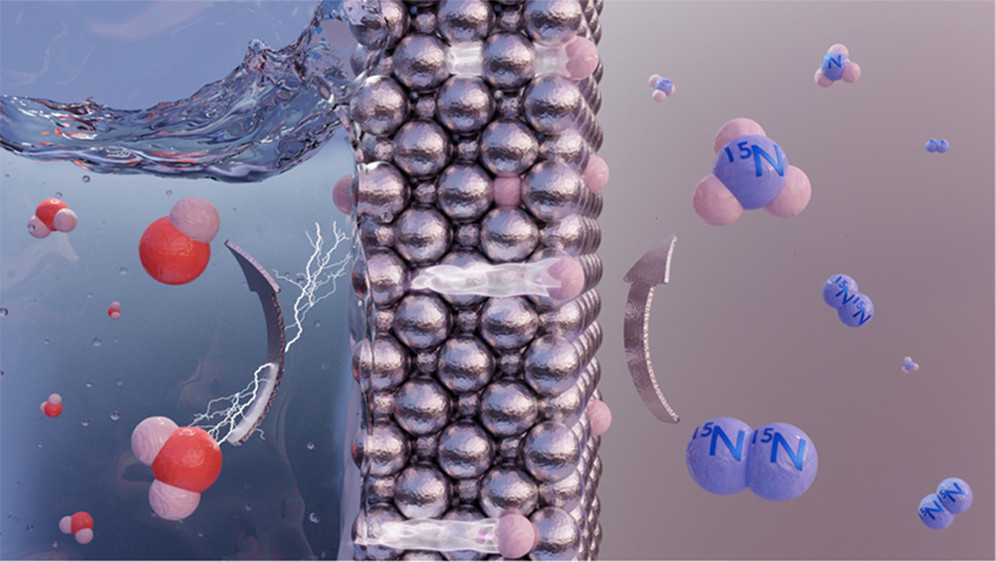
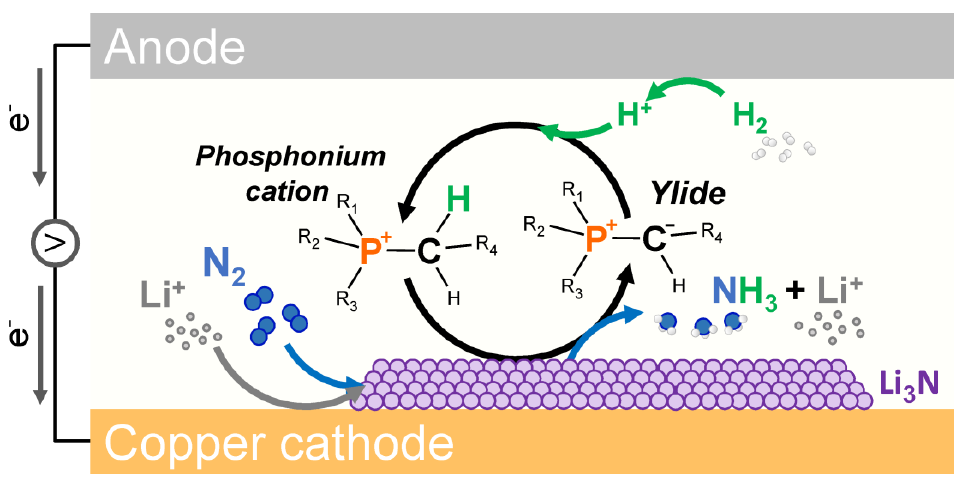
New ammonia-powered vessels: Newcastlemax & Panamax class
Rio Tinto and AngloEastern have announced they will develop Newcastlemax class, ammonia-powered bulk carriers. The dry cargo vessels will be the maximum size allowed to dock in the Port of Newcastle, Australia: an important coal & iron ore port in global maritime trade. Both AngloEastern and Rio Tinto are members of an Itochu-led maritime fuel study investigating the use of ammonia. In Japan, a "greener ships" consortium has produced its first-ever ammonia-powered design: a Panamax-class bulk carrier. And the China State Shipbuilding Corporation will develop two 93,000 m3 ammonia-powered ammonia carrier vessels, with Bureau Veritas granting AiP for the vessel design.