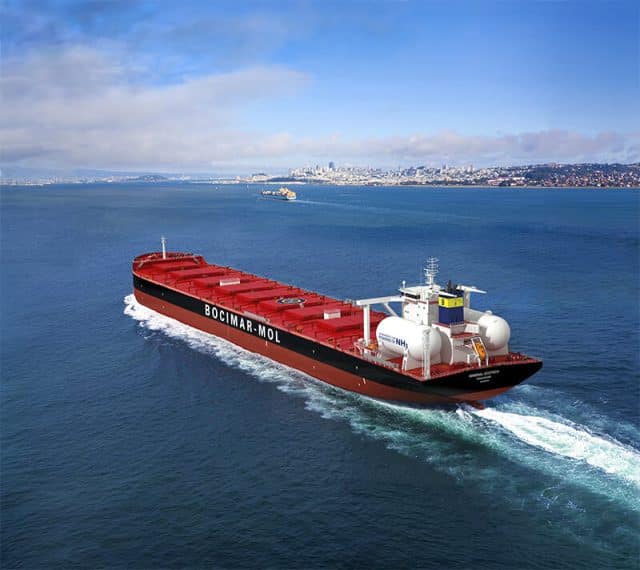
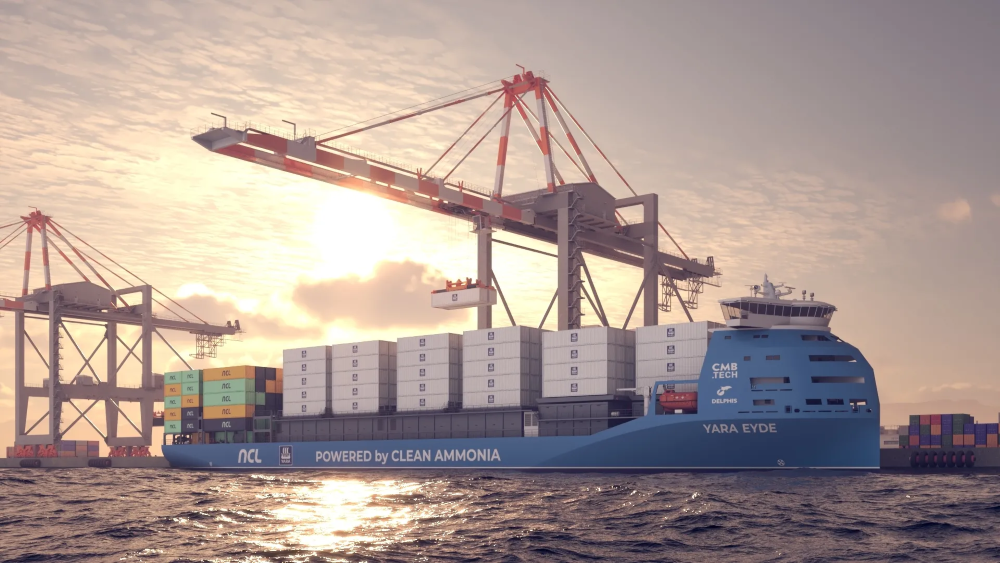
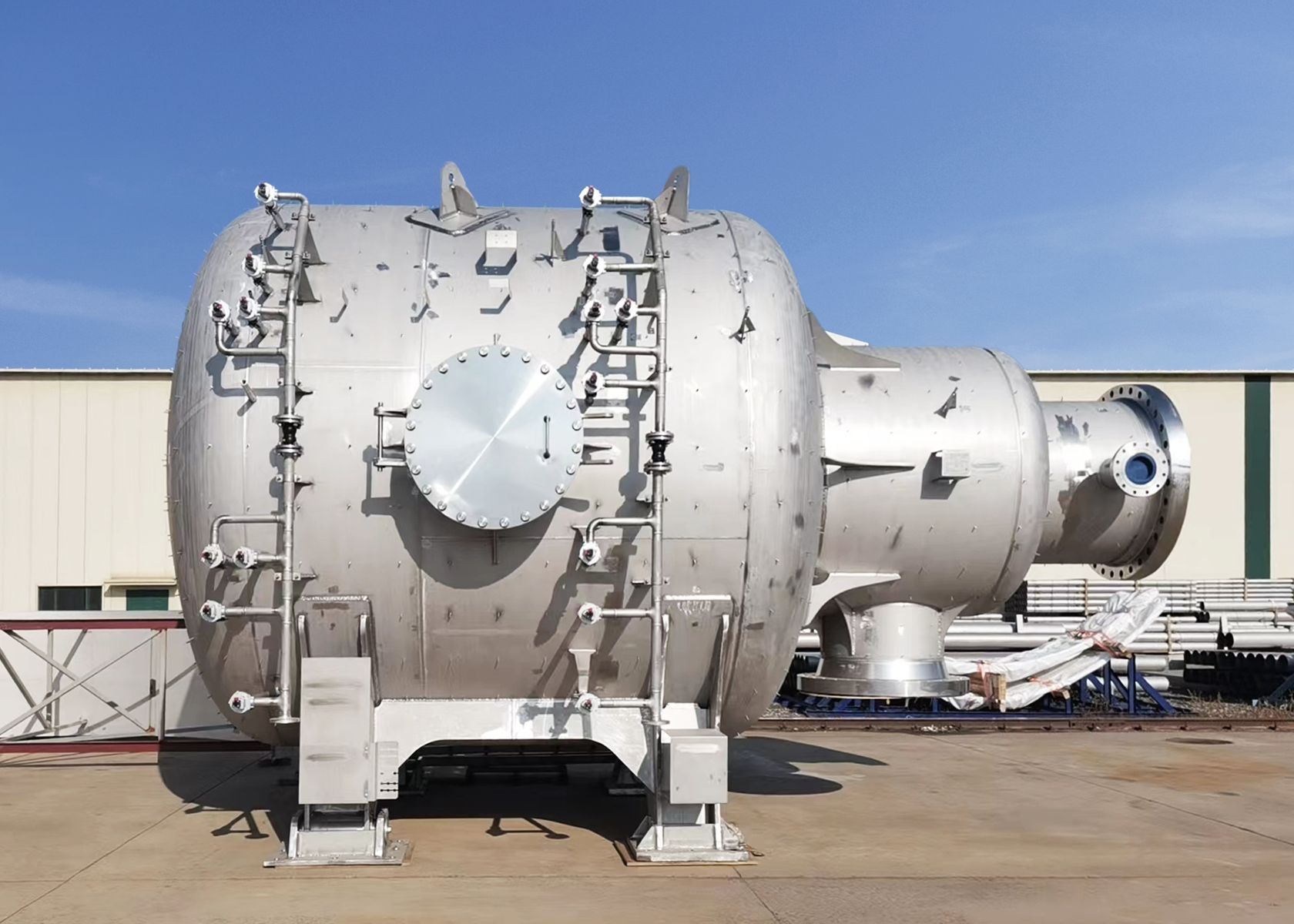
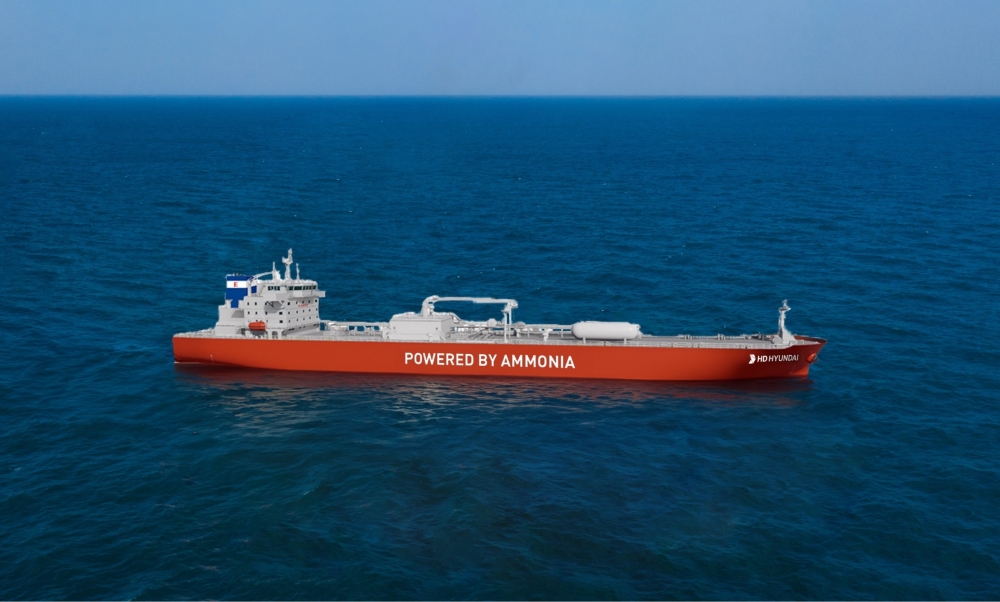
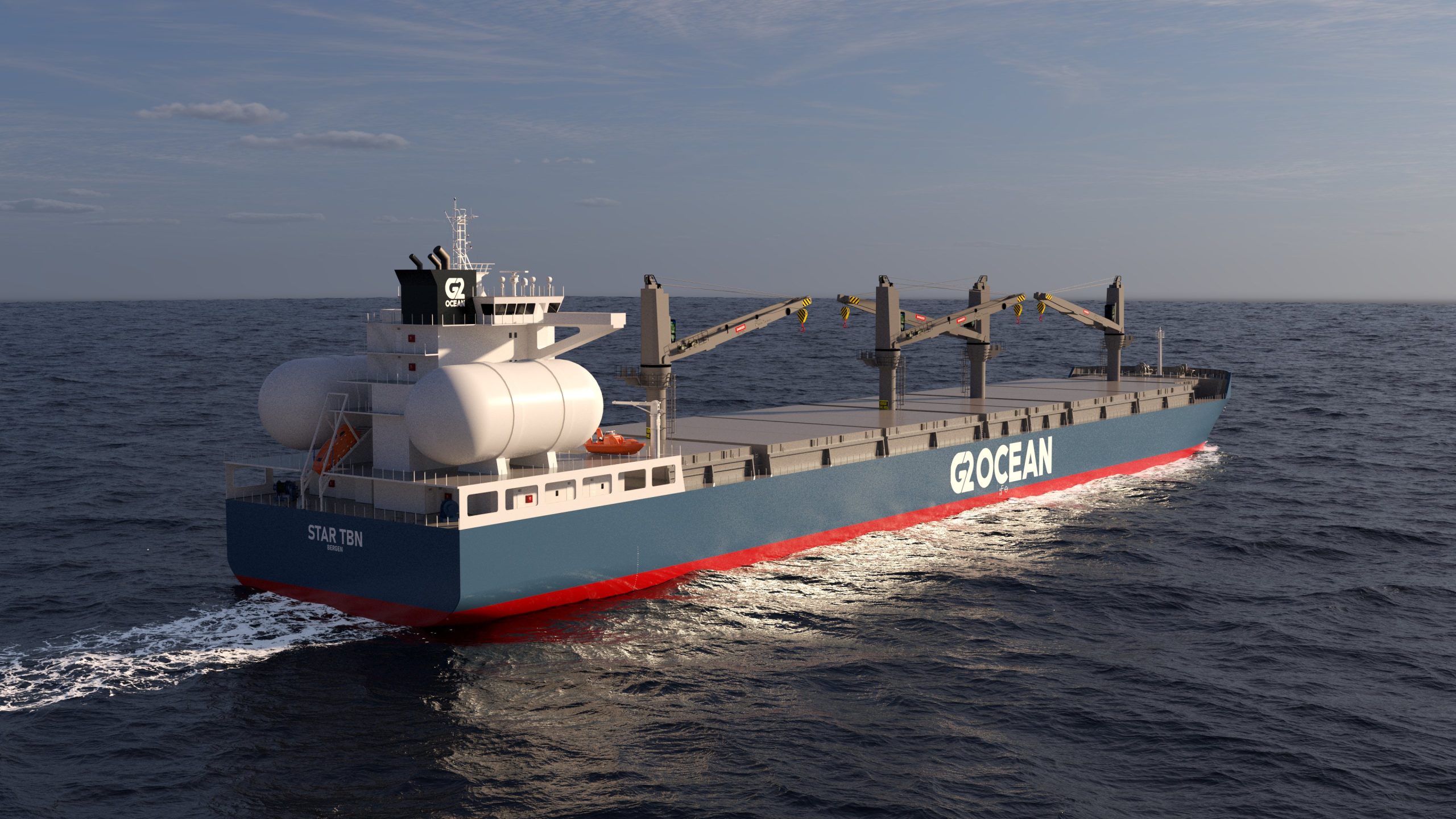
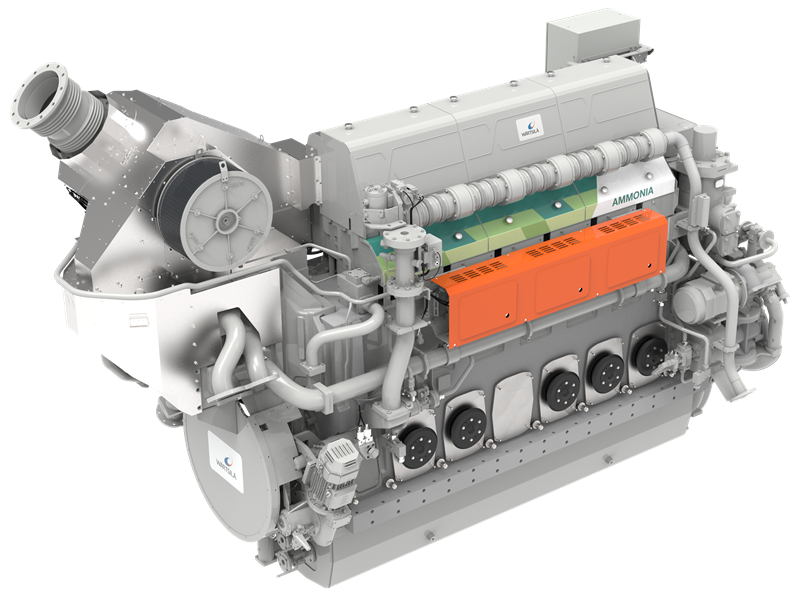
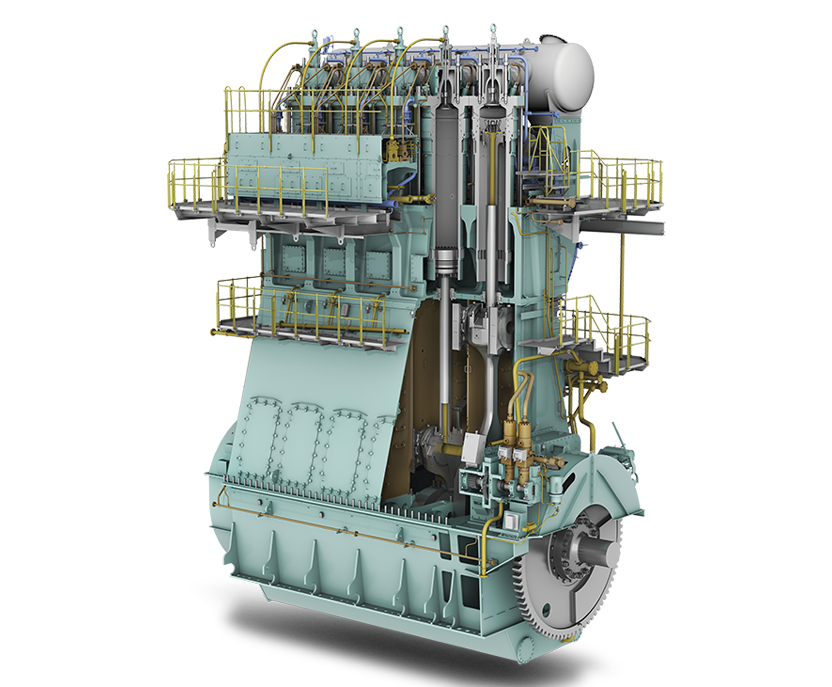
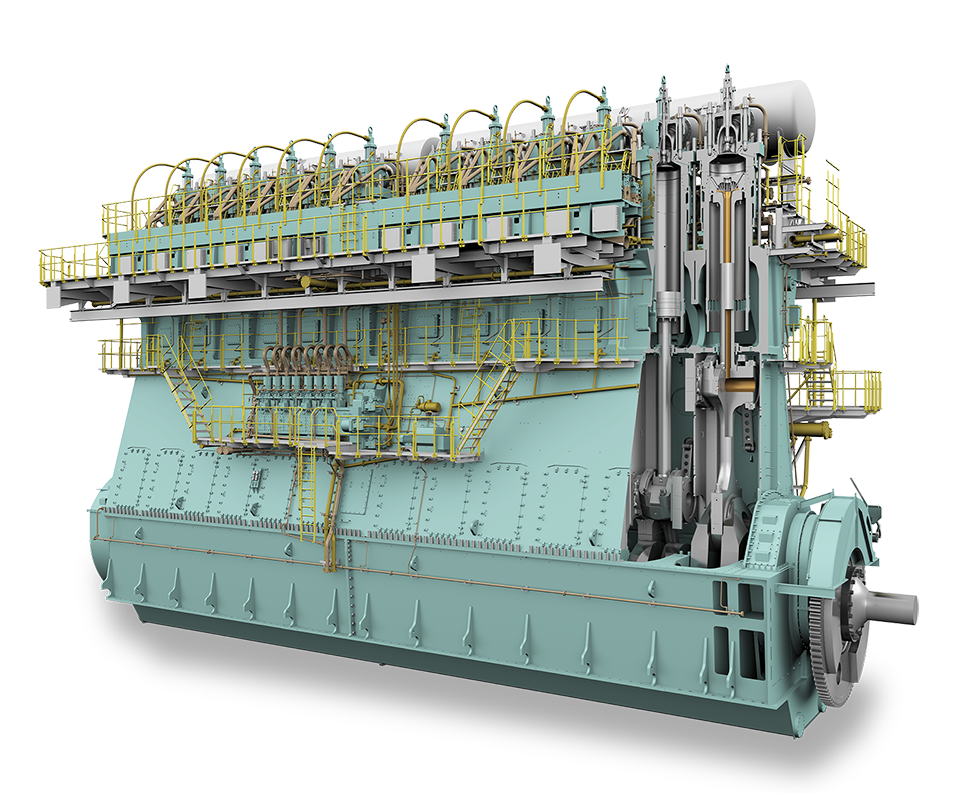
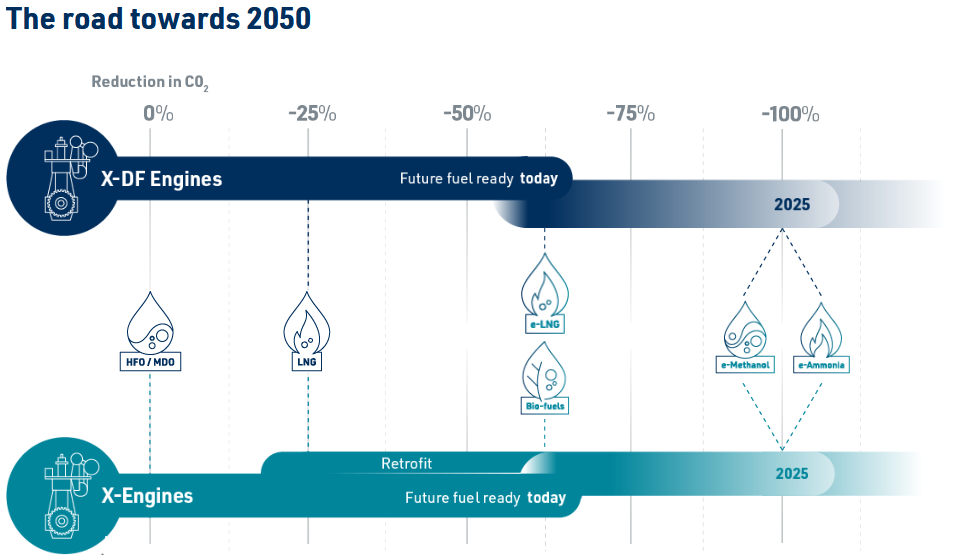
Anglo-Eastern announced that the first cohort has successfully completed its inaugural Pilot Training Course on Ammonia as a Marine Fuel. Already the ship manager for the ammonia-fueled vessel Fortescue Green Pioneer, Anglo-Eastern will soon take on that responsibility for a series of vessels coming out of Chinese shipyards, managing vessels for CMB.TECH.