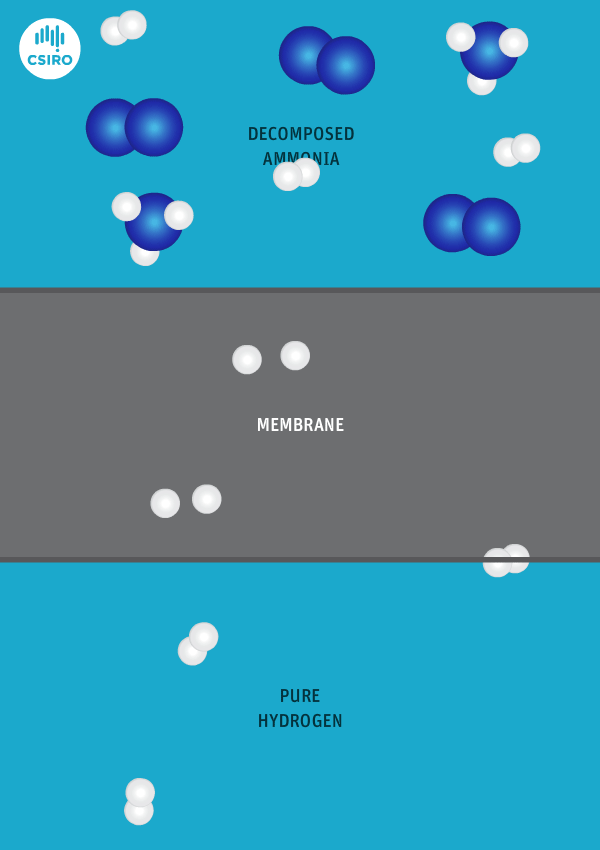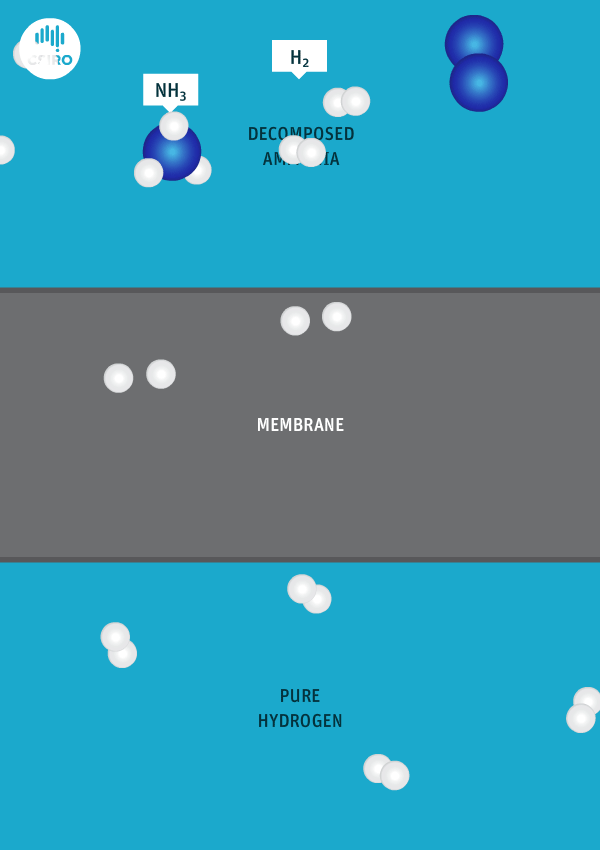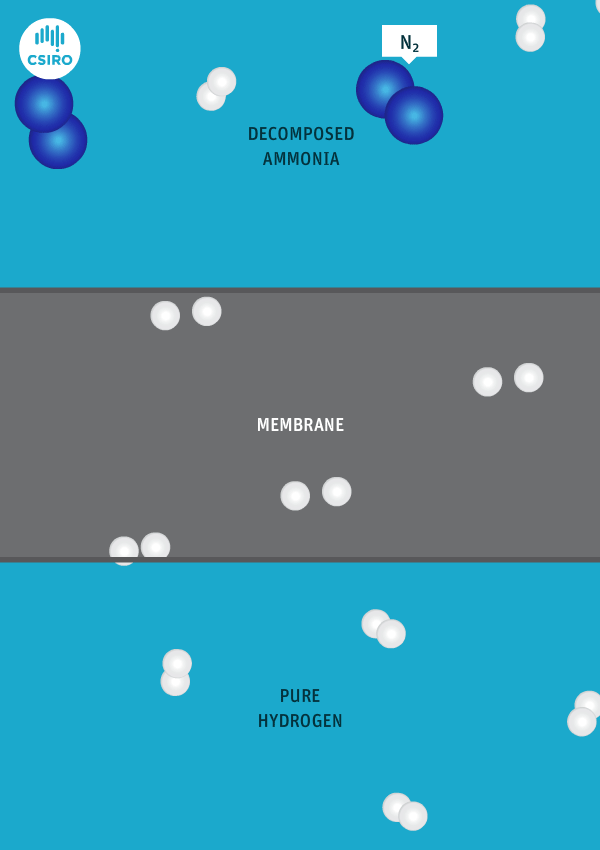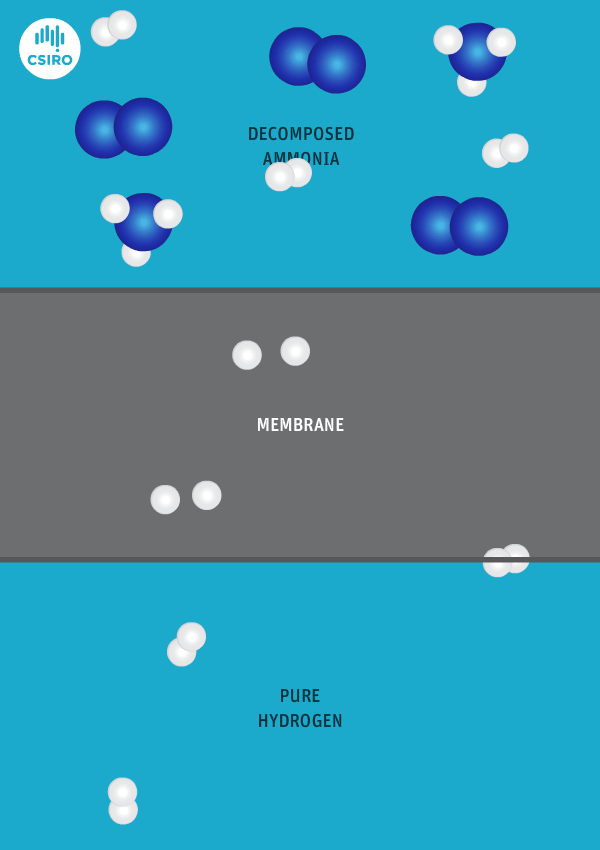
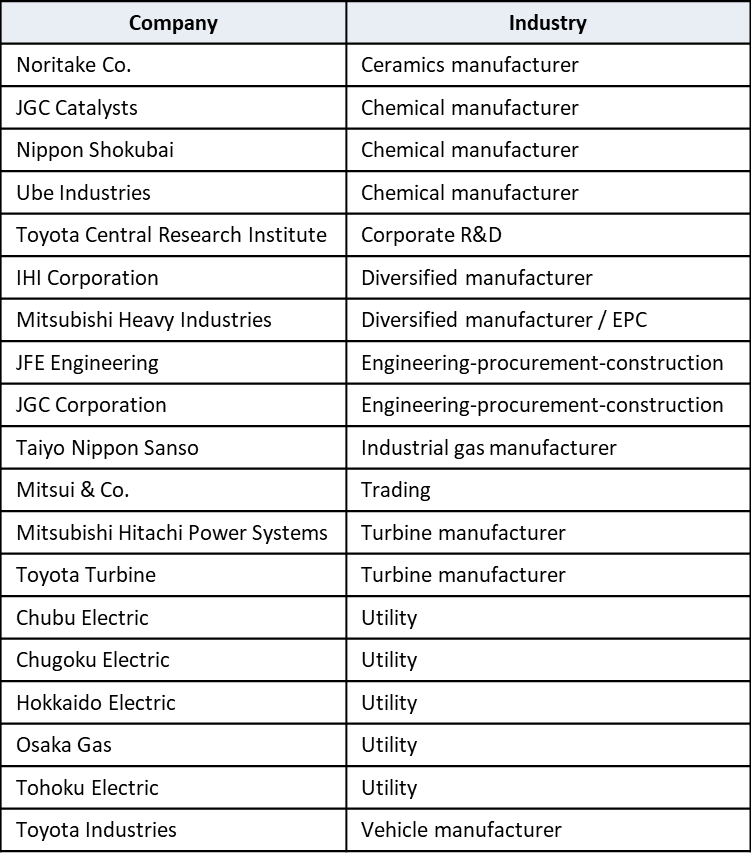
Japanese government funding via NEDO will support four critical ammonia energy projects, including JERA's new plan to demonstrate 50% ammonia-coal co-firing by 2030. Other projects include improved catalysts for ammonia production, low-temperature and low-pressure synthesis pathways, and developing 100% ammonia-fed boilers and gas turbines. In addition, a new cooperation agreement between ASEAN countries will see Japan support other members to adopt their ammonia energy solutions, particularly coal co-firing.