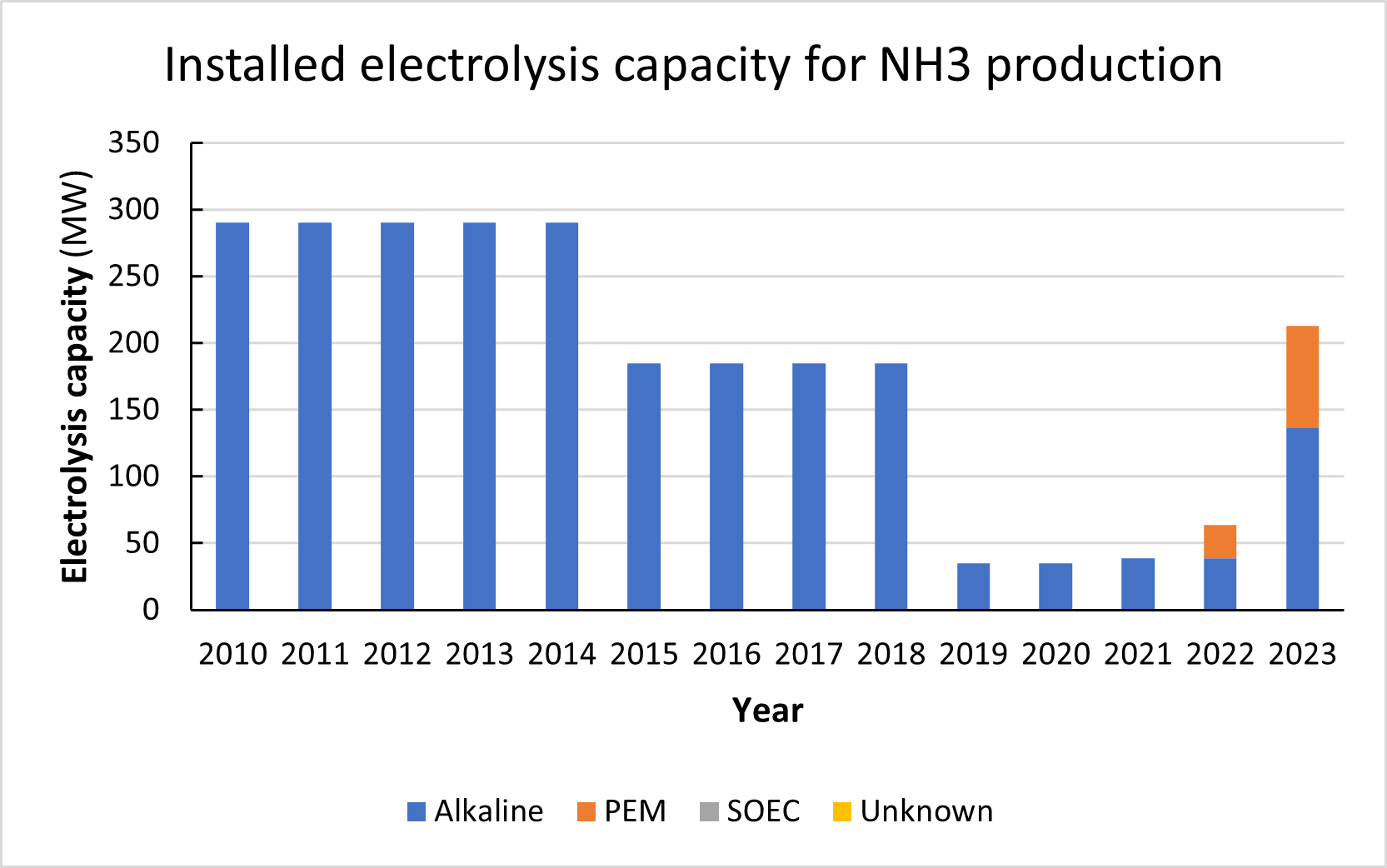
Electrolysis-based ammonia production peaked worldwide around 1970, before the economies of scale and cheap gas feedstock led to its decline. With decarbonization and climate-neutral industrial processes now a critical priority, electrolysis-based ammonia production has re-emerged as a long-term solution. From a base of 10,000 tonnes per year worldwide production in 2020, as much as 100 million tonnes per year of electrolysis-based ammonia could be produced by the end of this decade, driven by a dramatic roll-out of renewable energy generation and installed electrolyzer capacity.