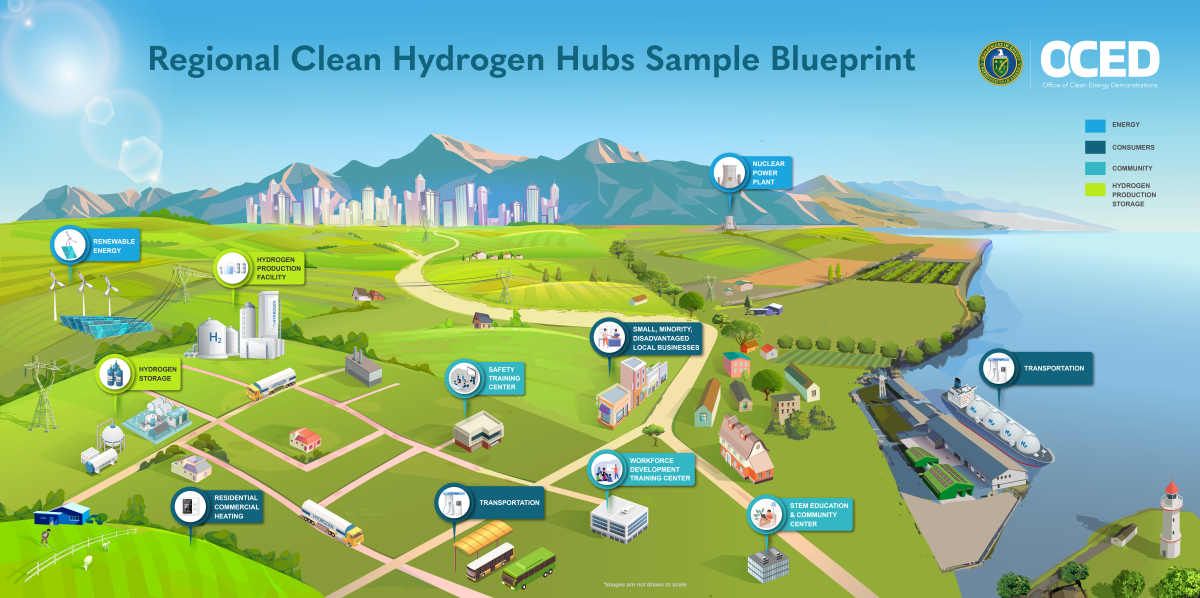
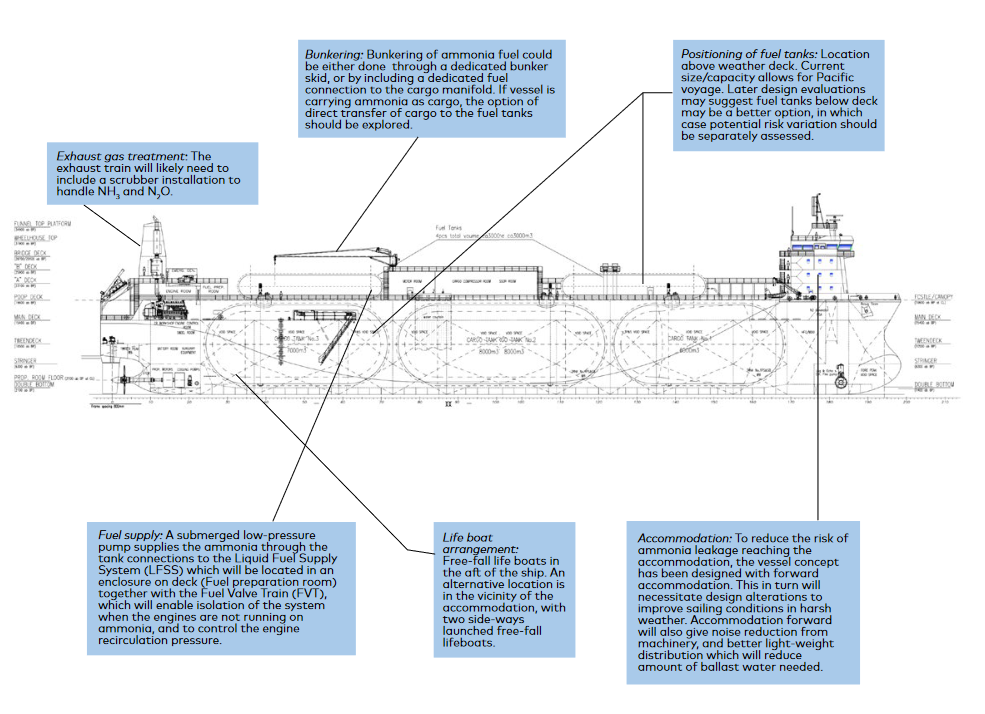
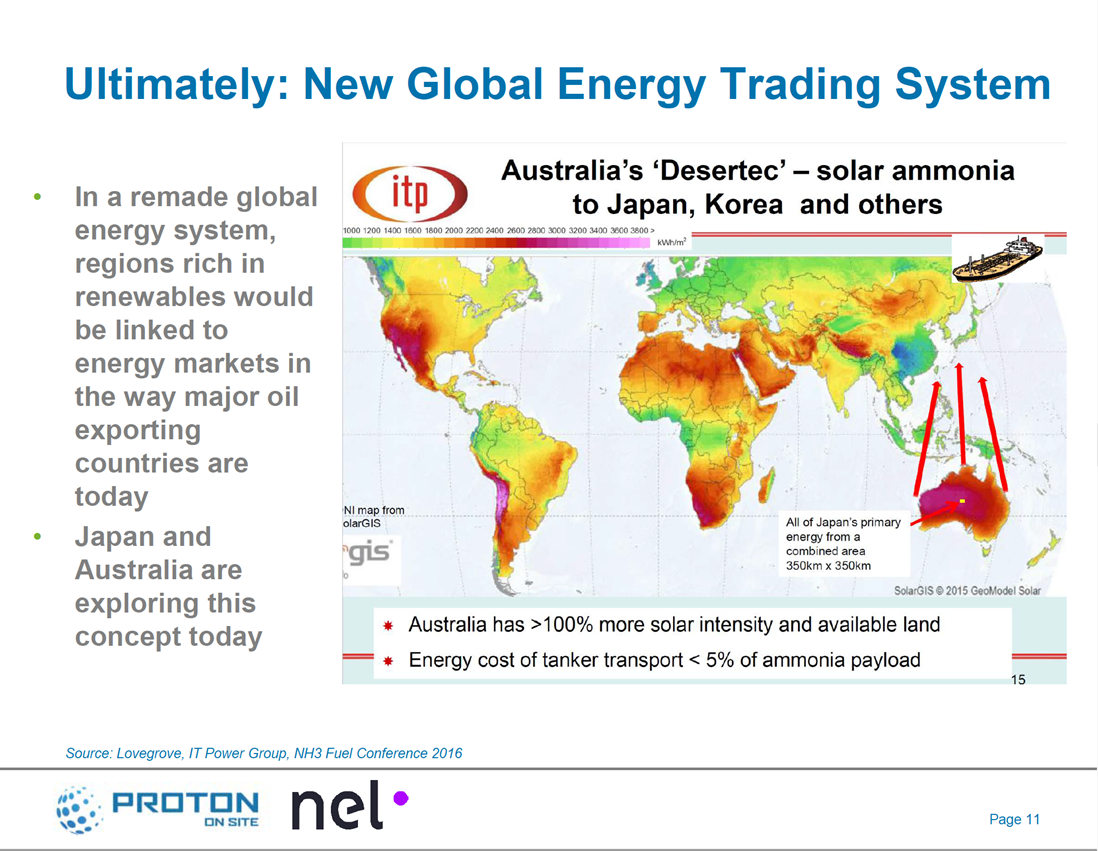
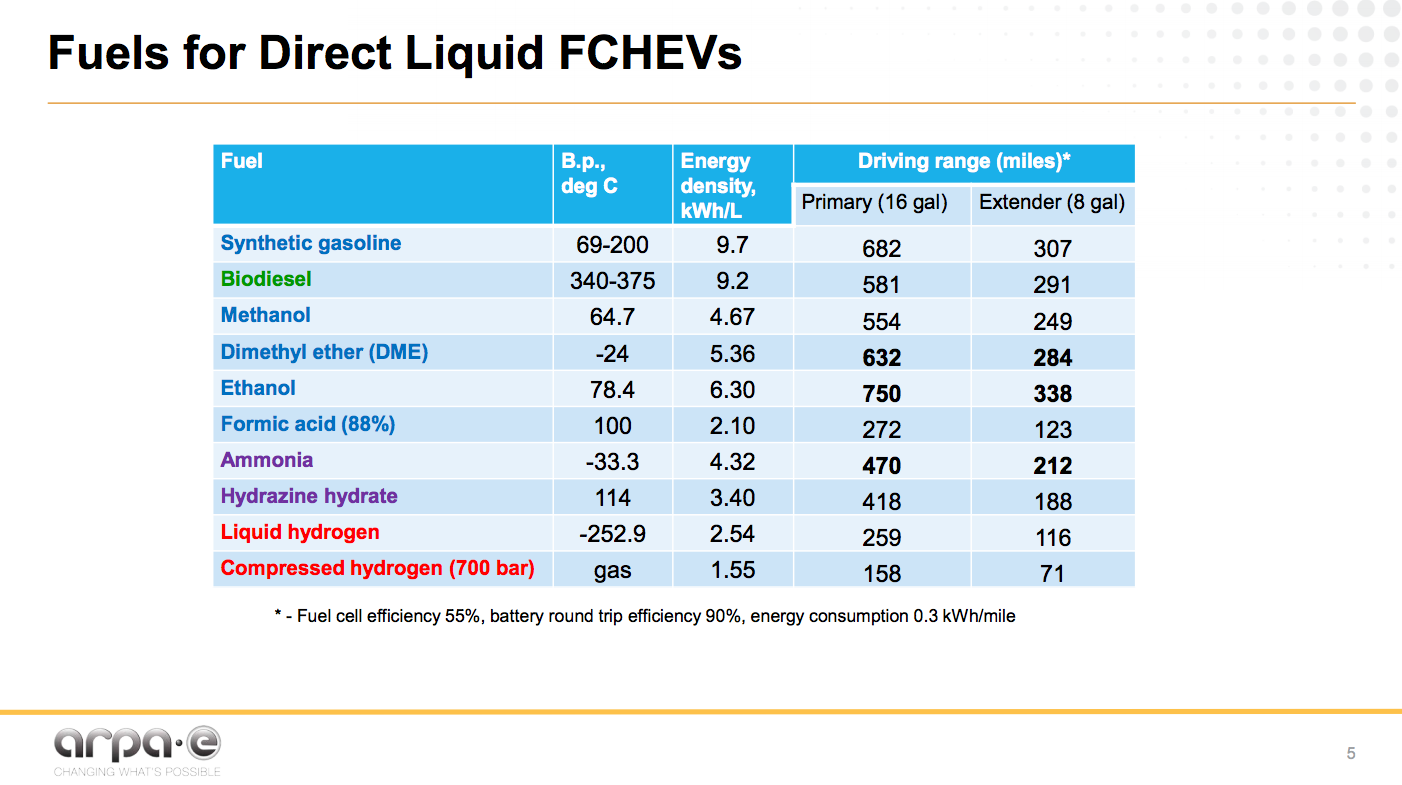
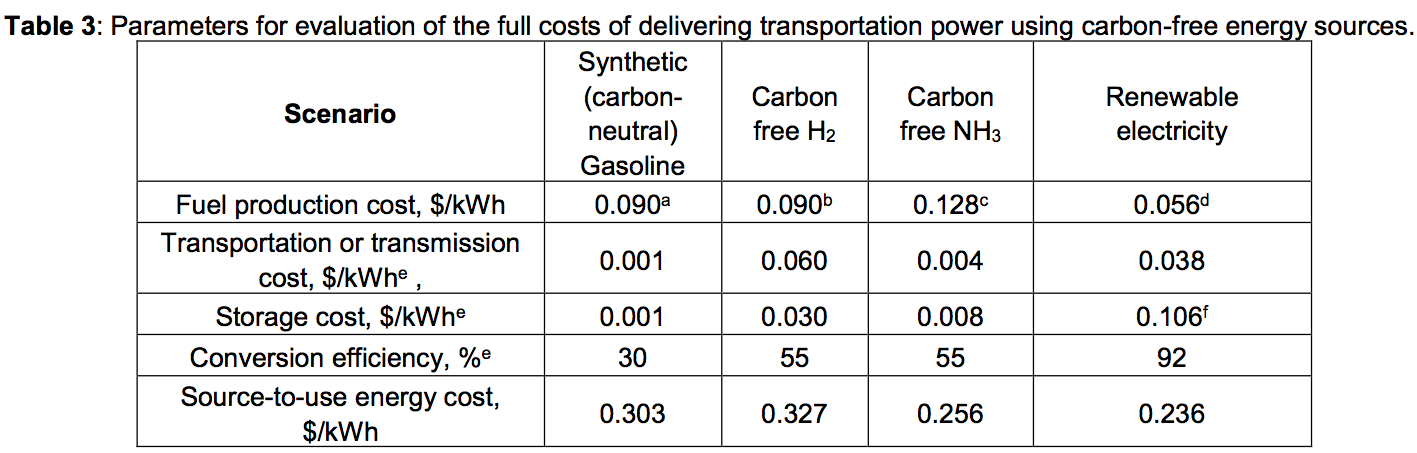
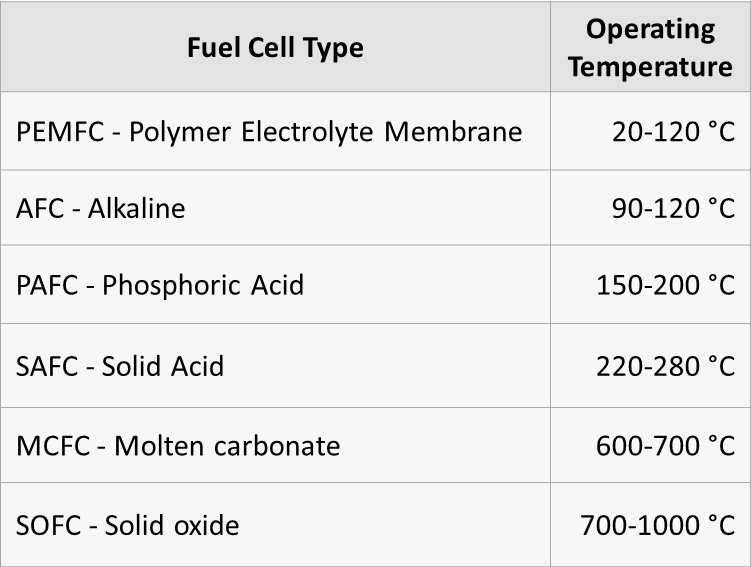
Following the passage of new legislation in the USA, the timeline has been set for hydrogen and ammonia producers to benefit from 45V tax credits. Construction on renewable hydrogen projects must begin by January 1, 2028, providing a short window of opportunity, particularly for the regional Hydrogen Hubs.
Content Related to US Department of Energy
Article
US funding for decarbonised ammonia production
Julian Atchison January 30, 2025
Via a new round of funding from the US Department of Energy, several ammonia production projects will advance. GTI Energy will lead a $1.5 million pre-FEED study to apply advanced CCS to steam methane reforming at the Mosaic Faustina facility in Louisiana. Also granted funds, Ammobia will continue to progress its new, improved version of the Haber Bosch process.
Article
Final tax credit rules for clean hydrogen production in the US released
Julian Atchison January 15, 2025
Long-awaited guidelines for tax credits for the production of “clean” hydrogen in the USA have been released, which include “significant changes” and additional flexibility compared to the first draft.
Article
Pathways to electrolysis success for USA, Australia
Julian Atchison December 16, 2024
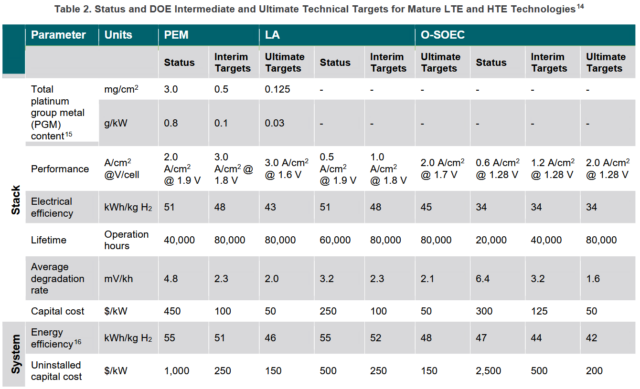
In order to achieve the aggressive Hydrogen Shot initiative goal of $1/kg production cost by 2030, the US Department of Energy sets out a series of performance and capital cost targets for established and lower-TRL electrolyser technologies. Meanwhile, Australia's national science agency CSIRO projects that Australia’s hydrogen electrolyser manufacturing sector could generate AU$1.7 billion in revenue annually by 2050.
Article
US Department of Energy: new action plans for decarbonizing transport
Julian Atchison December 16, 2024
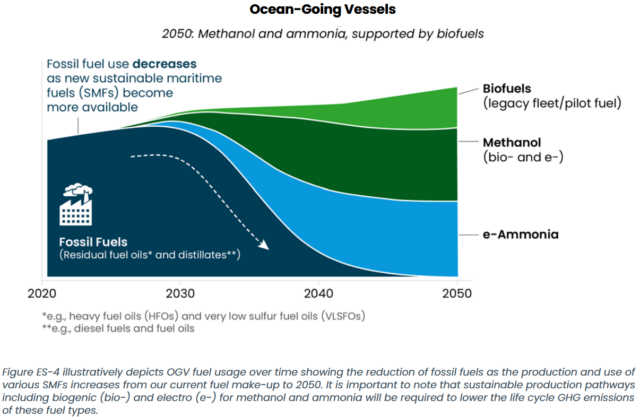
The marine action plan urges the federal government to prioritize the implementation of electrolytic ammonia and methanol fuel in ocean-going vessels by 2050. A detailed action roadmap is presented, including infrastructure deployment, retrofits and upgrades to existing vessels.
Article
US Hydrogen Hubs: two more consortia secure full funding
Julian Atchison December 01, 2024
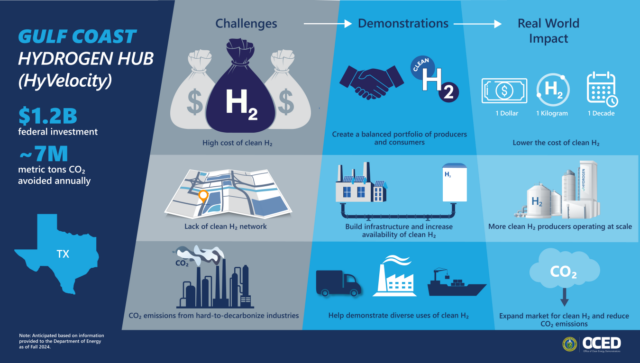
The US Department of Energy has concluded negotiations with two more Hydrogen Hub consortia, committing funding to the Gulf Coast Hydrogen Hub (up to $1.2 billion) and the Midwest Hydrogen Hub (up to $1 billion).
Article
Wabash Valley Resources to receive $1.6 billion in DoE support
Julian Atchison September 20, 2024
The US Department of Energy will provide up to $1.6 billion in loan guarantees for Wabash Valley Resources to finance their CCS-based ammonia production project in Terre Haute, Indiana. Once completed, the project would be Indiana’s only ammonia plant, producing low-emission fertilizer for use in the US Corn Belt.
Article
US Treasury proposes rules for 45V clean hydrogen
Julian Atchison January 08, 2024
For producers to qualify for 45V tax credits, the US Treasury has proposed a set of new rules for renewable hydrogen that closely align with EU standards. The three pillars approach already adopted by the EU is proposed, as is the use of Argonne National Laboratory’s GREET model for lifecycle emissions analysis.
Article
Impact of pre-certification on project finance
Geofrey Njovu November 26, 2023
In this session at our 2023 annual conference, panelists discussed how unified certification will help solve the chicken and egg relationship between offtake and project development. Moderated by Vibeke Rasmussen from Yara, the discussion featured Ed Davis from the Loan Program Office (US DoE), Tomoaki Ichida from Mitsui OSK Lines, Oleksiy Tatarenko from RMI and Dolf Gielen from the World Bank Group.
Long-term offtake will be made easier with unambiguous, harmonised certification standards, which will in turn have a positive impact on ammonia projects reaching financial close. Certification schemes like the one under-development by the AEA are sorely needed to break the impasse between project development and offtake.
Article
US hydrogen hubs revealed: coast-to-coast projects to anchor new industry
Julian Atchison October 16, 2023
The US Department of Energy has selected seven hydrogen hub applications to proceed to a funding negotiation stage, with $7 billion to be split between them. Fertiliser, power generation, industrial decarbonisation and heavy vehicle transport are all target markets for the new hubs, with locations to range from the Gulf Coast, Appalachia, the Midwest to the Californian coast.
Article
DoE launches $1 billion, demand-side scheme to complement Hydrogen Hubs
Julian Atchison July 06, 2023
The US Department of Energy has launched a new scheme to help “catalyze durable, bankable demand” for clean hydrogen & ammonia production. A request for information notice seeks feedback on potential demand-side measures the US government could implement to complement the regional Hydrogen Hubs program.
Article
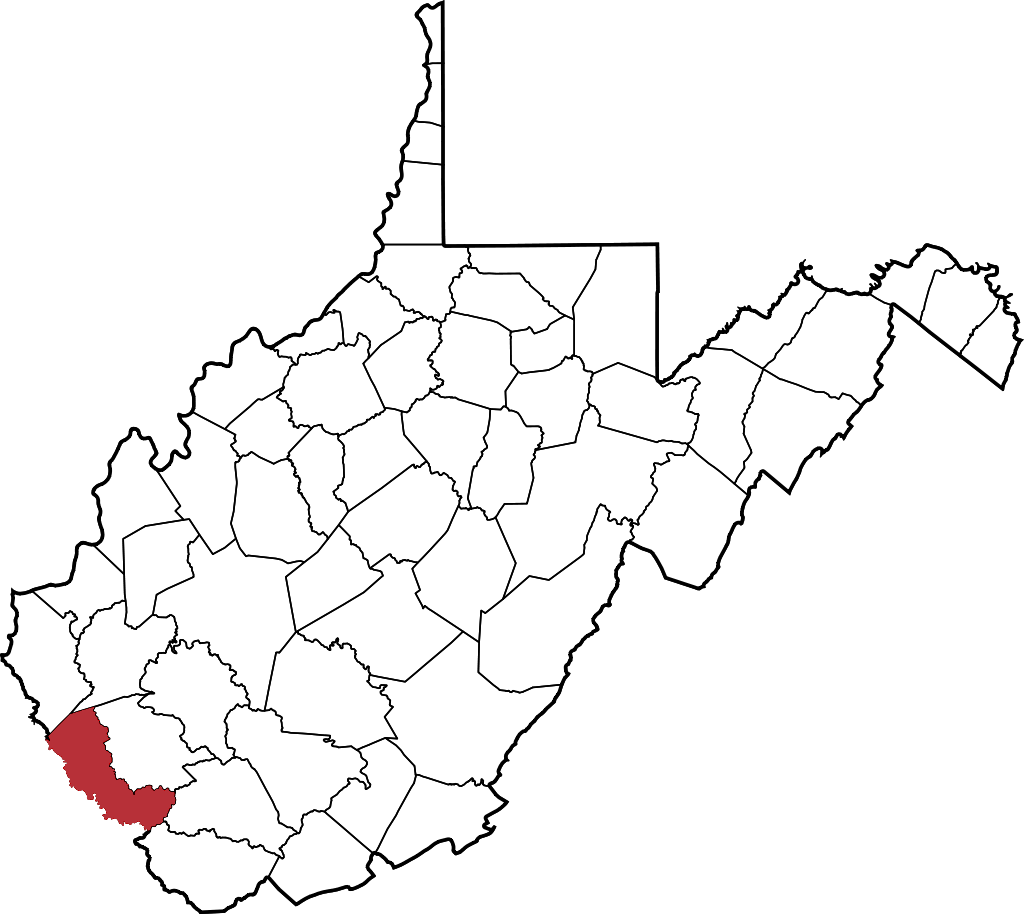
Clean ammonia production in West Virginia
Julian Atchison April 11, 2023
The Adams Fork Energy clean ammonia project will produce up to 2.16 million tonnes per year of ammonia, based on gas feedstock and CCS. The project will serve as the anchor for the Appalachian Regional Clean Hydrogen Hub, one of a number of applications being considered by the US Department of Energy for funding as part of a $7 billion jump-start program.
Article
$7 billion in funding, new roadmap for the US hydrogen industry
Julian Atchison October 06, 2022
The Biden administration has launched a $7 billion funding program to create regional clean hydrogen hubs across the US. Between six and ten applications will be selected, drawing on a diverse range of geographical locations, technology pathways and end-use applications. Alongside the funding announcement, the Department of Energy launched a draft of a new national hydrogen roadmap, outlining the key opportunities on offer for the emerging US clean hydrogen industry.
Article
Monolith Materials: new deal with Goodyear, $1 billion loan from DoE
Julian Atchison January 12, 2022
Monolith and Goodyear Tire & Rubber (the only US-headquartered tire manufacturer) will cooperate on the potential use of carbon black byproduct from its Olive Creek ammonia plant in Hallam, Nebraska. In relevant news, a $1.04 billion, Title XVII loan from the US Department of Energy has secured Monolith's expansion plans for Olive Creek, which will see it become the largest producer of carbon black in the US by 2025.
Article
Hydrogen & ammonia developments in the USA
Julian Atchison September 01, 2021
This week: Mitsui & Co., CF Industries team up to explore blue ammonia opportunities (and to link up US and Japan), CCS hydrogen in Pennsylvania, and the Infrastructure Bill.
Article
The Ammonia Wrap: no major obstacles for NoGAPS success and more
Julian Atchison June 08, 2021
Welcome to the Ammonia Wrap: a summary of all the latest announcements, news items and publications about ammonia energy. This week: latest report from NoGAPS, Viking Energy project takes another step, more collaborations for Yara, thyssenkrupp to invest in cracking R&D, investment in clean hydrogen technology in the USA, world-first visualisation of ammonia combustion in a spark-ignition engine and our numbers of the week.
Article
The Ammonia Wrap: commercial turbines, another GW of green ammonia, Viking Energy updates, and "any-fuel" high-temp PEM fuel cells
Julian Atchison March 04, 2021
Welcome to the Ammonia Wrap: a summary of all the latest announcements, news items and publications about ammonia energy. This week: commercialised ammonia gas turbines, TDK and GenCell join forces, another GW of green ammonia production, small-scale green ammonia in rural Japan, hydroelectric ammonia in Laos, Viking Energy vessel updates, new partnerships for Haldor Topsoe and "any-fuel" high-temp PEM fuel cells.
Article
Government Investments in Hydrogen: How Does Your Country Compare?
Stephen H. Crolius October 11, 2019
On September 3, the British renewable-energy news portal reNEWS.BIZ ran a story with an intriguing headline: “Scotland launches £3bn green project portfolio.” At first glance, that number (which equates to USD $3.7 billion) looks out of scale with Scotland’s relatively tiny population of 5.5 million. Close reading reveals that the £3 billion is not the amount that will be invested by the Scottish government, but rather the value of the “investment portfolio” of green businesses the program is intended to galvanize over the next three years. But still one wonders, how does £3 billion stack up against other national programs aimed at supporting the sustainability transition?
Article
Japan, U.S., E.U. Agree to Cooperate on Hydrogen
Stephen H. Crolius August 01, 2019
On June 18, Japan, the United States, and the European Union released a joint statement on “future cooperation in hydrogen and fuel cell technologies.” Represented, respectively, by the Ministry of Energy, Trade, and Industry (METI), the Department of Energy (DoE), and the Directorate-General for Energy (ENER), the jurisdictions pledged “to accelerate the development of sustainable hydrogen and fuel cell technologies in the world.” A central point of agreement in the statement is “the importance of reducing the cost of hydrogen.”
Article
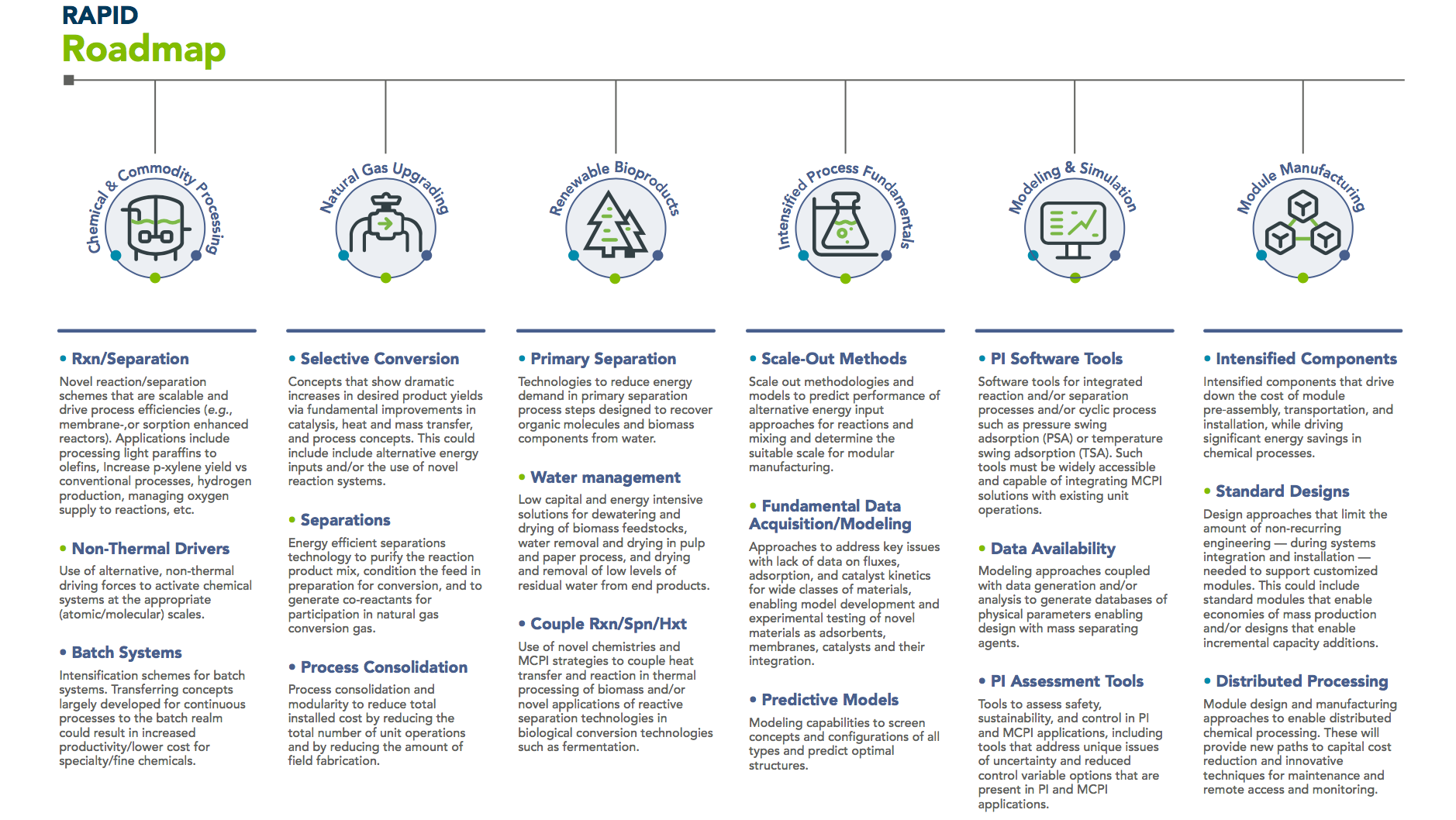
RAPID: supporting modular manufacturing and process intensification for small-scale ammonia
Joel Maul March 04, 2019
Using greener feedstocks at low pressures and temperatures, with higher conversion rates and less greenhouse gases is considered a pipe dream. The technology and equipment simply wasn’t available ... until now. The case for small-scale, energy efficient ammonia production is well documented, but access to funds may not be. Now, Manufacturing USA and the Manufacturing Extension Partnership may offer a new path to success.
Article
H2@Scale in California: A Role for Ammonia?
Stephen H. Crolius January 25, 2018
The U.S. Department of Energy H2@Scale program’s November 2017 workshop in California included mention of ammonia as a constituent of a future hydrogen economy. It also highlighted the relevance ammonia energy could have in California. California stands out globally as a large economy that is strongly committed to development of a hydrogen economy. The state’s strategy for hydrogen-powered transportation involves reducing the production cost of renewable hydrogen and the capital and operating costs of hydrogen fueling stations. It does not explicitly address the cost of intermediate hydrogen logistics. The question of cost is of utmost importance because California has so far put $120 million of public funds into hydrogen fueling stations and intends to invest an additional $20 million per year through 2022. The state’s aspiration is to move to a point where hydrogen that is used as a motor fuel is free of public subsidy. So it clearly behooves the state to investigate how ammonia could be used as a cost-reducing energy carrier. Toyota is active in California’s hydrogen movement and has announced plans to build a renewable hydrogen plant that will use cow manure as a feedstock. A project with a different conception, one that draws upon the solar and wind resources of the Mojave Desert to produce renewable hydrogen and logistically advantaged ammonia, would align better with the state’s sustainability objectives.
Article
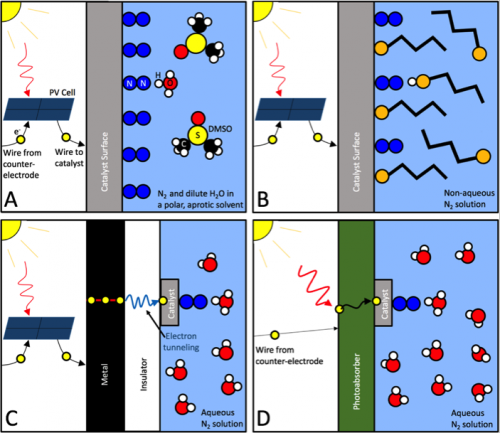
Future Ammonia Technologies: Electrochemical (part 3)
Trevor Brown December 28, 2017
This series of articles on the future of ammonia synthesis began with a report on the NH3 Energy+ conference presentation by Grigorii Soloveichik, Program Director at the US Department of Energy's ARPA-E, who categorized the technologies as being either improvements on Haber-Bosch or electrochemical (with exceptions). ARPA-E invests in "transformational, high-risk, early-stage research," and recently began funding ammonia synthesis technologies, not to make renewable fertilizer but to produce "energy-dense zero-carbon liquid fuel." This article will introduce the six electrochemical technologies currently in development with funding from ARPA-E.
Article
Future Ammonia Technologies: Electrochemical (part 2)
Trevor Brown December 27, 2017
Last week, in Part 1 of this series on electrochemical ammonia synthesis technologies, I quoted a recent article by researchers at MIT that identified avenues for future research and development. One option was a biomimicry approach, learning from "enzymatic catalysts, such as nitrogenases," which can "either be incorporated into or provide inspiration for the design of electrocatalytic processes." The nitrogenase enzyme, nature's ammonia synthesis technology, was developed in an iterative innovation process, otherwise known as evolution, that took hundreds of millions of years to reach this level of efficiency. According to one group of electrochemists, who presented their results at the recent NH3 Energy+ conference, nitrogenase produces ammonia in nature with an enviable 75% process efficiency - so it's no surprise that they are basing their industrial technology on it.
Article
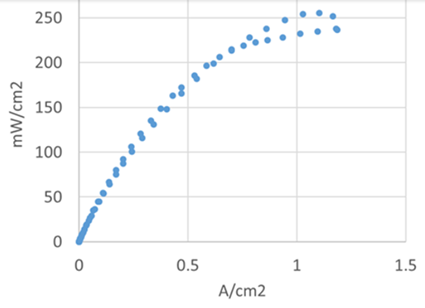
Progress for Low-Temperature Direct Ammonia Fuel Cells
Stephen H. Crolius December 14, 2017
Speaking at the NH3 Energy+ Topical Conference last month, University of Delaware Adjunct Professor Shimshon Gottesfeld reported on progress made by the university’s direct ammonia fuel cell (DAFC) project. Evidently, the UDel team is now a big step closer to its goal of establishing the DAFC as a viable automotive power plant.
Article
Improvement of Haber-Bosch: Adsorption vs. Absorption
Trevor Brown December 01, 2017
At the recent NH3 Energy+ Topical Conference, Grigorii Soloveichik described the future of ammonia synthesis technologies as a two-way choice: Improvement of Haber-Bosch or Electrochemical Synthesis. Two such Haber-Bosch improvement projects, which received ARPA-E-funding under Soloveichik's program direction, also presented papers at the conference. They each take different approaches to the same problem: how to adapt the high-pressure, high-temperature, constant-state Haber-Bosch process to small-scale, intermittent renewable power inputs. One uses adsorption, the other uses absorption, but both remove ammonia from the synthesis loop, avoiding one of Haber-Bosch's major limiting factors: separation of the product ammonia.
Presentation
Future of Ammonia Production: Improvement of Haber-Bosch Process or Electrochemical Synthesis?
Ammonia, the second most produced chemical in the world (176 million tons in 2014), is manufactured at large plants (1,000 – 1,500 t/day) using Haber-Bosch process developed more than hundred years ago. A simple reaction of nitrogen and hydrogen (produced by steam methane reforming or coal gasification) consumes about 2% of world energy, in part due to the use of high pressure and temperature. With the global transition from fossil fuels to intermittent renewable energy sources there is a need for long term storage and long range transmission of energy, for which ammonia is perfect fit. To make it practical,…
Article
ARPA-E talks advanced hybridization, carbon-neutral liquid fuels
Stephen H. Crolius October 26, 2017
In the race to place the automotive sector on a sustainable footing, the field is dominated by just two horses: battery-electricity and hydrogen fuel cells. The economic implementation of BEVs is already well underway, with motor companies on track in 2017 to sell more than a million vehicles globally for the first time. The economic implementation of FCVs is also in progress, albeit at a much earlier stage, and has the backing of major motor companies and public-sector agencies. Given the huge leads enjoyed by electricity and hydrogen, ammonia is scarcely seen as a contending fuel. Earlier this month, though, the U.S. Department of Energy’s ARPA-E unit published an interview with two of its program managers that has an intriguing implication: the race is far from over and ammonia may yet break to the front of the pack.
Article
NH3 Fuel Association announces New Sponsor; Evening Reception at AIChE Annual Meeting on November 1st
Trevor Brown October 11, 2017
The NH3 Fuel Association has finalized details of its Sponsors Reception on Wednesday November 1 at the AIChE Annual Meeting in Minneapolis, and has also announced an additional sponsor for the conference: Starfire Energy.
Article
Overcoming the Selectivity Challenge in Electrochemical Ammonia Synthesis
Trevor Brown October 06, 2017
In the last 12 months ... The research community has made great progress toward solving the "selectivity challenge" in electrochemical ammonia synthesis. Although, rather than an actual solution, mostly what we have is a range of sophisticated work-arounds that succeed in making this problem moot.
Article
Development of Direct Ammonia Fuel Cells
Trevor Brown October 05, 2017
In the last 12 months ... Researchers from three continents have pushed the boundaries for direct ammonia fuel cells, setting records in power generation and continuous operation.
Article
Ammonia Energy Gains Recognition from U.S. Department of Energy
Stephen H. Crolius October 05, 2017
In the last 12 months ... Ammonia energy has gained recognition from the United States Department of Energy, in both bottom-up and top-down programs. This establishes ammonia energy in the world’s largest economy as a legitimate target for both public- and private-sector investment.
Article
Japan-Brunei MCH Energy Carrier Demonstration
Stephen H. Crolius August 02, 2017
Chiyoda Corporation, the multinational chemical engineering firm that is arguably the leading proponent of the methyl cyclohexane (MCH) method of hydrogen transport, will start work this month on a project to demonstrate MCH technology in a real-world context. As reported in a July 27 company press release, the project will involve the transportation of hydrogen from Brunei to Japan in what the company states is "the world's first global hydrogen supply chain demonstration project" -- an assertion that many ammonia energy proponents will no doubt find preposterous.
Article
REFUEL Is Back on Track
Stephen H. Crolius June 28, 2017
The U.S. Department of Energy’s ARPA-E REFUEL Program, whose continued existence seemed to be in doubt two months ago, now appears to be back on track. Invitations were sent a week ago for the ARPA-E REFUEL Program Kickoff, an event that was originally scheduled for April 25 and 26 in Houston. It is now scheduled to take place in Denver on August 16, 17, and 18. Attendance will be by invitation only.
Article
Ammonia Energy at the H2@Scale Workshop
Stephen H. Crolius June 08, 2017
“Carbon-free ammonia needs to be a significant contributor to the H2@Scale initiative.” This was one of the “key takeaways” offered by Steve Szymanski, Director of Business Development at the hydrogen generator company Proton On-Site, during his presentation at the H2@Scale Workshop that was held on May 23-24 at the University of Houston in the U.S. By the time Szymanski left the podium, ammonia energy had moved a good distance from the periphery of the H2@Scale conceptual map toward its center.
Article
The new generation of fuel cells: fast, furious, and flexible
Trevor Brown April 12, 2017
At ARPA-E's recent Energy Innovation Summit in Washington, DC, Program Director Grigorii Soloveichik presented his vision for the future of transportation: hybrid electric vehicles that combine the advantages of both plug-in battery and fuel cell technologies. This "optimal solution" will require a new generation of fuel cell that is "fast, furious, and flexible." Fast, in terms of start-up / shut-down time. Furious, in terms of energy density. And flexible, in terms of fuel choice - specifically sustainable liquid fuels, like ammonia.
Article
Ammonia for energy storage: a "revolutionary disruption"
Trevor Brown March 16, 2017
A recent opinion piece in The Japan Times predicts a "revolutionary disruption coming to the energy sector," and suggests that using ammonia for energy storage will prove to be "a game-changer at least on the scale of the shale oil and gas revolution."
Article
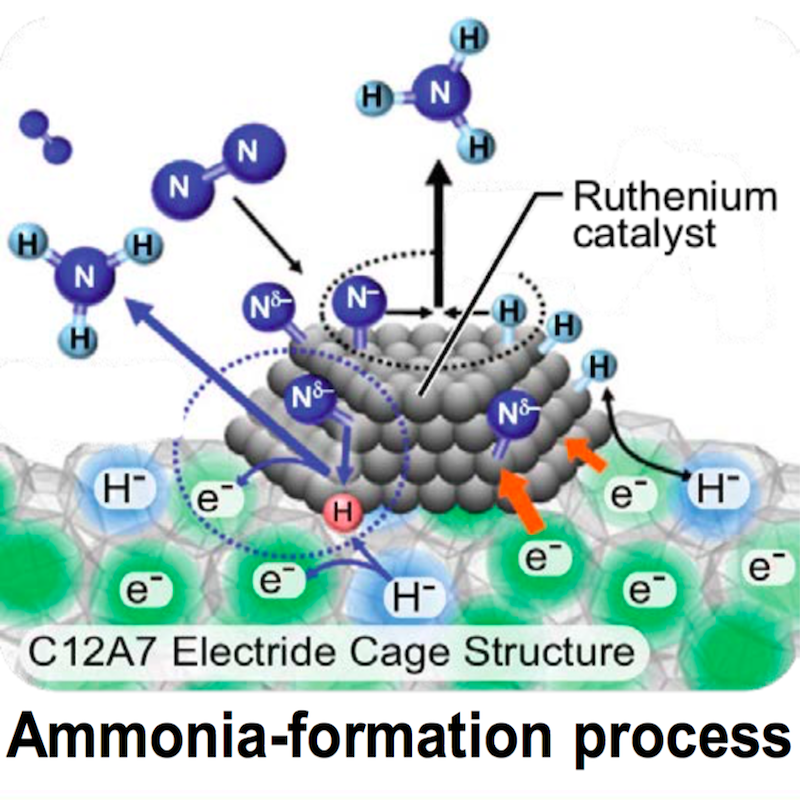
US DOE funding research into sustainable ammonia synthesis
Trevor Brown January 27, 2017
The US Department of Energy (DOE) is currently supporting six fundamental research projects that will develop "novel catalysts and mechanisms for nitrogen activation," which it hopes will lead to future sustainable ammonia synthesis technologies. These projects, announced in August 2016 and administered by the Office of Basic Energy Sciences, aim "to investigate some of the outstanding scientific questions in the synthesis of ammonia (NH3) from nitrogen (N2) using processes that do not generate greenhouse gases."
Article
ARPA-E's vision for carbon neutral liquid fuels
Trevor Brown January 11, 2017
We wrote last month about the US Department of Energy funding ammonia fuel projects through ARPA-E's "REFUEL" program ("Renewable Energy to Fuels through Utilization of Energy-dense Liquids"). Although we introduced the funded projects in both the ammonia synthesis category and the ammonia fuel-use category, the REFUEL project merits further analysis as a whole because it describes a roadmap for the development of ammonia fuel systems, and identifies benchmarks for their commercial success.
Article
REFUEL Ammonia Use-Side Funding Awards
Stephen H. Crolius December 23, 2016
Six of the projects designated for funding by the ARPA-E REFUEL announcement on December 15 involve technologies on the use side of the ammonia energy space. Three focus on generating hydrogen from ammonia. Two focus on fuel cells that convert ammonia to electricity. One project involves both ammonia synthesis and use.
Article
ARPA-E funding for renewable ammonia synthesis technologies
Trevor Brown December 23, 2016
Last week, ARPA-E announced funding for eight technologies that aim to make ammonia from renewable electricity, air, and water. The technological pathways being developed include adaptations of the Haber-Bosch process - seeking improvements in catalysts and absorbents - as well as novel electrochemical processes.
Article
Grand Challenges in Sustainable Ammonia Synthesis - DOE Roundtable Report, 2016
Trevor Brown December 08, 2016
Earlier this year, the US Department of Energy (DOE) hosted a day-long meeting "to explore the scientific challenges associated with discovering alternative, sustainable processes for ammonia production." The report that came out of this roundtable discussion presents the participants' views on "the current state-of-the-art and the potential challenges and research opportunities ... for heterogeneous catalysis and homogeneous and enzyme catalysis."
Article
ARPA-E’s “transformative” ammonia synthesis technologies
Trevor Brown October 28, 2016
The US Department of Energy's Advanced Research Project Agency (ARPA-E) is funding projects with a view to commercializing low- and zero-carbon ammonia synthesis technologies. Grigorii Soloveichik, ARPA-E Program Director, described the aims and challenges of his agency's initiative and introduced the technologies currently in development in his keynote presentation at the recent NH3 Fuel Conference, in September 2016.
Article
H2 @ Scale: US DOE's Request for Information
Stephen H. Crolius October 07, 2016
The ammonia energy community has an opportunity to provide input to the United States Department of Energy (USDOE) as it defines priority areas for its new "H2 @ Scale" initiative. The USDOE posted a Request for Information (RFI) on September 9. Interested parties are invited to comment on all aspects of the H2 @ Scale concept. The deadline for comments is November 4. A link to the RFI is provided below.
Article
US DOE: The REFUEL Project
Stephen H. Crolius September 19, 2016
In April 2016, the United States Department of Energy (DOE) released a Funding Opportunity Announcement (FOA) for its Renewable Energy to Fuels through Utilization of Energy-dense Liquids (REFUEL) program. The focus of the program is carbon-neutral liquid fuels (CNLFs). In the DOE’s formulation, CNLFs are to be produced “from air and water using electrical or thermal energy from renewable sources.”
Presentation
Ammonia for Energy Storage and Delivery
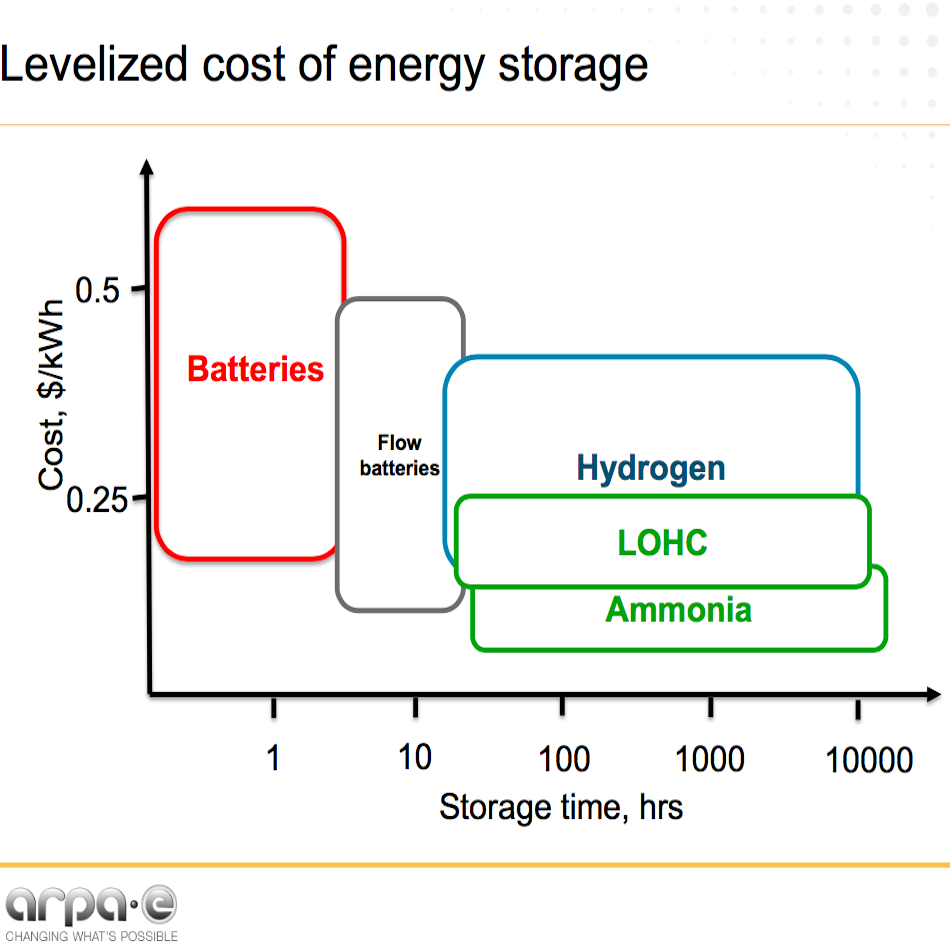
The Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA-E) funds high risk, high reward transformational research to reduce energy related emissions, reduce imports of energy from foreign sources, improve energy efficiency across all economic sectors, and ensure US technological lead in advanced energy technologies, including electrochemical energy storage and transformation for grid scale and automotive applications. Storing energy in the form of liquid fuels has numerous advantages compared to conventional methods of energy storage (ES) such as batteries (high cost, short cycle life), pumped hydro and compressed air (low energy density). Low costs of storage and transportation of liquid fuels enables long-time ES…
Presentation
Potential Roles of Ammonia in a Hydrogen Economy: Public Opinion and Input
Potential Roles of Ammonia in a Hydrogen Economy: Public Opinion and Input George Thomas, US DOE/Sandia National Laboratories (ret.) and George Parks, ConocoPhillips