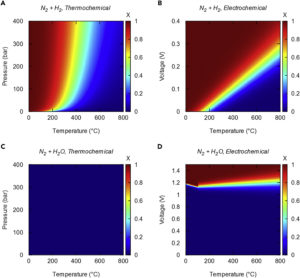
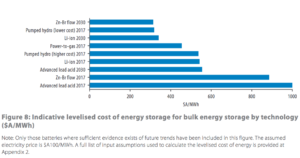
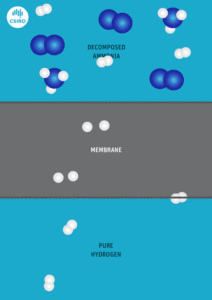
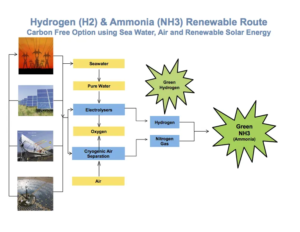
Australian Renewable Energy Agency Issues H2 Fuel Carriers RFP
One of Ammonia Energy’s “top ten” stories of 2017 described Australia’s early steps toward export of renewable hydrogen in the form of green ammonia. The story said that “Agencies such as the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) made it clear during the year that the country intends to build on [its historical] position” as a supplier of fossil energy to countries such as Japan. ARENA took a tangible step in this direction on December 20, 2017 with the release of a Request for Proposal for a AUD$20 million (USD$16 million) renewable hydrogen R&D funding program. Included in the scope, per ARENA’s 2017 Investment Plan, could be “demonstration of renewable production methods for transportable energy storage options (such as hydrogen or ammonia).”