Fossil Energy Companies Turn to Ammonia
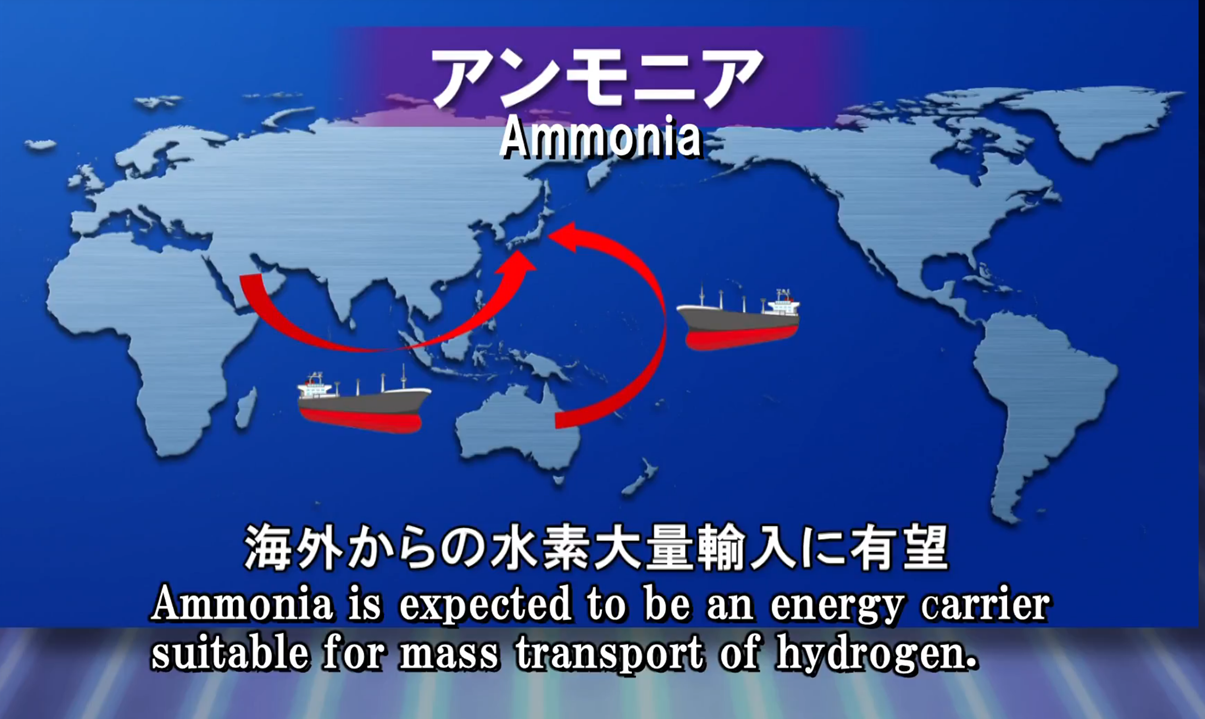
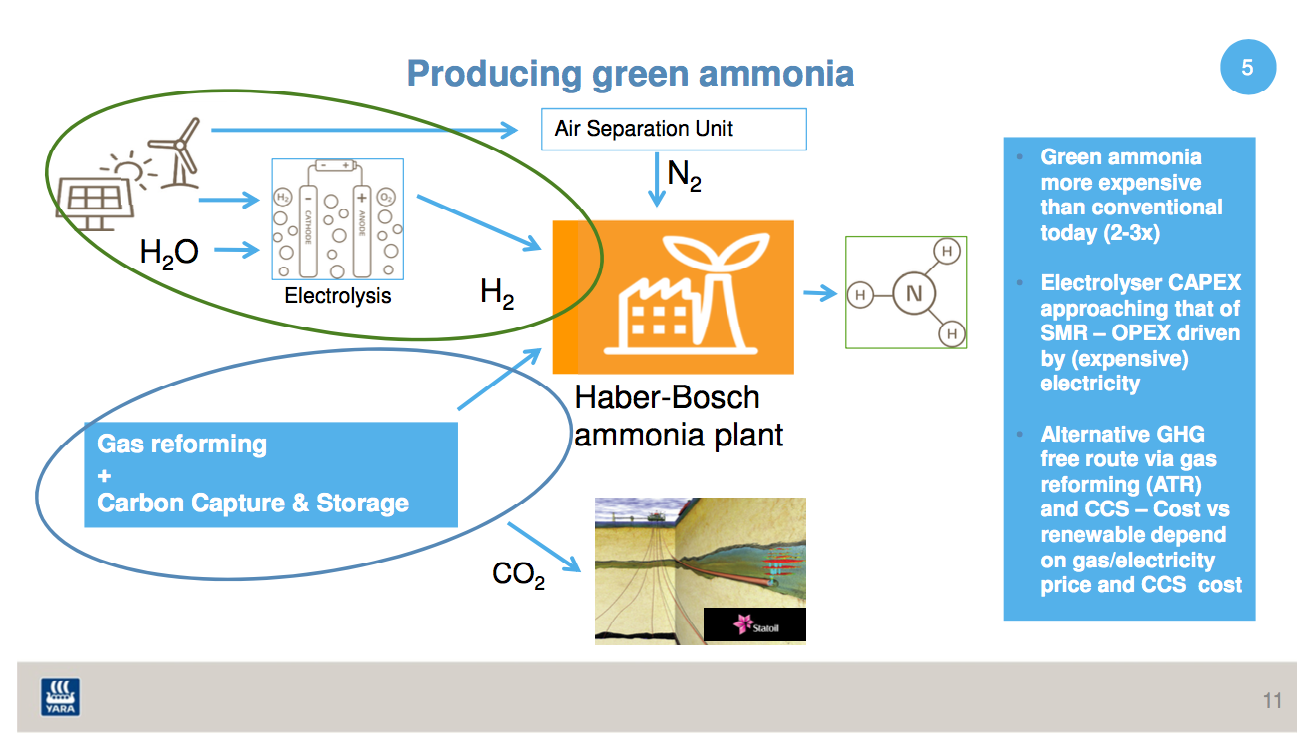
In the last 12 months ... National oil companies in Europe and the Middle East are looking to satisfy East Asian demand for clean hydrogen by exporting carbon-free ammonia. One of the biggest global LNG exporters is investigating ammonia for the same market, as it considers Australia's future as a renewable energy exporter. Oil majors are assessing ammonia's role in implementing an affordable hydrogen economy, looking toward fuel markets in California and Europe. And the biggest coal producer in China is funding the development of "the world’s first practical ammonia-powered vehicle."