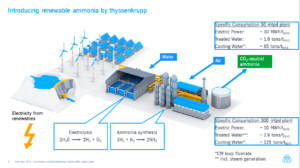
The newest ammonia plant on the planet has opened in Freeport, Texas.
A joint venture between Yara and BASF, this world-scale ammonia plant uses no fossil fuel feedstock. Instead, it will produce 750,000 metric tons of ammonia per year using hydrogen and nitrogen delivered directly by pipeline. The plant's hydrogen contract is structured so that the primary supply is byproduct hydrogen, rather than hydrogen produced from fossil fuels, and therefore the Freeport plant can claim that its ammonia has a significantly reduced carbon footprint.
This new ammonia plant demonstrates three truths. First, low-carbon merchant ammonia is available for purchase in industrial quantities today: this is not just technically feasible but also economically competitive. Second, carbon intensity is measured in shades of grey, not black and white. Ammonia is not necessarily carbon-free or carbon-full, but it has a carbon intensity that can quantified and, in a carbon-constrained economy, less carbon content equates to higher premium pricing. Third, the ammonia industry must improve its carbon footprinting before it can hope to be rewarded for producing green ammonia.