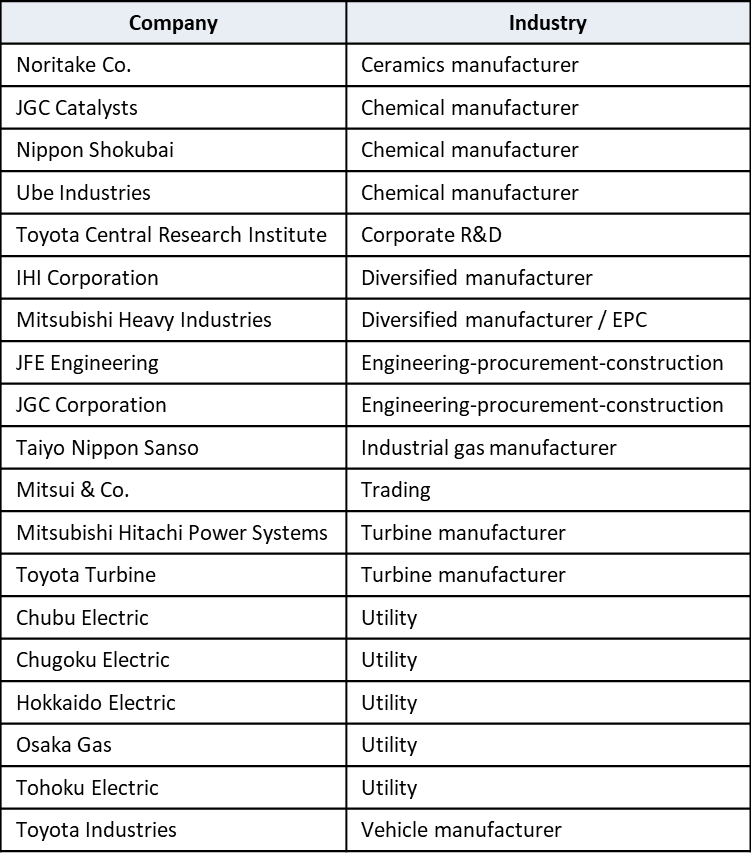
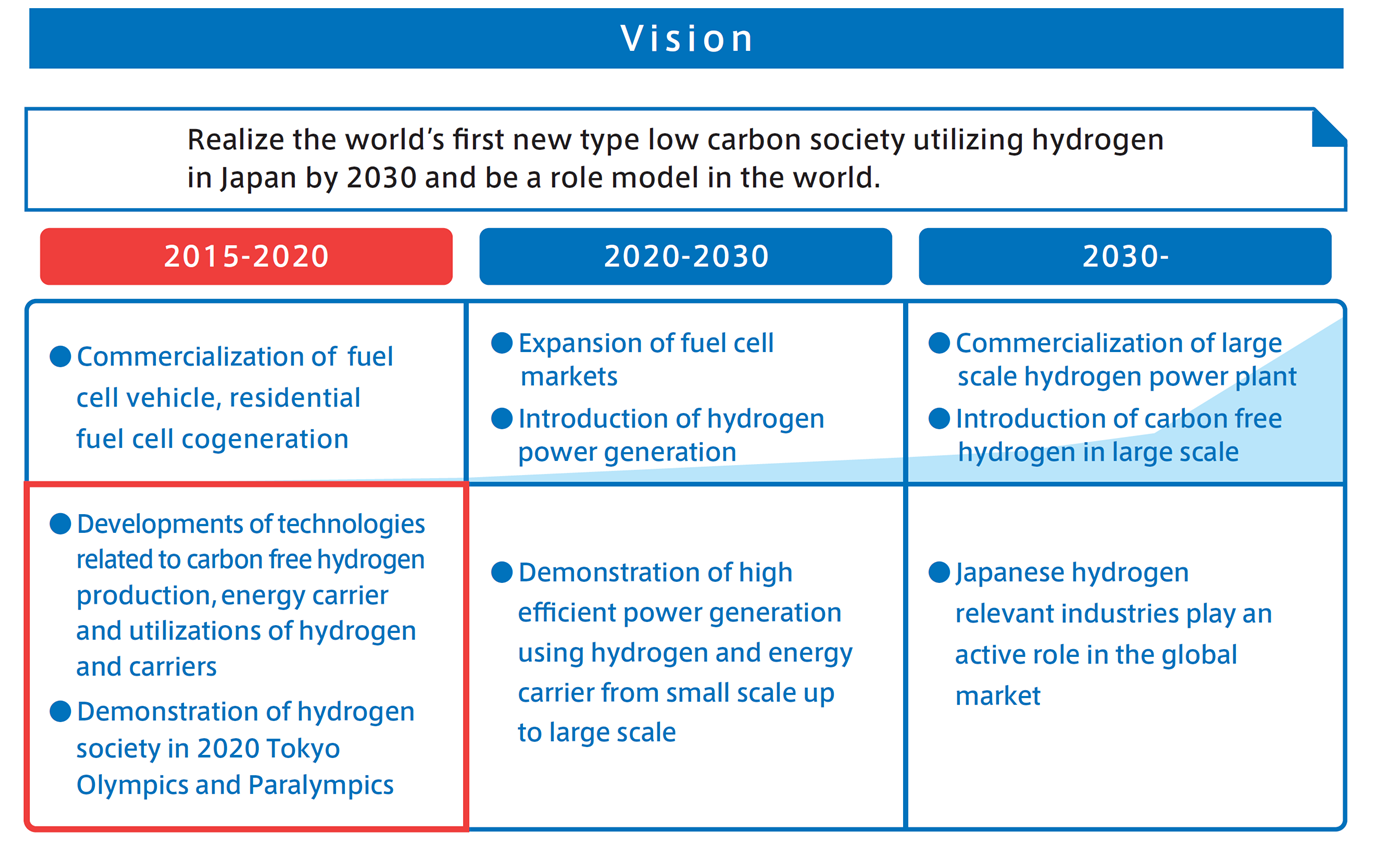
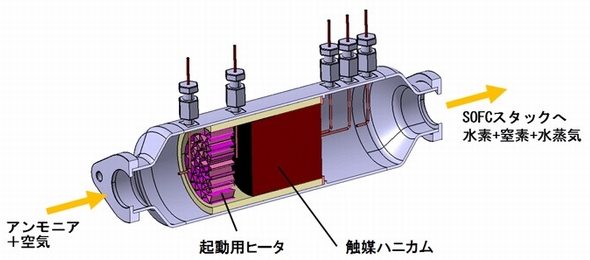
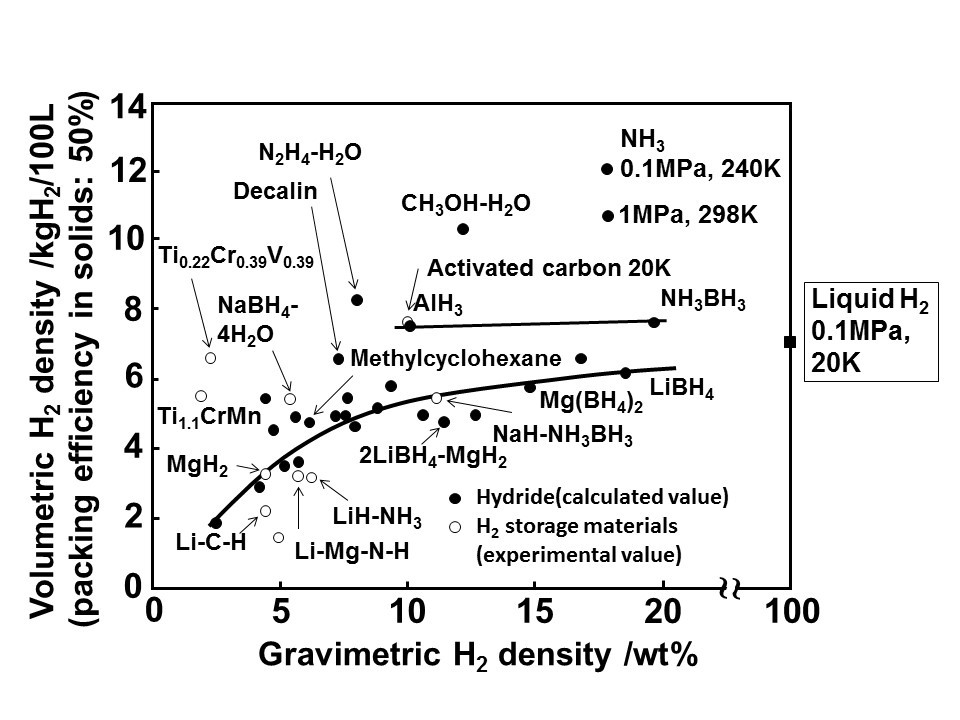
Recent “On the Ground in Japan” posts have considered the path forward for Japan’s “Hydrogen Society.” Two weeks ago, a post entitled “FCV Uptake and Hydrogen Fueling Stations,” pointed to a lack of marketplace momentum for the products that are supposed to drive the hydrogen society forward in the near term. The uptake of fuel-cell vehicles is off to a very slow start and the construction of hydrogen fueling stations is “not proceeding.”
The same day the post appeared, the Japanese market research firm Fuji Keizai announced the release of a report projecting robust growth for the country’s hydrogen economy. As reported by the on-line news service Smart Japan, the market for selected hydrogen-related goods will start to hit its stride with the arrival of the Tokyo Olympics in 2020. At that time, Fuji Keizai projects the market will have a value of approximately ¥700 billion ($6.4 billion). By 2030, the report says, the market will have a value of ¥5,903 billion ($54 billion). This is good news for hydrogen proponents but its import for ammonia energy is not clear.