This week we explore four updates in ammonia combustion R&D:
1. A team from the University of Cambridge has shown merchant vessels are the strongest candidates for conversion to run on ammonia powertrains, with cargo capacity losses of 4-9% able to be feasibly offset by operators.
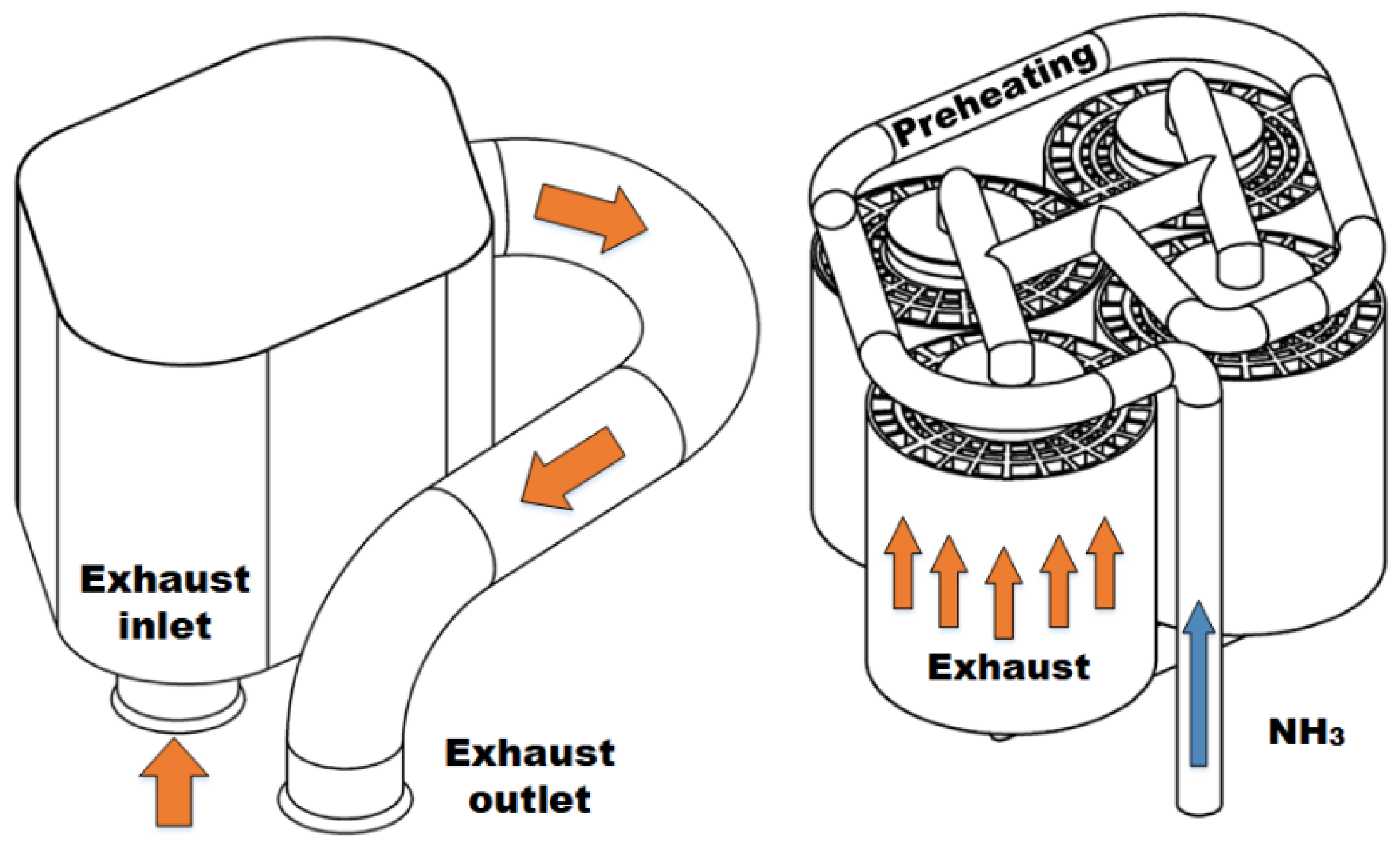
2. Researchers at the University of Minnesota have successfully tested a thermochemical recuperation (TCR) reactor to improve the efficiency of a dual-fuel, diesel-ammonia compression ignition engine by minimising ammonia slip.
3. A global team led by Cardiff University researchers has revealed some of the inner workings of ammonia combustion in gas turbine flames.
4. A global team has produced a cradle-to-gate environmental assessment for ammonia production and ammonia-based electricity generation, suggesting that renewable and nuclear ammonia have a significant role to play in decarbonising the power sector.