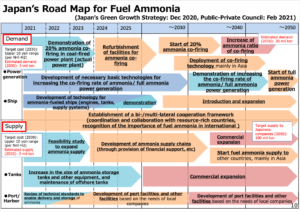
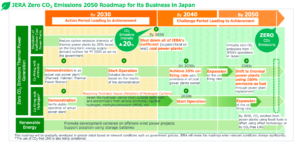
Ammonia Energy Live February - 2021
Last week we presented the first episode in our monthly webinar series: Ammonia Energy Live. Every month we’ll explore the wonderful world of ammonia energy and the role it will play in global decarbonisation - with an Australian twist. To kick things off we wanted to set the scene for 2021 and give you a sense of where the ammonia transition is at - key projects, key milestones and things to be excited about going forward. And, since this is an Australian-focused series, we wanted to explore what’s important about Australia to the ongoing work of the AEA.