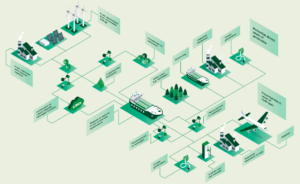
Amon Maritime unveils ammonia-powered, offshore platform supply vessel
Amon Maritime has launched a new subsidiary - Amon Offshore - which will build, own and operate a fleet of ammonia-powered platform supply vessels, to operate off Norway’s coast. The new PSV design has already received AiP for ammonia notation from DNV, and preliminary flag approval from Norwegian Maritime Authorities. We also explore two more AiP for ammonia-powered vessels in China: a 16,000 TEU container ship and a 50,000 tonne, mid-range oil/chemical tanker.