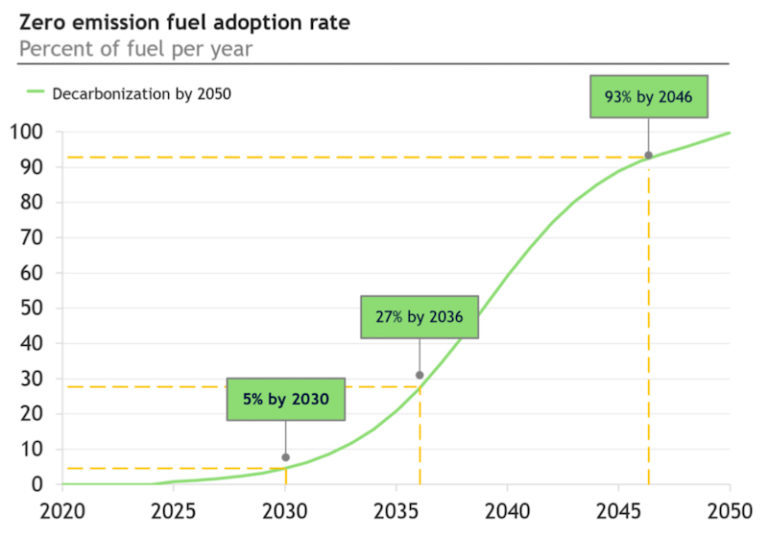
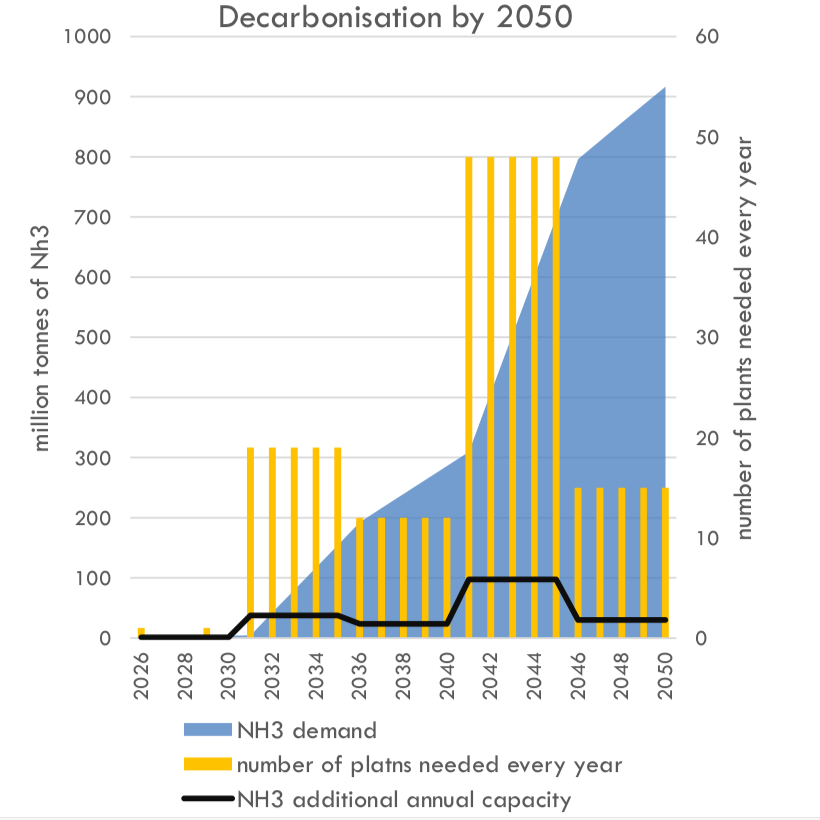
Based on their analysis, UMAS and the University College of London conclude that scalable e-fuels have the highest potential to meet shipping’s new decarbonization targets, but that the next decade is critical to ensure supply chains are ready to supply these fuels. Ammonia-LNG dual-fuel vessels represent the lowest-risk, cheapest decarbonization option to the mid 2030s.
Content Related to UMAS
Article
Setting the scene for ammonia maritime fuel: regulatory needs and timelines to decarbonize shipping
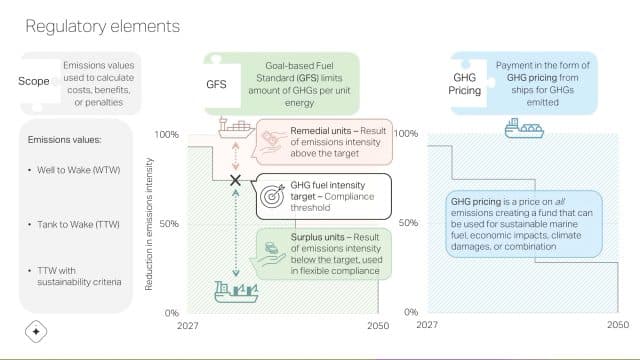
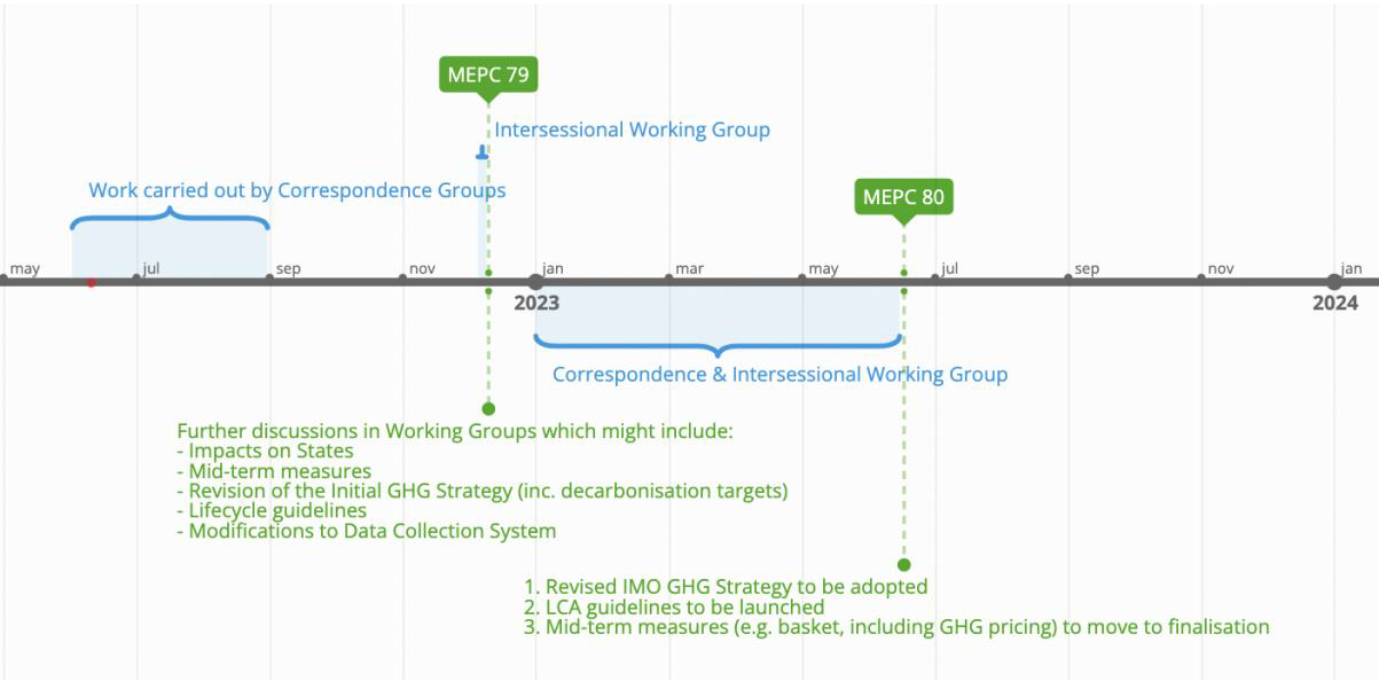
2025 is a critical year for the adoption of ammonia fuel in shipping. Here, we preview important upcoming meetings of the International Maritime Organization, what regulatory gaps are being filled by this work, potential candidates for decarbonization measures, and progress in engine development. All this sets the scene for incredible progress to be made in the coming years.
Article
Order book for alternative-fueled vessels grows in 2023
Julian Atchison January 16, 2024
Clarksons Research and DNV have provided their analysis of global ship orders for 2023. Last year saw the first orders for ammonia-fueled vessels, with container ships & car carriers dominating the order book for alternative fuel propulsion ships. But UMAS & the Global Maritime Forum warn that the current order book trajectory may only be a fifth of what is needed to achieve the IMO’s 2030 target for alternative fuel uptake.
Article
Harmonised certification – opportunities and challenges across different markets
Geofrey Njovu November 26, 2023
In this session at our 2023 annual conference, panelists explored the challenges and opportunities for designing certification schemes for different markets. Moderated by Madhav Acharya, the discussion featured Emily Wolf from Ambient Fuel, Claire Behar from Hy Stor Energy, Domagoj Baresic from the UCL Energy Institute and Patrick Hastwell from KBR.
Compliance with EU standards offers flexibility for producers and will facilitate the immediate scale-up of export markets, but progress towards an umbrella-style certification scheme remains in focus for the AEA. Broad-based certification schemes will help create new voluntary demand markets and avoid a sector-by-sector approach to developing certification.
Article
Maritime buyers alliance launches tender for zero-emissions shipping
Julian Atchison October 24, 2023
The Zero Emission Maritime Buyers Alliance has launched a tender process for container shipping powered by zero-emissions fuels. The twenty-member Alliance includes major global consumer brands, and is seeking bids to meet an aggregate demand of 600,000-plus TEUs over 3 years, with a book-and-claim approach to be used for fuel certification. The demand-side initiative comes as a new report from UMAS and the Getting to Zero Coalition finds the window of opportunity for the global shipping industry to meet its 2030 goals is closing.
Article
Reflections on the last meeting of the Marine Environment Protection Committee: the time is ripe for maritime ammonia
Conor Furstenberg Stott July 04, 2022
To develop sufficient ammonia supply to meet future maritime fuel demands, we face a herculean task. The recent meeting of the IMO’s Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC 78) gives us an insight into the key next steps to address financial & regulatory challenges. For the first time, MEPC 78 introduced the idea of a “Zero by 2050” goal for global shipping: a steep change in ambition. The use of funds from mechanisms like carbon pricing to ensure a fair, just and equitable transition, the necessity of high-impact investment to drive the fuel transition, and the adoption of new LCA guidelines in the next twelve months were also discussed. The drive & ambition shown at MEPC 78 indicates that the time is ripe for maritime ammonia to position itself as the fuel of choice for the global shipping industry.
Article
Closing the Gap for Zero-Emission Fuels
Sofia Furstenberg Stott March 27, 2022
In January 2022, UMAS and the Getting To Zero Coalition (GtZC) released a report with policy options for closing the competitiveness gap between conventional & future maritime fuels. Such measures will be necessary to enable an equitable transition to zero-emissions shipping. So how might these potential policy routes may impact and enable the scaling of maritime ammonia?
Article
The Ammonia Wrap: OCI to charter ammonia-fueled vessels, Japanese CCGT units await ammonia, more green ammonia for Chile, new South Korea and Uruguay updates
Julian Atchison March 10, 2021
Welcome to the Ammonia Wrap: a summary of all the latest announcements, news items and publications about ammonia energy. This week: OCI to charter ammonia-fueled vessels, new carbon-free maritime fuels forecast, Hokkaido Electric postpones CCGT deployment, awaits ammonia, more green ammonia for Chile, Net-zero Teesside to include CF Industries ammonia production, South Korea and Uruguay.
Article
Maritime decarbonization is a trillion dollar opportunity
Trevor Brown February 06, 2020
In January 2020, the Global Maritime Forum published new analysis that calculates "the capital investment needed to achieve decarbonization" in line with the International Maritime Organization's Initial GHG Strategy. The result of this analysis, which assumes that ammonia will be "the primary zero carbon fuel choice adopted by the shipping industry," is an aggregate investment of between $1 trillion and $1.4 trillion dollars, from 2030 to 2050, or roughly $50 to $70 billion per year across two decades. Ship-side costs are only 13% of this number. The bulk of the investment will be directed towards green ammonia plants for maritime fuel synthesis. By 2050, this global fuel demand is estimated to be more than 900 million tons per year of green ammonia, more than five time today's total global output of conventional ammonia.
Presentation
Fuel Transition Scenarios for the Maritime Industry up to 2050
This paper will present some of the University College London Energy Institute’s recent and ongoing work on likely fuel transition scenarios for the maritime industry, and discuss potential scenarios under which ammonia could become a substantial fuel for shipping (i.e. carbon price, developments vs hydrogen, costs, and non-market factors).
Article
Bunker Ammonia: new report quantifies ammonia as "the most competitive" fuel for zero-emission maritime vessels in 2030
Trevor Brown December 15, 2017
This week, Lloyd's Register published the most significant comparative assessment so far of ammonia's potential as a zero-emission maritime fuel. The new report compares ammonia, used in either internal combustion engines (ICE) or fuel cells, to other low-carbon technologies, including hydrogen, batteries, and biofuels, estimating costs for 2030. It concludes that, of all the sustainable, available options, ammonia "appears the most competitive."
Article
Bunker Ammonia: momentum toward a "sustainable and future-proof" maritime fuel
Trevor Brown June 15, 2017
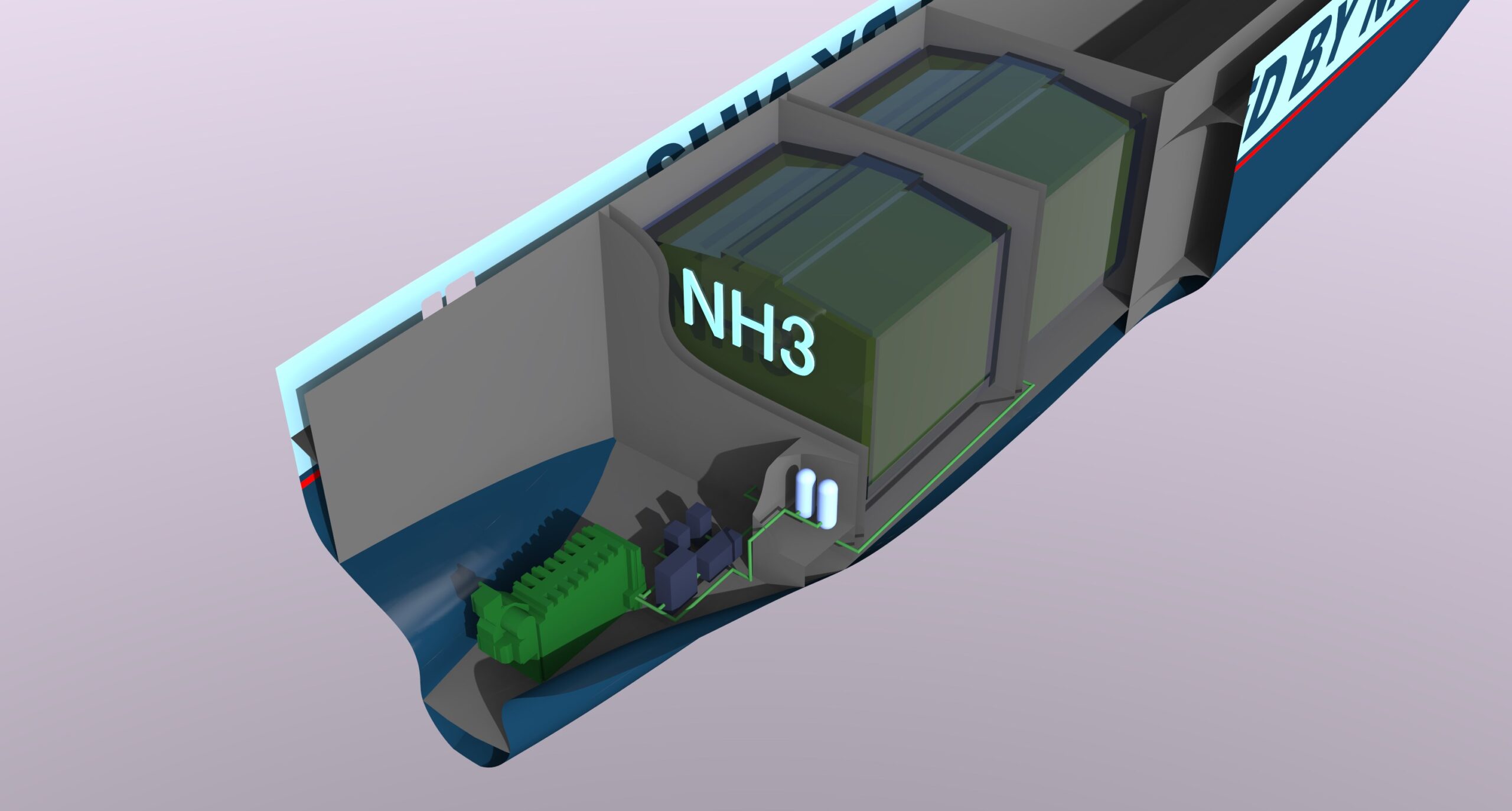
The maritime industry is beginning to show significant interest in using ammonia as a "bunker fuel," a sustainable alternative to the highly polluting heavy fuel oil (HFO) currently used in ships across the world. In recent months, a firm of naval architects and a new maritime think tank have both been evaluating ammonia as a fuel. This includes a road map for future research, and collaborations for a demonstration project that will allow them to design and build a freight ship "Powered by NH3."