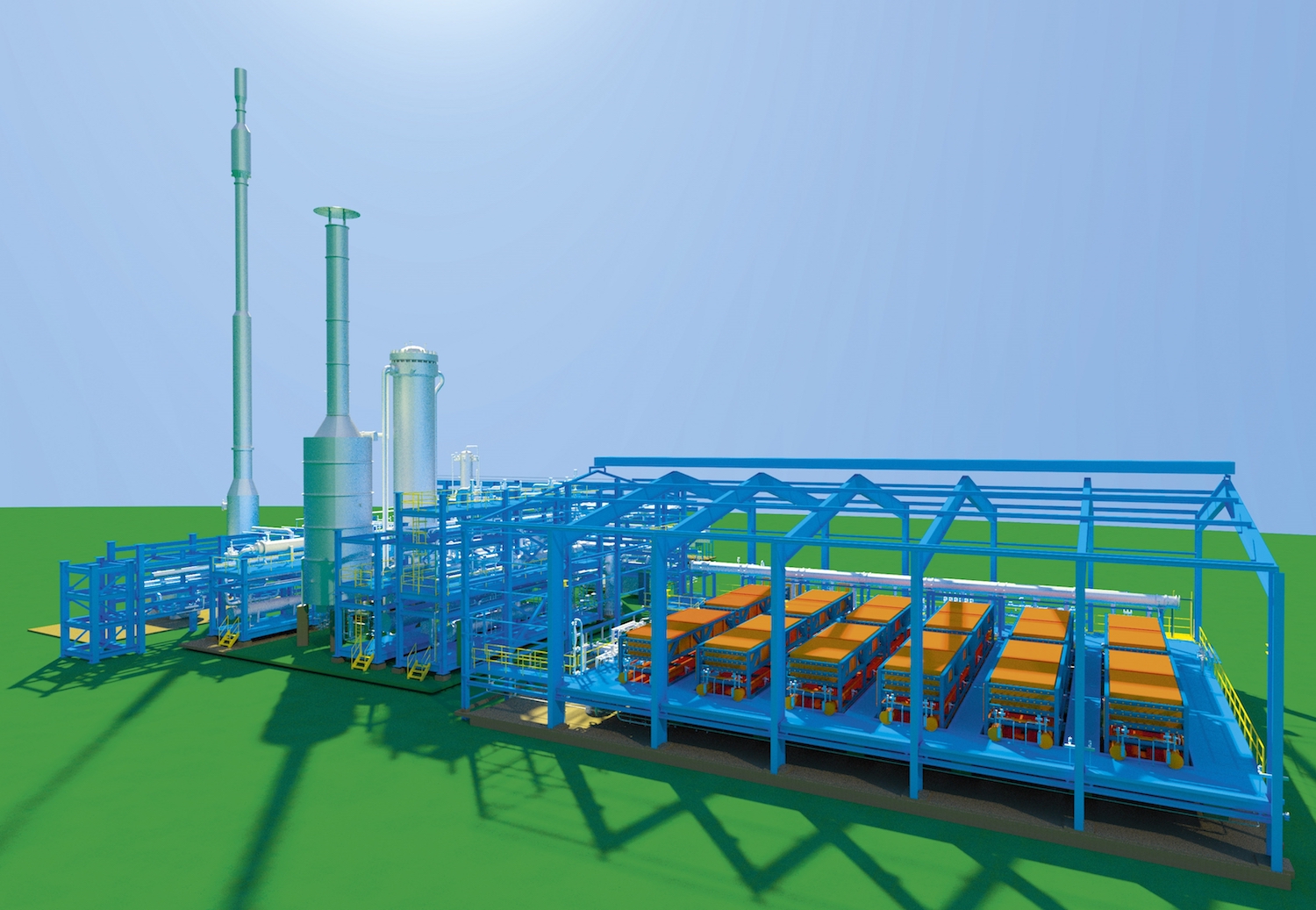
ThyssenKrupp's "green hydrogen and renewable ammonia value chain"
In June, ThyssenKrupp announced the launch of its technology for "advanced water electrolysis," which produces carbon-free hydrogen from renewable electricity and water. This "technology enables economical industrial-scale hydrogen plants for energy storage and the production of green chemicals." Two weeks later, in early July, ThyssenKrupp announced that it was moving forward with a demonstration plant in Port Lincoln, South Australia, which had been proposed earlier this year. This will be "one of the first ever commercial plants to produce CO2-free 'green' ammonia from intermittent renewable resources." The German conglomerate is one of the four major ammonia technology licensors, so its actions in the sustainable ammonia space are globally significant.