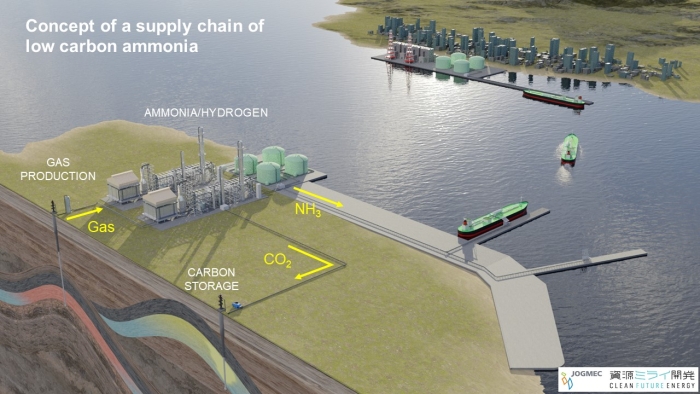
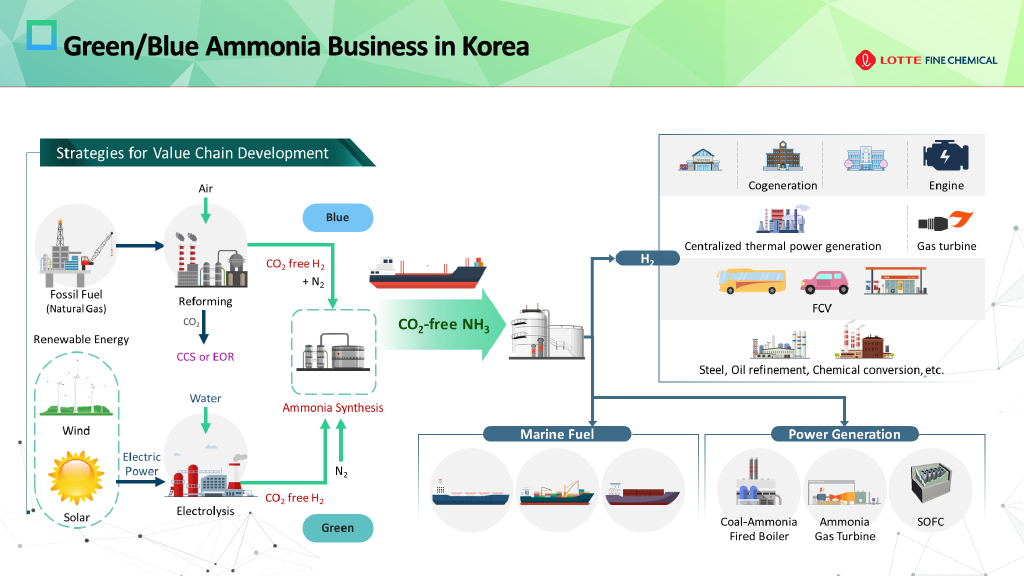
Green ammonia in Bolivia
A new agreement between H2 Bolivia and the Government of Oruro will see a 500,000 tonne per year green ammonia plant built in the country. Taking advantage of the "unmatched solar irradiance" in the Oruro region, a solar farm will power 490 MW of electrolysers at the plant, with enough land acquired to expand the project well beyond the initial capacity target.