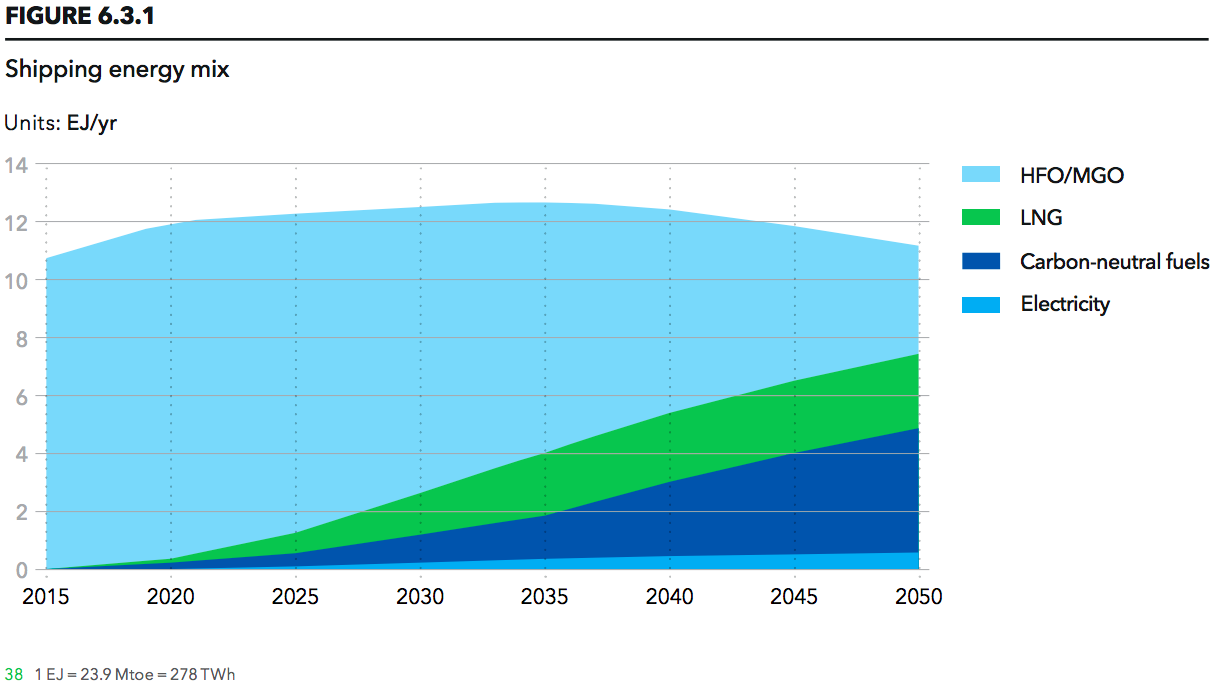
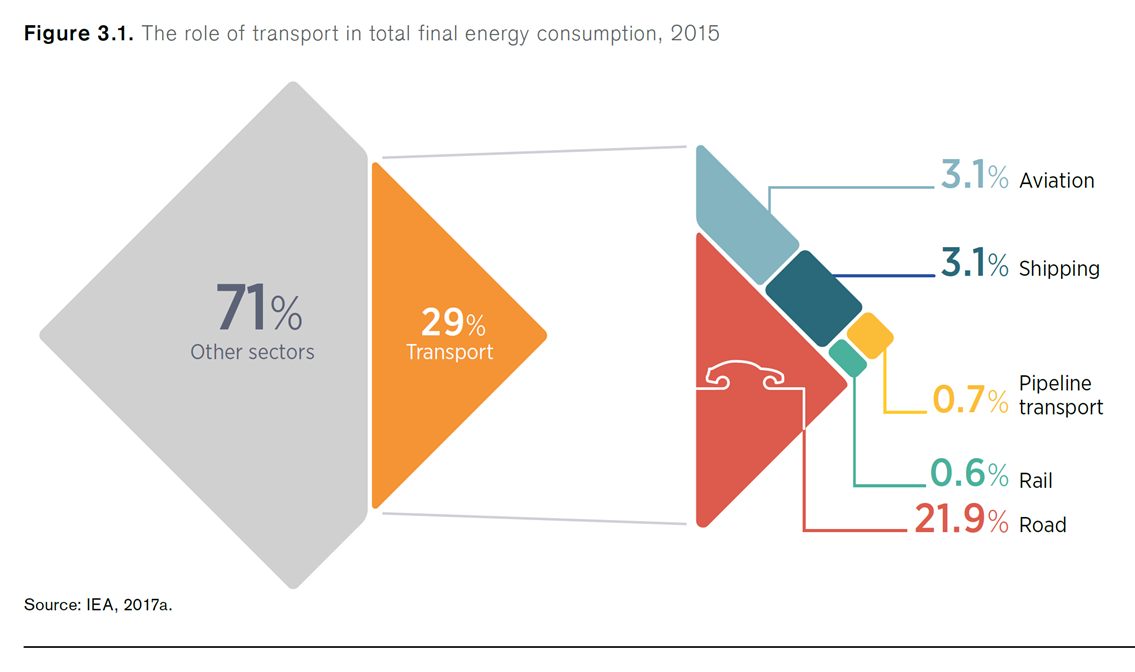
In the last 12 months ... The International Maritime Organization issued its Initial GHG Strategy, committing the global shipping industry to emission reductions that cannot be achieved with carbon-based fuels. This single action is the regulatory trigger that unleashes a three-decade transition to carbon-free liquid fuels like ammonia. The target date for this 50% reduction in emissions is 2050 but, given the long economic life of ocean vessels, the transition must begin immediately.
Content Related to OECD
Maritime Industry Targets Ammonia Fuel to Decarbonize Shipping
P2X, Ammonia Highlighted for Long-Haul Road Transport, Shipping
The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), in partnership with the International Energy Agency (IEA) and Renewable Energy Policy Network for the 21st Century (REN21), released a report this month entitled "Renewable Energy Policies in a Time of Transition." The 112-page document is a comprehensive survey of technologies, policies, and programs that have current or prospective roles in the global transition to a sustainable energy economy. For the ammonia energy community, one of its conclusions stands out in vivid relief: "Developing P2X is crucial because it plays a key role in decarbonising long haul road transport, aviation and shipping sectors that are difficult to decarbonize ... The overall recommendation for developing P2X is to focus on the development of ammonia for the shipping sector as well as long haul road transport, where few or no competing low carbon technologies exist and P2X is expected to be economically viable."
Decarbonising Maritime Transport: OECD report sees ammonia fuel enabling carbon-free shipping by 2035
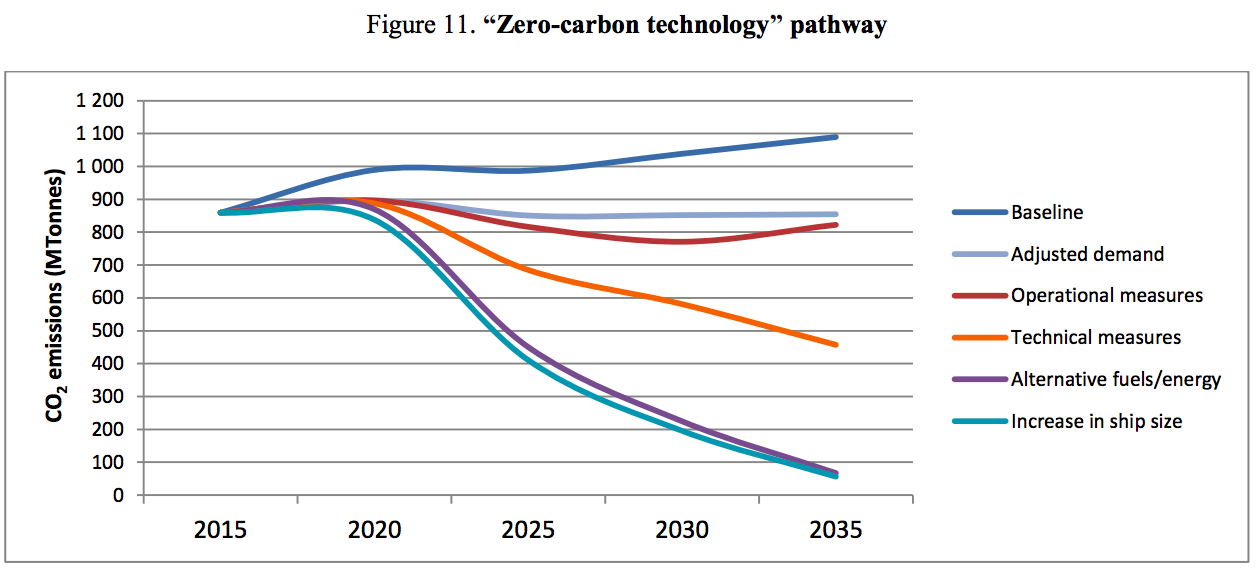
Twelve months ago, I wrote here that "the shipping industry is beginning to evaluate ammonia as a potential 'bunker fuel,' a carbon-free alternative to the heavy fuel oil (HFO) used in maritime transport." Around that time, I described the obstacle to adoption of ammonia fuel as an information gap, rather than a technology gap, because no new technology was required: the industry simply did not know about ammonia. This information gap had allowed the industry to believe that "CO2 reduction objectives will only be achievable with alternative marine fuels which do not yet exist." I'm glad to announce that this information gap is closing, and fast. According to a report published last week by the International Transport Forum, the OECD's "think tank for transport policy," the use of "currently known technologies could make it possible to almost completely decarbonise maritime shipping by 2035." This conclusion requires the adoption of ammonia as a zero-carbon fuel.