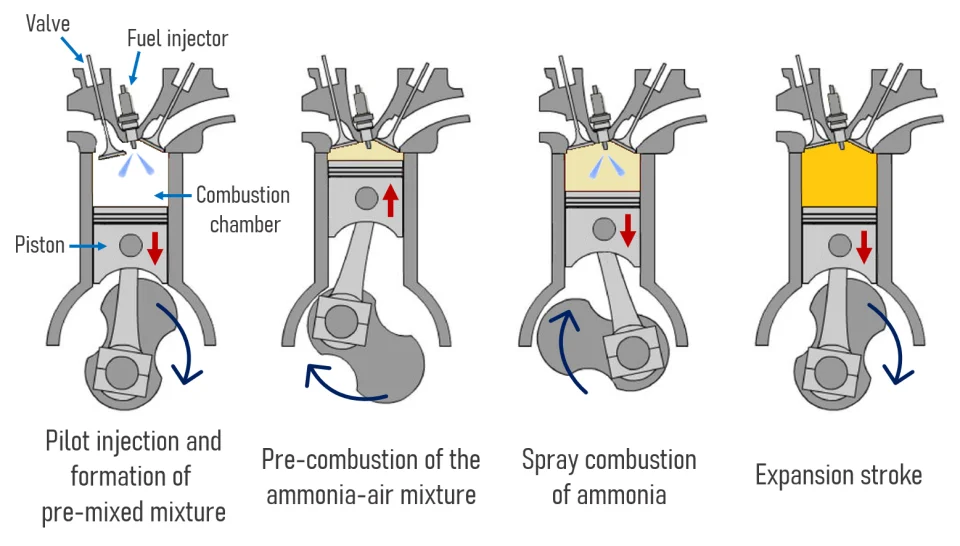
Ammonia Engine
Ammonia as an Energy Carrier: Leveraging technologies and infrastructure to decarbonise global energy systems
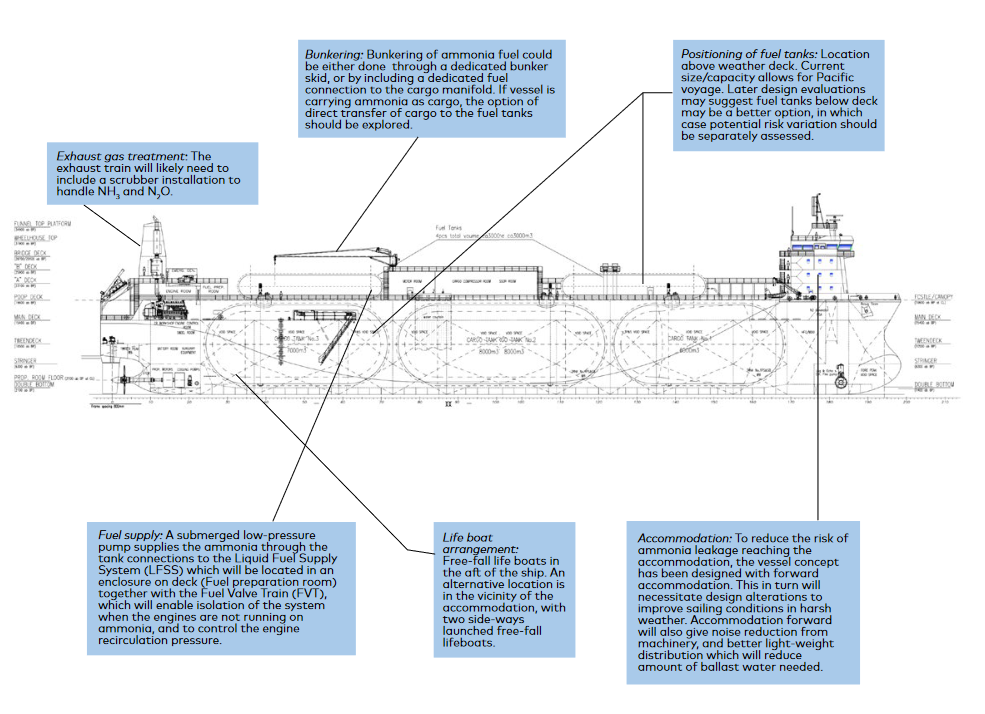
GTT to deliver ammonia-ready fuel tanks for container vessels
French organisation Gaztransport & Technigaz (GTT) will design the fuel tanks for five LNG-fueled container vessels (15,000 CTU each) based on its Mark III, ammonia-ready membrane containment system. Vessel deliveries are scheduled for late 2023 to early 2024.
Nutrien and Exmar partner up to build an ammonia-powered vessel
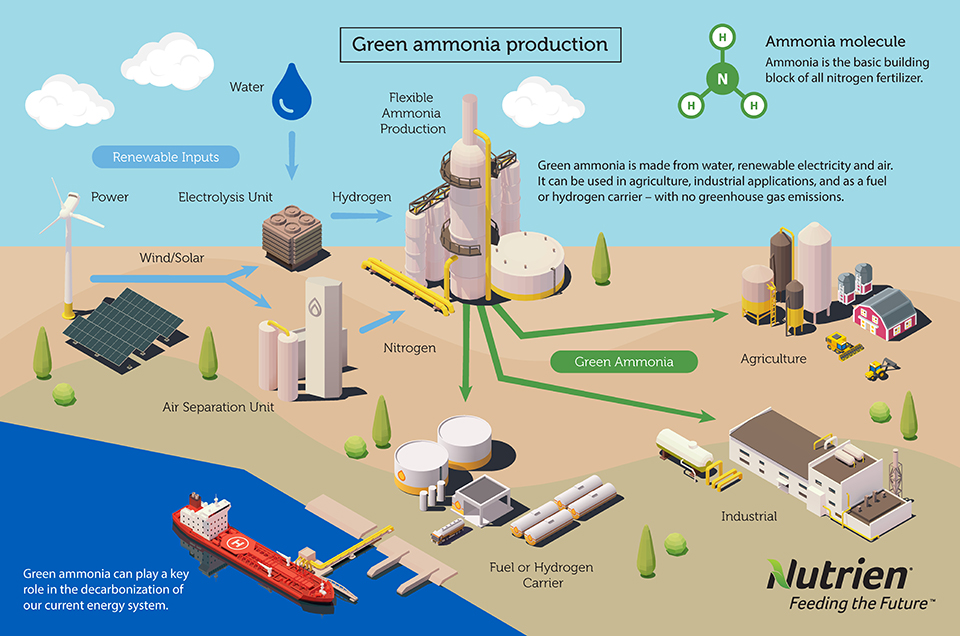
Nutrien and Exmar will cooperate to deploy an ammonia-powered vessel on the water by 2025, with the fuel to be sourced from Nutrien's low-carbon ammonia production facility in Geismar, Louisiana. Together, the two organisations will select an ammonia-powered engine, a supply system manufacturer and a shipyard capable of constructing the vessel.
ENGIMMONIA project gets EU funding
Led by RINA with 21 project partners, the ENGIMMONIA project aims to transfer demonstrated, terrestrial clean energy solutions to the maritime sector. As of May, ENGIMONNIA is now fully-funded (€9.5 million) by the EU's Horizon 2020 program. The end result will see the MAN ES ammonia engine installed and demonstrated in three vessels: an oil tanker, a container ship, and a ferry.
Wärtsilä launches major hydrogen and ammonia test program
This week Wärtsilä announced: i) some key updates in its ammonia and hydrogen-powered engine testing research to date and ii) some key upcoming milestones for its R&D program.
The Ammonia Academic Wrap: a new breakthrough for eNRR research and more
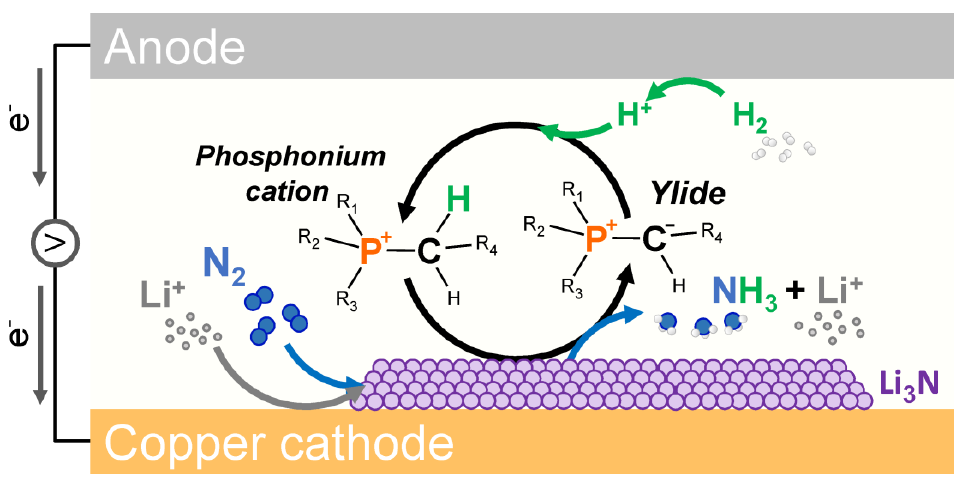
This week: a new breakthrough for eNRR research, ammonia production from food waste and brown-water, the huge potential of green ammonia production from hybrid solar-wind across the globe, predicted cost dynamics of electrolyser technology, and hydrogen production using selective ion membranes.
The Ammonia Wrap: no major obstacles for NoGAPS success and more
Welcome to the Ammonia Wrap: a summary of all the latest announcements, news items and publications about ammonia energy. This week: latest report from NoGAPS, Viking Energy project takes another step, more collaborations for Yara, thyssenkrupp to invest in cracking R&D, investment in clean hydrogen technology in the USA, world-first visualisation of ammonia combustion in a spark-ignition engine and our numbers of the week.
The Ammonia Wrap: 30 GW Power-to-X project in Mauritania and more
Welcome to the Ammonia Wrap: a summary of all the latest announcements, news items and publications about ammonia energy. This week: a 30 GW Power-to-X project in Mauritania, green hydrogen and ammonia in Egypt, €8 billion for 62 hydrogen projects in Germany, Cummins' electrolyser gigafactory in Spain, Ammonia engine development in Portugal and Shchekinoazot gets a new decarbonisation partner.
The Ammonia Wrap: two new large-scale ammonia projects in the UAE and more
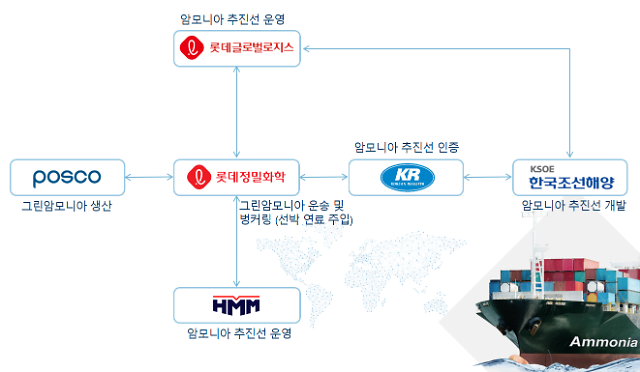
Welcome to the Ammonia Wrap: a summary of all the latest announcements, news items and publications about ammonia energy. This week: two new large-scale ammonia projects in the UAE, RWE, BASF combine for 2 GW "Offshore-to-X" project, green ammonia exports from Tasmania, coal co-combustion trials in Japan, Japanese shipping industry chases decarbonisation, South Korean companies join together in local green ammonia consortium, new funding for ammonia-from-wastewater research and Horisont Energi and Equinor join forces for the Polaris project.