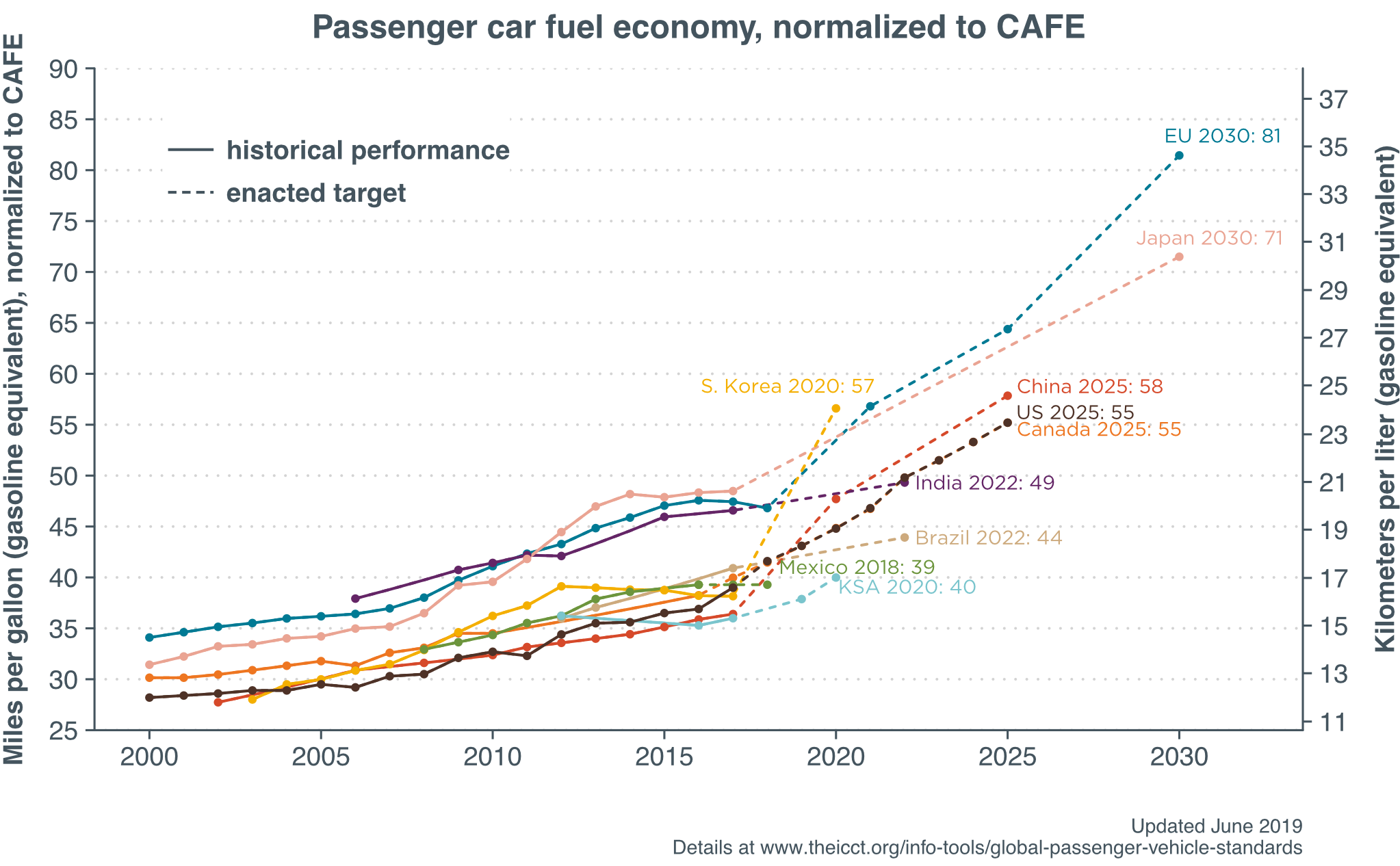
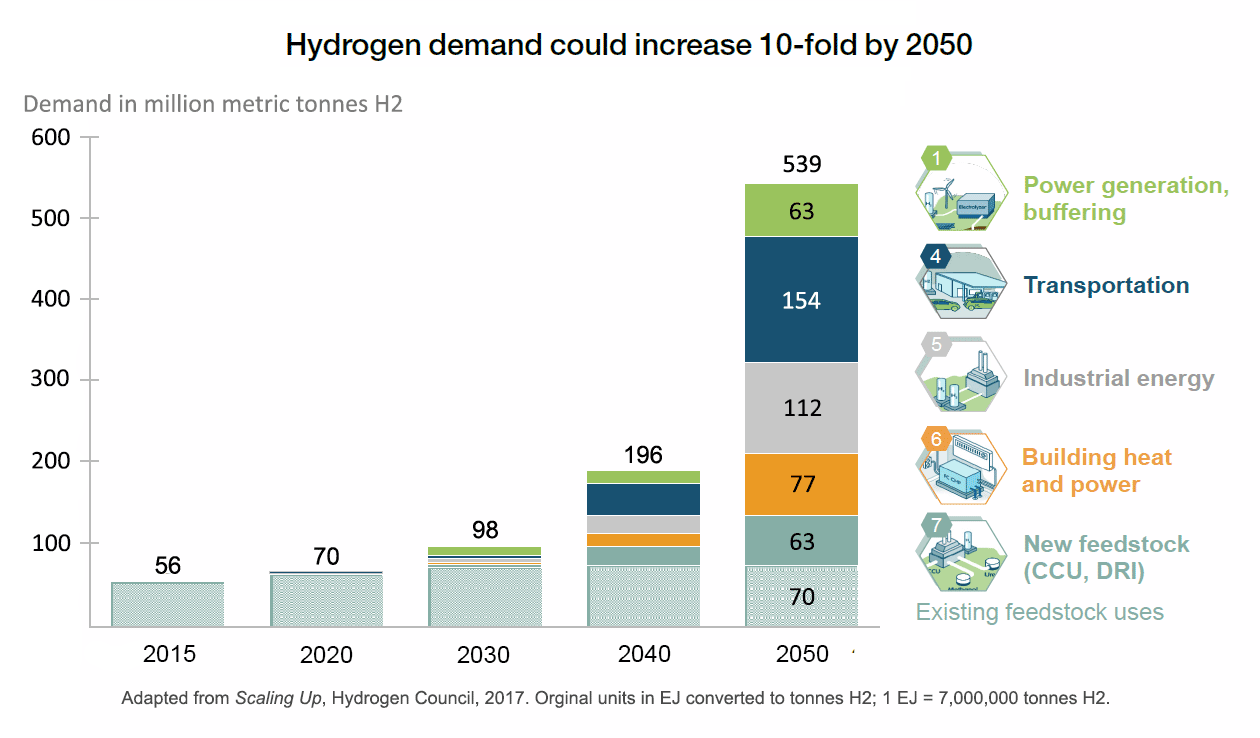
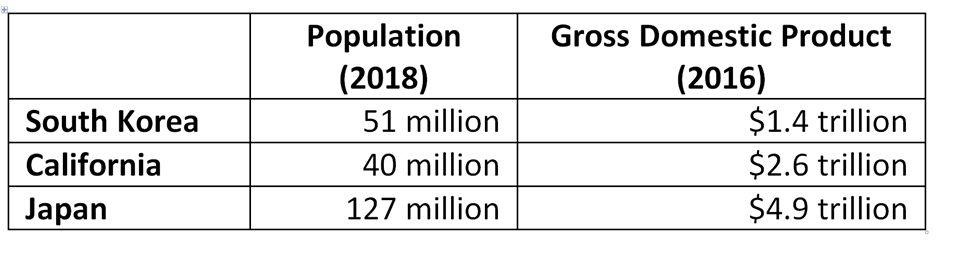
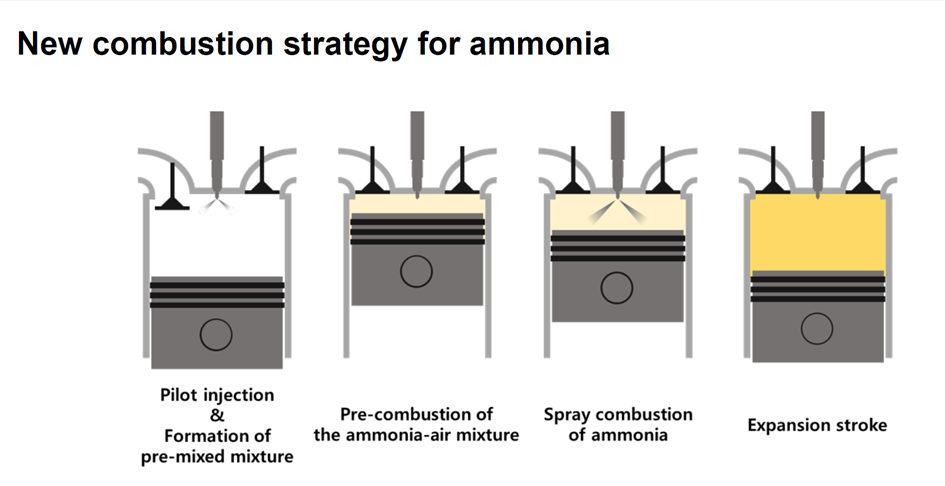
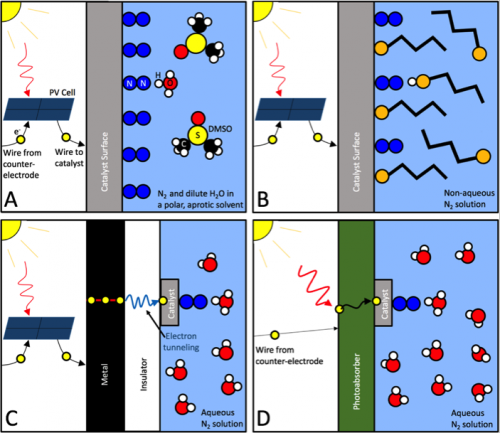
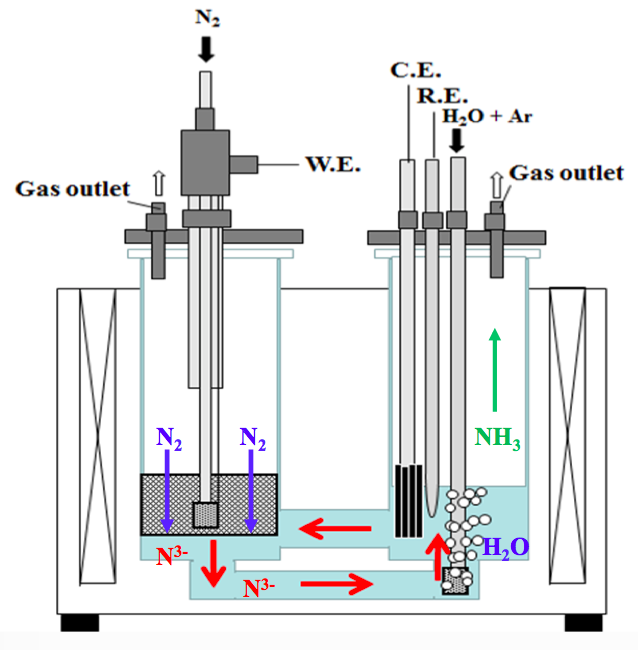
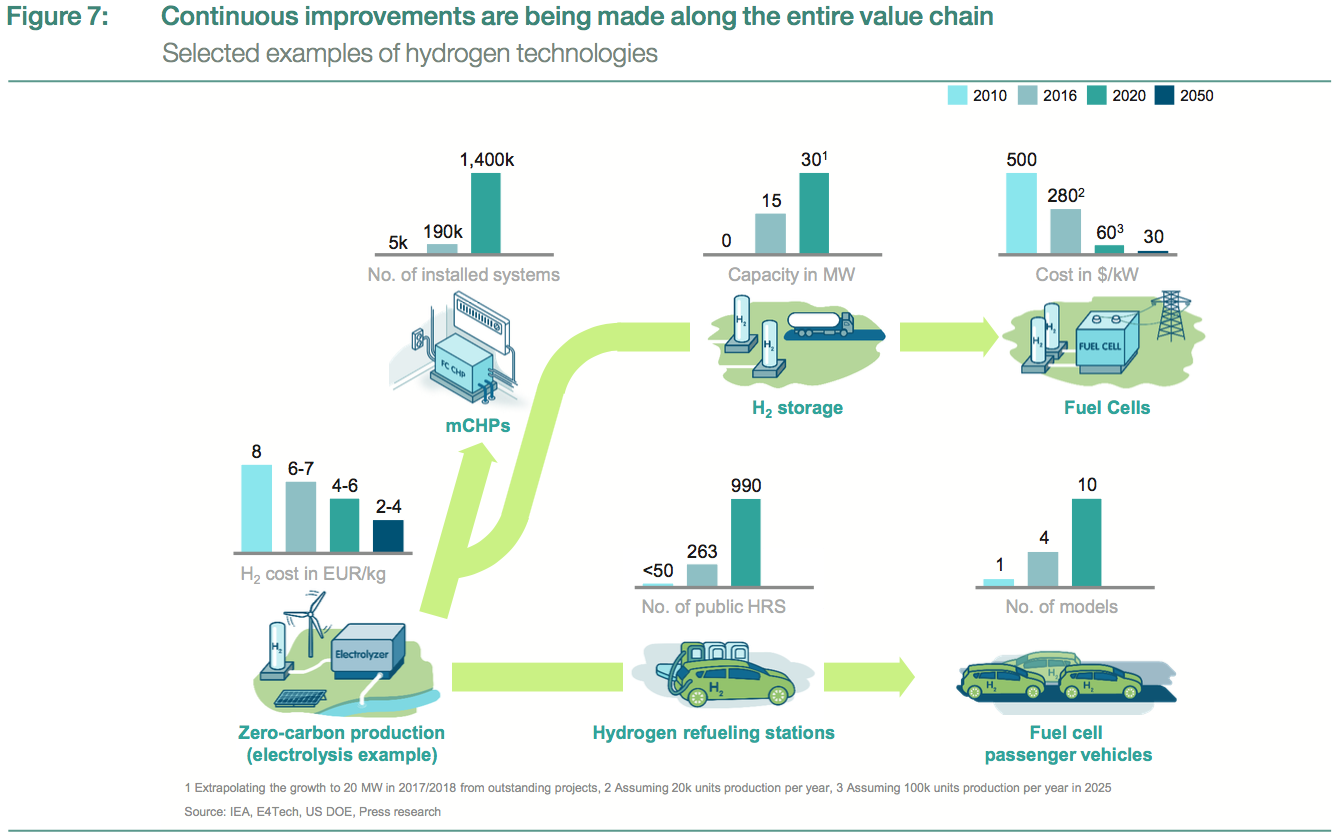
Where will fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) first achieve critical mass? Japan and California spring to mind as likely jurisdictions. South Korea not so much. That situation could change, though, with recent announcements from the Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy (MTIE) in Seoul. In fact, planned public and private sector investments could push South Korea to the front of the FCV pack. But while hydrogen-related activity of this nature can create opportunities for ammonia energy, the question always looms: are the key players in the implementing jurisdiction aware of the enabling roles ammonia can play? Hyundai is unquestionably a key player in South Korea’s FCV landscape, and, courtesy of its support for the Australian ammonia-to-hydrogen fueling demonstration that will kick off in August, Hyundai is certainly aware, and could even become a champion, of ammonia-based FCV fueling.