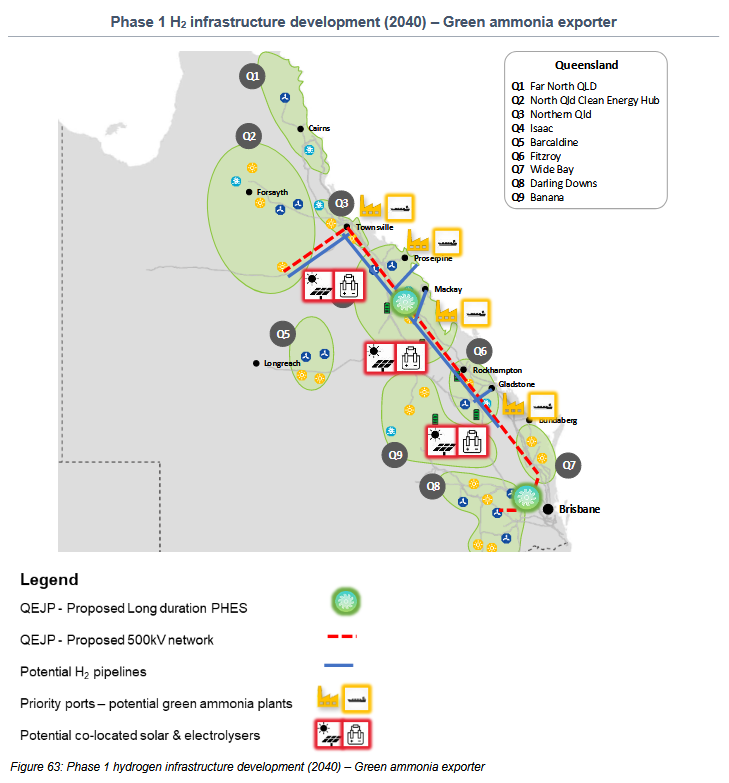
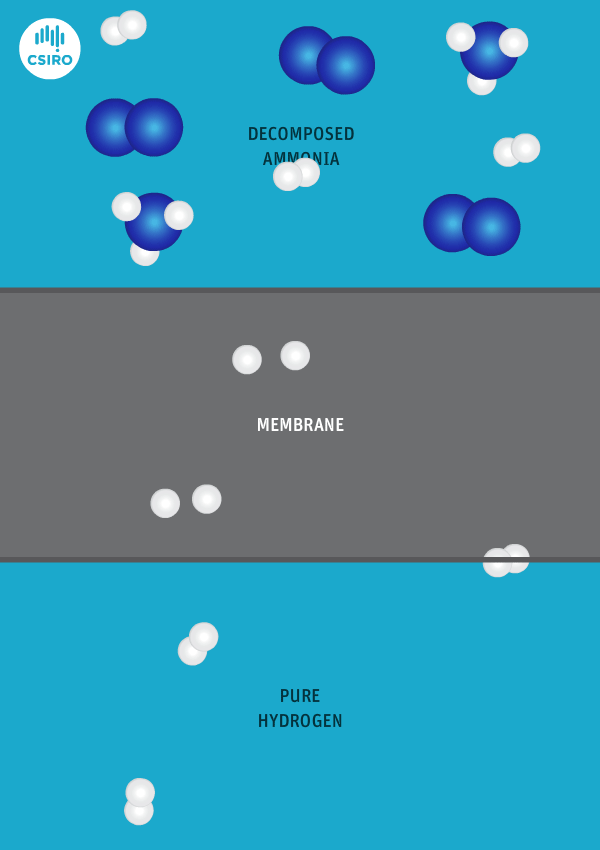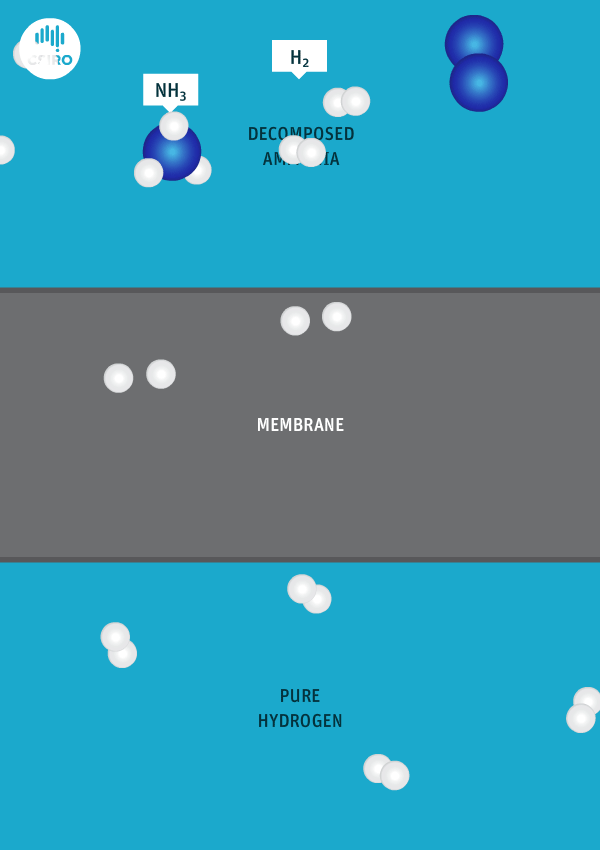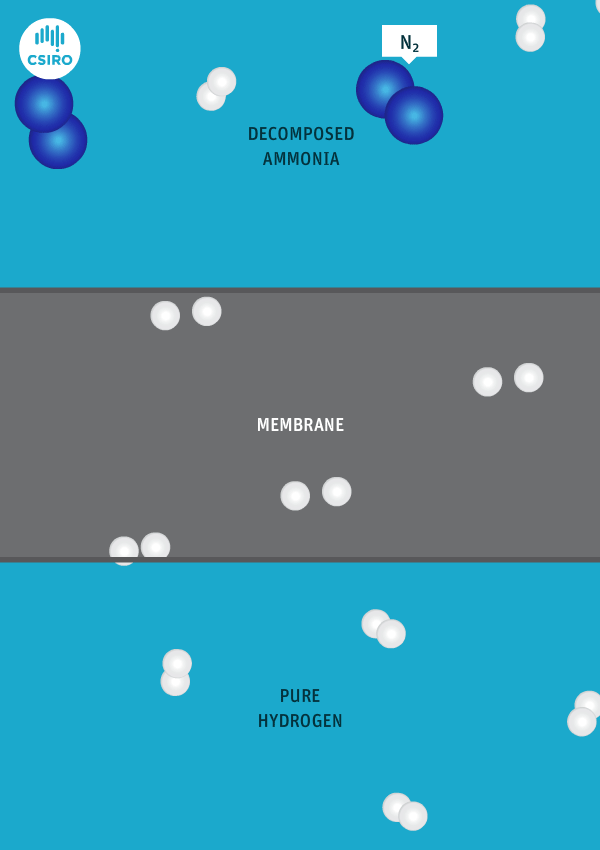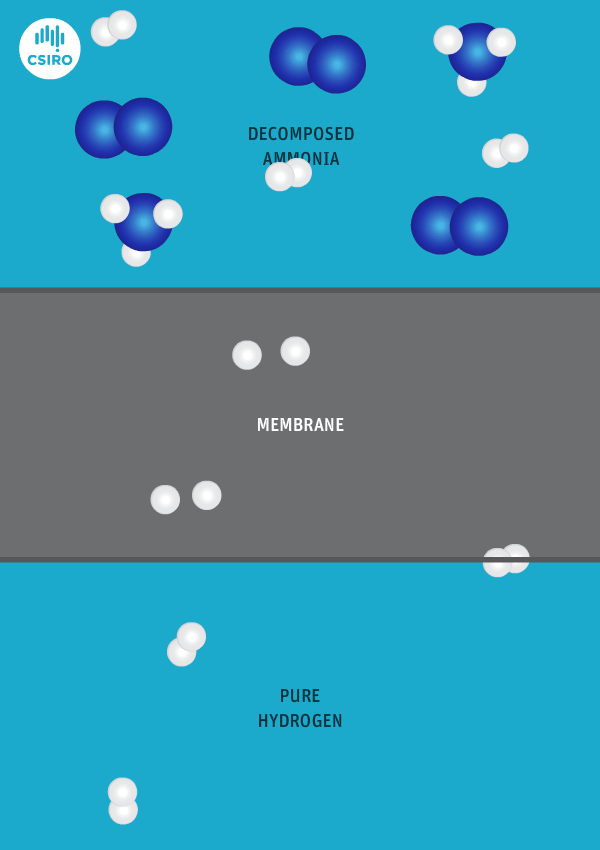
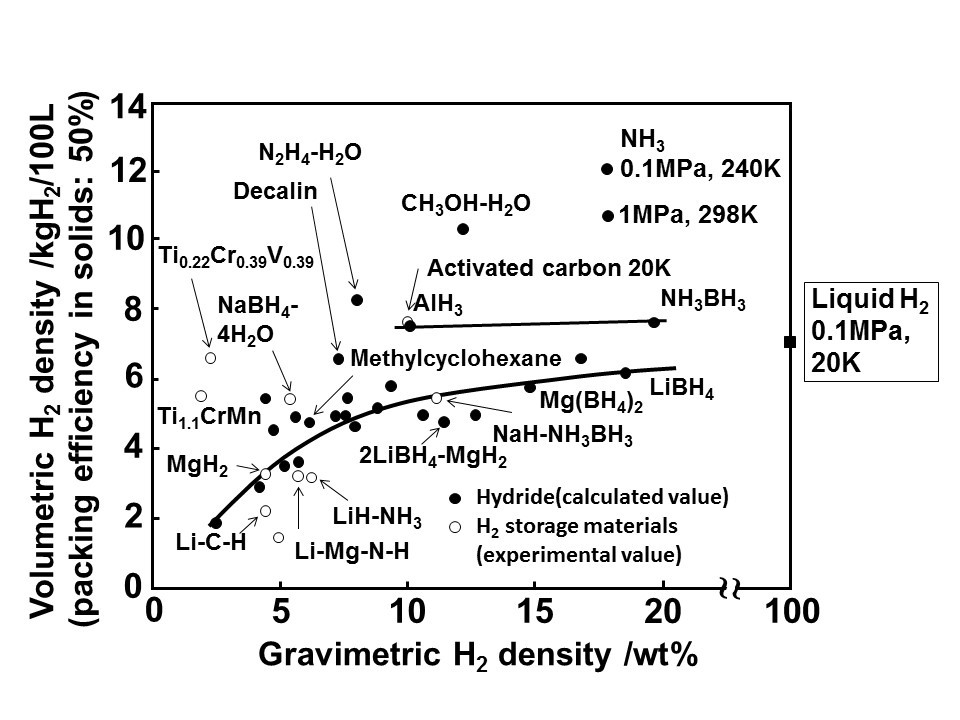
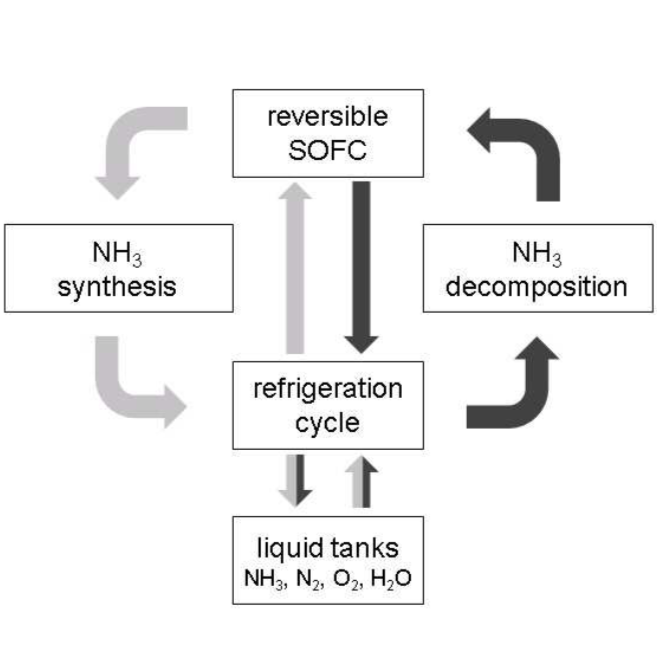
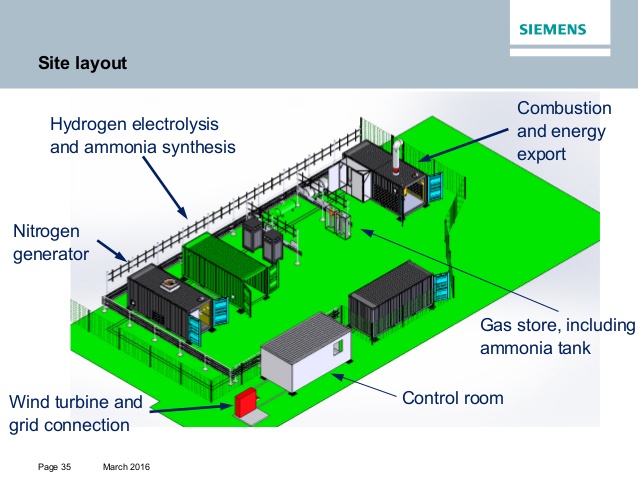
New Oxford research finds that over 60% of global shipping fuel demands could be met by renewable ammonia in 2050, which can be achieved by targeting renewable ammonia fuel supplies at the “top 10 regional ports”. The team also predicts that conventional maritime fuel production could be replaced by a more “regionalised industry”, producing up to 750 million tons of renewable ammonia per year in tropical and sub-tropical countries.